
Полная версия:
Живи долго! Научный подход к долгой молодости и здоровью
Тот факт, что висцеральный жир сокращает продолжительность жизни, был доказан на крысах. Его хирургическое удаление привело к значительному увеличению средней и максимальной продолжительности жизни[3004]. А что же у людей? Те, кому была проведена бариатрическая операция по снижению веса, действительно живут значительно дольше, чем контрольные группы, сопоставимые по весу, которые такой операции не делали[3005] (подробности смотрите в видео see.nf/bariatric), но рандомизированных исследований, подтверждающих это, не проводилось. Однако есть рандомизированные исследования по снижению веса с использованием диеты и образа жизни.
Не все жировые калории одинаковы
Метаанализ 15 исследований, в которых мужчины и женщины наблюдались до 12 лет, показал, что потеря лишних килограммов не только снижает воспаление, артериальное давление и уровень сахара в крови, но и продлевает жизнь, уменьшая риск преждевременной смерти примерно на 15 %[3006]. Так какая же диета для похудения самая лучшая?
В медицинской литературе встречаются данные о том, что наибольшую потерю веса дает цельная растительная диета. Исследования проводились в течение 6 и 12 месяцев; эта диета сравнивалась с любой другой диетой; калории не ограничивались и физические нагрузки не предписывались[3007]. Одной из причин этого может быть более низкое потребление жиров. Люди в группе с низкожировой растительной диетой естественным образом потребляли примерно на 600 калорий в день меньше, чем те, кто следовал высокожировой кетогенной диете. Это привело к значительной потере жира и сохранению мышечной массы; у участников кетогенной диеты наблюдался противоположный эффект: у них не было значительной потери жира, но произошло снижение мышечной массы, поскольку их организм, как оказалось, питался собственным белком (хотя они и потребляли больше белка)[3008].
Однако не все жиры одинаковы.
В книге «Не сдохни на диете» я развенчиваю миф о том, что «калория – она всегда калория». Калории из одного источника не всегда так же жирны, как калории из другого. Если, например, потреблять примерно одинаковое количество калорий и жиров, но заменить мясо и сливочное масло орехами, авокадо и оливковым маслом, то всего за месяц можно потерять почти 3 килограмма жира[3009]. Насыщенные жиры также могут вызывать вдвое большее накопление висцерального жира по сравнению с тем же количеством других жиров[3010]. Почему? Одна из причин, по которой насыщенные жиры могут быть «более жирными», заключается в том, что они с большей вероятностью будут сразу откладываться, а не сжигаться. Например, олеиновая кислота, основной мононенасыщенный жир, содержащийся в орехах, авокадо и оливках, сжигается примерно на 20 % быстрее, чем пальмитиновая кислота[3011], которая поступает в основном из мяса и молочных продуктов и является преобладающим насыщенным жиром в американском рационе[3012]. Более того, можно капнуть пальмитиновую кислоту на мышечные клетки в чашке Петри и увидеть подавление утилизации жиров[3013].
О других причинах, по которым здоровое питание может быть столь эффективным для снижения веса, читайте в книге «Не сдохни на диете».
Бурый против белого
При рождении мы, мокрые и скользкие, выходим из материнской утробы с температурой 37 °C прямо в помещение с комнатной температурой. Для поддержания тепла около 150 миллионов лет назад у нас появился уникальный орган – бурая жировая ткань, или сокращенно БЖТ, которая позволяет теплокровным млекопитающим поддерживать высокую температуру тела[3014]. БЖТ вырабатывает тепло, расходуя жировые калории в ответ на воздействие холода. Белый жир хранится на животе, а бурый жир, расположенный в груди, сжигает жир. Активация БЖТ является не только потенциальным средством замедления возрастного снижения скорости метаболизма, но и может играть роль в увеличении продолжительности жизни[3015].
Активность БЖТ, по-видимому, выше у долгоживущих животных и снижается у тех, чья жизнь коротка[3016]. Было обнаружено, что ген, увеличивающий продолжительность жизни у мышей, повышает активность БЖТ[3017]. Эксперименты на животных по хирургическому удалению и пересадке бурого жира подтвердили роль БЖТ в здоровом старении, по крайней мере у мышей[3018]. Если то же самое справедливо и для человека, то это поможет объяснить, почему женщины живут дольше мужчин: у женщин на протяжении всей жизни откладывается больше БЖТ[3019]. Активация БЖТ усиливает секрецию гормона голодания и долголетия FGF21 (см. главу «Ограничение белка»), но, к сожалению, с возрастом активность БЖТ снижается[3020]. У людей моложе 40 лет активность БЖТ, стимулированная холодом, может достигать 100 %, а у пожилых людей она может снижаться до 10 %[3021].
Однако вы не должны оставаться в стороне. Как я описываю в книге «Не сдохни на диете», существуют пищевые компоненты, способные усиливать активацию БЖТ. Например, это могут сделать соединения перца чили, которые были протестированы на людях в возрасте до 64 лет[3022]. Дозировка: целый сырой перец халапеньо или половина чайной ложки порошка красного перца в день[3023]. Чтобы уменьшить остроту, мелко нарежьте халапеньо или добавьте красный перец в суп или в овощной смузи из цельных продуктов, о котором я рассказываю в одном из своих кулинарных видео на сайте NutritionFacts.org. В качестве альтернативы можно использовать молотый имбирь. Он способствует снижению веса (возможно, за счет активации БЖТ[3024]) – достаточно одной чайной ложки в день[3025], ее можно просто размешать в горячей воде и приготовить имбирный чай.
Каков идеальный вес для долголетия?
Надеюсь, я уже убедил вас в том, что ожирение несет смертельную угрозу. Если вернуться на полвека назад, когда ожирение еще не стало обыденностью, и почитать медицинскую литературу, то описания будут мрачными: «Ожирение всегда трагично, а его опасность ужасающа»[3026]. Но дело не только в ожирении. Из 4 миллионов смертей, ежегодно объясняемых избытком жира в организме, почти 40 % жертв имеют просто избыточный вес, а не ожирение[3027].
А как же так называемый парадокс ожирения – доказательства того, что люди с избыточным весом живут дольше? Объединение ученых The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration разрушило этот миф, используя данные более чем 10 миллионов человек из сотен исследований, проведенных в десятках стран мира[3028]. (Подробности смотрите в видео see.nf/paradox.) Итак, каков же оптимальный индекс массы тела?
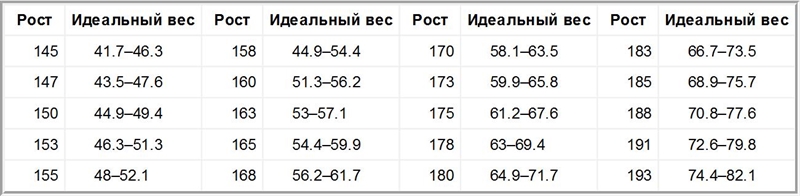
Крупнейшие исследования, проведенные в США[3029] и во всем мире, показали, что нормальный индекс массы тела – от 20 до 25 – связан с наибольшей продолжительностью жизни[3030]. Если собрать воедино все лучшие исследования с наиболее длительным периодом наблюдения, то идеальный диапазон можно еще сузить – до ИМТ 20–22[3031], что составляет примерно 56–62 килограмма для человека ростом 168 сантиметров[3032]. Вы можете воспользоваться таблицей, чтобы узнать, каков ваш оптимальный вес в зависимости от вашего роста.
Оптимальный вес в зависимости от роста
Сон
Я думаю, что назвать этот раздел «Делай, как я говорю, а не как я делаю», было бы более точным. (Я недавно обнаружил, что не так продуктивен, когда нахожусь в бессознательном состоянии!) На самом деле сегодня утром я подумал, что мне нужно встать и написать главу о сне! Это то, над чем я работаю.
Бытует мнение, что время, потраченное на сон, – напрасно потерянное[3033], но недостаточный сон связан с множеством острых и хронических заболеваний и может приводить к повышению риска смерти и болезней[3034]. Если заставить людей спать по шесть часов в сутки в течение одной недели, это приведет к изменению экспрессии более 700 генов[3035]. Наиболее тяжелым последствием может быть дисфункция эндотелия[3036]. Эндотелий – это тонкий слой клеток, покрывающий внутреннюю поверхность кровеносных сосудов и отвечающий за правильное расслабление и расширение артерий[3037]. Если разделить людей на две группы по продолжительности сна: одни в течение недели будут спать по 7 часов, а другие – по пять часов, то разница всего в два часа за ночь приведет к значительному ухудшению работы артерий[3038]. Но насколько именно?
Недостаток сна – это не шутка. Масштабы ухудшения самочувствия после недели сна по пять часов ежедневно аналогичны тем, которые отмечаются у курящих людей, больных диабетом или ишемической болезнью сердца. При этом более четверти населения регулярно спит по шесть и менее часов в сутки[3039]. Достаточно продолжительный, спокойный сон каждую ночь считается «бесспорным краеугольным камнем хорошего здоровья»[3040]. Однако вопрос о том, является ли связь между сном и смертностью причинно-следственной, остается спорным.
Живительный свет
В ходе работы над этим блоком, посвященным возможностям светотерапии в борьбе с бессонницей, я столкнулся с некоторыми весьма странными результатами исследований, например со статьей «Зеленый свет продлевает жизнь дрозофилы», опубликованной в журнале Experimental Gerontology. Исследователи обнаружили, что им удалось «резко» – на 24 % – увеличить продолжительность жизни плодовых мушек, выращивая их под зеленым светом[3041]. И наоборот, при воздействии синего света продолжительность жизни мух резко сокращалась, причем это происходило даже у мутантов, не имевших глаз! Такие мухи вообще не могли распознать цвет света, но продолжительность их жизни значительно сокращалась. Как?
Разгадка была найдена, когда исследователи обнаружили, что эффект зеленого света, способствующий увеличению продолжительности жизни, значительно снижается, если мух кормить антибиотиками, что позволяет предположить, что в этом может быть замешана микрофлора кишечника[3042].
У людей воздействие ультрафиолетового излучения на кожу может изменять микробиом кишечника, но предполагается, что это влияние витамина D[3043]. Логично предположить, что мухи могут «питаться» зеленым цветом, преобладающим в их естественной среде[3044]. На сайте NutritionFacts.org есть видеоролики о благотворном влиянии «лесных ванн» на человека, хотя, по-видимому, оно связано не с цветом леса, а с ароматическими соединениями, такими как пинен, которые выделяют деревья[3045].
Чтобы у вас не возникло соблазна заказать зеленые лампы, учтите: у крыс зеленый свет (но не красный или синий) вызывает непереносимость глюкозы, что означает повышение уровня сахара в крови[3046].
Cон – это важно
За всю историю наблюдений были проведены десятки проспективных исследований взаимосвязи продолжительности сна и смертности. Наиболее распространенным результатом является отсутствие какой-либо связи. Второй по частоте вывод – связь между преждевременной смертью и слишком высокой продолжительностью сна, обычно превышающей девять часов за ночь. Четверть результатов подтверждает U-образный эффект, когда те, кто не высыпается (обычно менее шести или семи часов) или спит слишком много (более девяти часов), умирают чаще, чем те, кто находится в оптимальной зоне, имея около семи-восьми часов сна. В 5 % случаев риск смерти был выше только у тех, кто не высыпался[3047]. Неудивительно, что метаанализ, проведенный в 2020 году, пришел к выводу: лишь одна характеристика сна может повышать риск смерти пожилых мужчин и женщин: ее высокая продолжительность, более восьми часов[3048].
Семи часов сна за ночь может показаться недостаточно, но на самом деле это естественная норма для нашего вида. Ученые исследовали три доиндустриальных общества, изолированных друг от друга на двух континентах, и обнаружили удивительное сходство. Несмотря на отсутствие электрического освещения и электронных устройств, они обычно ложились спать примерно через три часа после захода солнца, а вставали перед рассветом, получая шесть с половиной часов сна из примерно семи с половиной часов в «постели»[3049]. Даже в тех исследованиях, где риск наблюдался на обоих концах спектра продолжительности сна, как правило, он был выше там, где сон длился дольше[3050].
Механизм, который делает избыток сна вредным, остается неустановленным, поэтому причинно-следственная связь между сном по восемь и более часов в сутки и повышенным риском смерти и заболеваний некоторыми отвергается как неправдоподобная[3051]. Может быть, это обратная причинно-следственная связь: например, болезнь приводит к увеличению времени, проведенного в постели, а не наоборот? Может быть, дело в сбивающих факторах, таких как статус занятости[3052]? В конце концов, кто может быть более склонен к ночному отдыху? Те, у кого нет работы. Люди, долго спящие (не менее девяти часов за ночь), чаще ведут малоподвижный образ жизни, страдают ожирением, депрессией, диабетом, не состоят в браке, а также имеют целый ряд заболеваний, которые могут мешать выявлению связи между смертностью и долгим сном[3053]. В исследованиях учитывались социально-экономический статус и состояние здоровья, но все проконтролировать сложно[3054]. Итог? Для взрослых в возрасте 65 лет и старше National Sleep Foundation (Национальный фонд сна) рекомендует спать семь-восемь часов в сутки[3055], что снижает риск развития старческой астении[3056] и возрастной потери мышечной массы[3057].
Как высыпаться
Тем, кто страдает апноэ во сне – распространенным следствием ожирения, мешающим спать, – полезно использовать Сипап-аппараты: они создают постоянное положительное давление в дыхательных путях, тем самым устраняя основную причину храпа[3058]. Но что делать, если это не ваша проблема, но вы испытываете трудности с засыпанием? Ознакомьтесь с моими четырьмя правилами подготовки и гигиены сна в ролике see.nf/sleeprules. Они включают в себя методы когнитивно-поведенческой терапии[3059] наряду с регулированием дозы и времени физических упражнений, кофеина, никотина и алкоголя, а также способы создания оптимального режима сна и условий для сна.
Риск без награды
Существует распространенное заблуждение, что пожилым людям требуется меньше сна[3060]. На самом деле с возрастом спать становится все труднее. Симптомы бессонницы усиливаются, причем у взрослых в возрасте 65 лет и старше их распространенность приближается к 50 %, а частота ремиссий за 3 года достигает 50 %[3061]. К счастью, симптомы бессонницы не коррелируют с риском смертности, хотя отчасти это может быть связано с тем, что большинство людей с диагнозом «бессонница» в действительности спят более шести часов сна за ночь, когда их сон измеряется объективными методами[3062]. По данным близнецовых исследований, наследуемость бессонницы составляет 40 %, то есть на наши гены приходится менее половины риска развития бессонницы[3063]. Что мы можем сделать, чтобы уменьшить ту часть риска, которую способны контролировать?
Снотворные средства – не лучший вариант. Гипнотики – это класс снотворных препаратов[3064]. Оказалось, что риск преждевременной смерти у людей, которым назначают их – даже половину дозы, – более чем в 3 раза выше, чем у тех, кто не получает никаких препаратов[3065]. Такие препараты принимает 10 % взрослого населения[3066], так что если эти таблетки действительно убивают людей, то это означает, что они могут быть причиной шестизначного числа смертей в год[3067]. Неудивительно, что производитель гипнотиков поставил под сомнение результаты исследования[3068], но оно не было единственным. Два десятка исследований выявили значительную связь между снотворными препаратами и преждевременной смертью[3069]. В ответ на критику за «распространение информации о высоком риске смерти от широко используемых лекарств, повышающей тревожность населения»[3070] главный исследователь Scripps Clinic Sleep Center (Центра сна клиники Скриппса) ответил следующее: «Мы не можем скрывать риски, даже если они могут напугать пациентов и заставить их отказаться от приема гипнотиков. Пациенты имеют право знать»[3071].
Мы также имеем право знать, что лекарства могут и не работать. Наиболее авторитетный метаанализ пришел к выводу, что гипнотики не увеличивают общее время сна[3072]. Как такое может быть? Мои пациенты рассказывали мне, насколько лучше они стали спать. Оказывается, люди только думают, что спят лучше. Хоть они и сообщали, что гипнотики дают им дополнительные полчаса сна, объективные измерения говорят о том, что они вовсе не стали спать значительно больше[3073]. Субъективное ощущение, что после приема таблетки вы спите лучше, объясняется амнезирующими свойствами препарата, то есть гипнотики могут стереть воспоминания о том, как плохо вы спали[3074]. Американская академия медицины сна не рекомендует использовать эти препараты в качестве основного лечения хронической бессонницы[3075].
Погрузитесь в воду
Прием пищи поздно вечером не только способствует набору веса, о чем я рассказываю в книге «Не сдохни на диете», но и может помешать заснуть. Обычно перед сном происходит снижение температуры тела[3076], что является одним из сигналов о том, что пора спать, но поздний прием пищи может помешать этому. Не будет ли в таком случае прием горячего душа контрпродуктивным? Нет. Как только вы выходите из ванны, быстрое снижение температуры кожи может усилить естественное ночное снижение и улучшить ваш сон[3077]. Простая теплая ножная ванночка может помочь вам заснуть примерно на пятнадцать минут быстрее[3078].
Теплую воду называют «безопасным, простым и нефармакологическим методом улучшения качества сна»[3079]. Метаанализ исследований показал, что теплый душ, ножная или полноценная ванна в течение всего десяти минут за 1–2 часа до сна помогают людям быстрее засыпать и лучше спать[3080].
Кровеносные сосуды, соединяющие артерии и вены на ладонях и подошвах ног, расширяются под воздействием теплой воды, усиливая передачу тепла от тела к рукам и ногам, где оно эффективнее расходуется, что снижает общую температуры тела и вызывает сон[3081]. У пожилых людей температурная реакция ослаблена, что, возможно, объясняет некоторые возрастные трудности со сном, и это потенциально делает меры по усилению кровообращения в руках и ногах еще более важными[3082].
Есть ли способ сделать это, не замочив ног? Можно приложить к ногам бутылку с горячей водой[3083]. А если просто надеть теплые носки? Исследование, в котором молодые люди надевали носки за час до сна, показало, что это субъективно не улучшило качество сна. Однако объективно они спали примерно на полчаса больше, чем без носков, благодаря тому что быстрее засыпали и реже просыпались в течение ночи[3084].
Мелатонин и долголетие
Некоторые эксперты рекомендуют мелатонин – гормон, выделяемый шишковидной железой, расположенной в центре головы, между двумя полушариями, – для лечения бессонницы у пожилых людей[3085]. The World Sleep Society (Всемирное общество сна) не согласно с этим мнением и считает это средство низкоэффективным[3086]. Субъективно люди отмечают, что при приеме мелатонина они лучше спят[3087], хотя объективно метаанализ исследований показал, что мелатонин помогает заснуть лишь на четыре минуты быстрее и увеличивает общую продолжительность сна на примерно на тринадцать минут[3088]. Были обнаружены и вредные примеси[3089] (see.nf/melatoninsupplements), хотя есть и естественные источники в рационе (see.nf/melatoninfoods). Меня больше заинтриговали его предполагаемые антивозрастные свойства, но, как я описываю в видео see.nf/melatoninaging, данные по этому вопросу разнятся[3090]. Например, у крыс мелатонин значительно повышал выживаемость, но и лекарство, блокирующее мелатонин, тоже[3091]!
Травяные средства для сна?
Валериана – одна из наиболее изученных трав для сна[3092]. Однако большинство исследований, включая все последние, наиболее методологически обоснованные, не выявили существенного преимущества перед плацебо[3093]. Рандомизированные контролируемые исследования показали, что вербена лимонная может помочь пациентам с бессонницей, по крайней мере субъективно[3094], а ромашка – нет[3095]. Однако, согласно метаанализу пяти исследований, ромашка может улучшать субъективное качество сна у людей, не страдающих бессонницей[3096].
Не ешьте рыбу перед сном
Что касается питания, то низкое потребление клетчатки и высокое – насыщенных жиров и сахара ассоциируется с более поверхностным и менее восстанавливающим сном[3097]. Мясная диета связана с дремотой, которая, как предполагается, является косвенным признаком сонливости[3098]. Возможно, бессонница – это побочный эффект низкоуглеводных и кетогенных диет[3099]. Даже после снижения веса более высокое потребление мяса, по-видимому, удваивает вероятность храпа, а каждая ежедневная порция мяса на 60 % ухудшает качество и количество сна у пожилых людей. В этом повинно как красное мясо, так и птица[3100]. При этом не было обнаружено существенных различий в объективных показателях сна у тех, кто ел рыбу или курицу, свинину и говядину[3101].
Исследователи предположили, что содержащиеся в мясе аминокислоты, например метионин, конкурируют с триптофаном, который является прекурсором мелатонина и «гормона счастья» серотонина, за возможность доставки в мозг[3102], [3103]. Это может объяснить, почему ограничение рыбы, птицы и красного мяса улучшило настроение участников эксперимента в течение 2 недель[3104]. С другой стороны, растительные белки содержат относительно меньше метионина, что, возможно, объясняет, почему в исследовании тысяч людей, прошедших через растительную адвентистскую программу CHIP (Coronary Health Improvement Project), у них было отмечено более чем 50 %-ное снижение числа случаев бессонницы и беспокойного сна, а также уменьшение количества легких эмоциональных расстройств и чувства страха или депрессии в течение 4 недель[3105], [3106].
Салатные ночи
А могут помочь какие-нибудь овощи? Lactuca sativa – растение, которое традиционно используется для лечения бессонницы[3107]. Что это за экзотически звучащий овощ? Латук![3108] Экстракт латука, очевидно, использовался еще во времена Римской империи для седации и индукции сна. В латуке содержится гипнотическое вещество лактуцин, из-за которого латук имеет слегка горьковатый вкус. Сон у мышей и крыс улучшает салат ромэн[3109], в котором содержание лактуцина выше, чем в других салатах[3110], но что насчет людей? Все исследования я привожу в видео see.nf/lettuce. Итог таков: в двойном слепом исследовании по улучшению качества сна четверть чайной ложки измельченных семян латука превзошла плацебо[3111].
Ссылки на источникиУправление стрессом
По мнению руководителя крупнейшего и наиболее полного в мире исследования столетних долгожителей[3112], средняя продолжительность жизни – при отказе от табака и алкоголя, регулярных физических нагрузках, вегетарианстве и эффективном управлении стрессом – должна достигать восьмидесяти с лишним лет. «Подавляющее большинство причин того, почему люди живут до шестидесяти или семидесяти лет, а не до восьмидесяти, – пишут они с коллегой, – объясняется выбором нездоровых привычек»[3113]. Я уже говорил о диете и физических упражнениях. Насколько важна борьба со стрессом?
Американская психологическая ассоциация провела общенациональные исследования и выяснила, что большинство американцев отмечают умеренный или высокий уровень стресса[3114]. Несмотря на то что распространенность тревожных расстройств за последние несколько десятилетий не претерпела существенных изменений, уровень общего психологического стресса, по-видимому, повышается[3115]. Как это отражается на продолжительности жизни?
При стрессе большинство людей не только едят больше[3116], но и тяготеют к продуктам с высоким содержанием калорий, жира и сахара[3117]. Например, когда участникам исследования предлагали решить словесные головоломки, те, кто находился в более стрессовой ситуации, выбирали менее полезные закуски – M&M's, а не виноград[3118]. Не зря существует термин «утешительная еда». Переедание может быть признаком того, что нас что-то гложет.
Аналогичные экспериментальные исследования показали, что острые стрессовые состояния могут также вызывать тягу к сигаретам[3119], увеличивать потребление алкоголя[3120] и способствовать рецидивам при употреблении наркотиков[3121]. Итак, когда исследования показывают, что стрессовые события в жизни, такие как смерть ребенка или супруга, связаны с сокращением продолжительности жизни[3122], что в действительности виновато? Может быть, это просто сопутствующее нездоровое поведение?

