
Полная версия:
Живи долго! Научный подход к долгой молодости и здоровью
Питание считается наиболее важным фактором образа жизни, влияющим на старение, продолжительность жизни и здоровье, а главное, оно поддается модификации[2135].
Когда говорят, что «оптимальное питание», «здоровый рацион» или «более высокое качество питания» способствуют увеличению продолжительности жизни, снижению риска всех видов хронических заболеваний[2136], более высокому качеству жизни[2137] или успешному старению, что подразумевают под здоровым питанием[2138]?
Потенциальное увеличение продолжительности жизни и снижение смертности от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний и рака базируется на четырех основных составляющих качественного питания[2139]. Это: больше фруктов, больше овощей, больше цельного зерна, больше орехов и бобовых[2140]. Это рацион, богатый растительной пищей. Модели питания, богатые рафинированными и животными продуктами и бедные растительной пищей, называемые западной диетой или вестернизированным питанием, связаны с повышенным риском развития болезней и преждевременного старения[2141].
В упомянутом выше «Исследовании глобального бремени болезней» четыре из пяти основных диетических факторов риска смерти были связаны с продуктами, которые мы употребляем в недостаточном количестве. Добавление овощей в рацион может спасти около полутора миллионов жизней в мире ежегодно. Больше орехов и семян? Два миллиона жизней. Больше фруктов? Почти два с половиной миллиона жизней. А недостаточное потребление цельного зерна может стать причиной ежегодной гибели трех миллионов человек. Спасение для миллионов людей может заключаться не в каком-то новом лекарстве или вакцине, а в употреблении большего количества цельной, здоровой растительной пищи[2142]. (Заметим, что маринованные овощи с добавлением соли и консервированные фрукты с сахаром принесут больше вреда, чем пользы[2143].)
Худшие продукты питания
На что ориентироваться при принятии жизненно важных решений, например касающихся того, чем лучше питаться самому и кормить свою семью? Я часто употребляю фразу «наилучший баланс доступных доказательств», но что она означает? Она означает следующее: мнение отдельного исследования менее значимо, чем совокупное мнение всех рецензируемых научных данных.
Отдельные исследования могут приводить к заголовкам вроде такого из журнала Forbes: «Исследование не выявило связи между пассивным курением и раком»[2144]. Чтобы понять, действительно ли нет связи между пассивным курением и раком легких, лучше обратиться к обзору или метаанализу, объединяющему результаты нескольких исследований. Проблема заключается в том, что даже эти сопоставленные результаты могут иногда противоречить друг другу. Например, в одних обзорах говорится, что пассивное вдыхание табачного дыма является причиной рака легких[2145], а в других утверждается не только, что эффект незначителен и подобные разговоры могут «вызывать иррациональные страхи», но и что можно даже выкуривать четыре-пять сигарет в день и не беспокоиться об этом[2146]. (Можно представить, кто финансировал эту работу.)
Почему в обзорных статьях о влиянии пассивного курения на здоровье человека делаются разные выводы? Возможно, вас не удивит тот факт, что около 90 % обзоров, написанных исследователями, связанными с табачной промышленностью, утверждают, что пассивное курение не вредно, в то время как около 90 % независимых обзоров приходят к выводу, что оно вредно. Вероятность того, что в обзорах, написанных авторами, связанными с табачной промышленностью, будет сказано о безвредности пассивного курения, очень высока[2147]. Все это, по словам консультантов по маркетинговым исследованиям Института табака США, было частью продуманной корпоративной стратегии по дискредитации науки путем «разработки и широкой рекламы… медицинских доказательств того, что пассивное курение не вредит здоровью некурящего человека»[2148].
В таком случае, может быть, стоит ограничиться независимыми обзорами? Конечно. Если бы только мы могли выяснить, какие из них действительно беспристрастны. Исследователи, финансируемые промышленностью, используют всевозможные хитроумные способы уклонения от декларирования конфликта интересов, так что уследить за деньгами непросто. Тем не менее, даже если не знать, кто и что финансировал, большинство обзоров все равно приходят к выводу, что пассивное курение вредно. Таким образом, как одно исследование может быть не так полезно, как подборка исследований, так и один обзор может быть не так полезен, как подборка обзоров. Обзор обзоров может дать лучшее представление о том, где находится наилучший баланс имеющихся доказательств. Что касается пассивного курения, то в 63 % обзоров делается вывод о его вреде для здоровья, в 37 % – о нейтральном влиянии, и ни в одном из них не говорится о защитных свойствах, поэтому, вероятно, табачный дым лучше не вдыхать[2149].
Как было бы здорово, если бы существовал обзор обзоров различных продуктов питания! И он есть. Наконец-то опубликован исчерпывающий обзор метаанализов и систематических обзоров, посвященных изучению связей между группами продуктов питания и напитков и основными хроническими заболеваниями. Для того чтобы сделать наиболее исчерпывающее заключение, исследователи сначала разделили группы продуктов питания на растительные и животные. В подавляющем большинстве (94 %) обзоров, посвященных цельным растительным продуктам, отмечено их либо защитное, либо, по крайней мере, нейтральное действие, в то время как в большинстве (77 %) обзоров, посвященных продуктам животного происхождения, отмечено опасное для здоровья или, в лучшем случае, нейтральное действие[2150]. (Обратите внимание, что из-за округления процентов не все итоговые значения равны 100.)
Данные объединенного / метаанализа или систематических обзоров, сообщающих о защитных, нейтральных или опасных свойствах продуктов при основных хронических заболеваниях, связанных с питанием (в процентах)
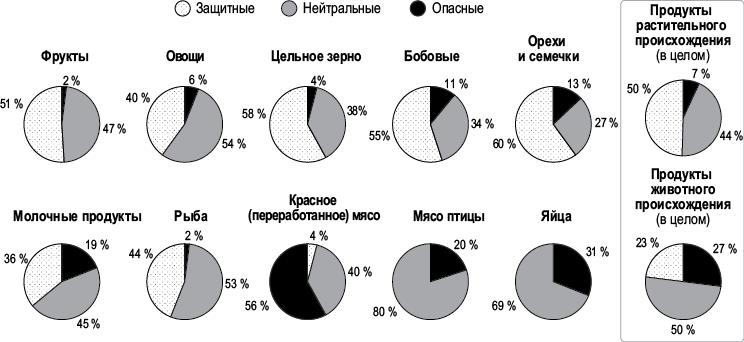
Растительная пища была разделена на пять групп: фрукты, овощи, цельное зерно, бобовые, орехи и семечки, и каждая из них неизменно получала хорошие оценки – от 87 до 98 % защитных или, по крайней мере, нейтральных. Однако результаты пяти групп продуктов животного происхождения значительно различались. Как видно из рисунка, если бы не молочные продукты и рыба, то все животные продукты были бы оценены почти полностью (98,7 %) как нейтральные или опасные[2151].
В главе «Напитки» я подробно расскажу о роли молочной промышленности, а также об эффектах замещения. Например, те, кто пьет молоко, с меньшей вероятностью будут пить газировку – напиток, еще более порицаемый во всем мире, поэтому любые защитные преимущества могут быть относительными, возникающими необязательно от того, что вы потребляете, а скорее от того, чего избегаете. Это может объяснить и данные исследования рыбы. В конце концов, типичный выбор – это выбор между курицей и рыбой, а не между курицей и нутом. Ни один обзор не выявил ни одного защитного эффекта от потребления птицы. Как видно из рисунка на с. 186, даже содовая показала 14 % защитного эффекта, но не курица и яйца – и это несмотря на все финансирование со стороны профильных национальных советов. Как и в случае с обзорами по пассивному курению, возможно, «обеление» – это иногда лучшее, что можно купить за деньги.
Молочные продукты содержат полезный кальций, а рыба – длинноцепочечные омега-3 жирные кислоты ЭПК (эйкозапентаеновая кислота) и ДГК (докозагексаеновая кислота). Однако они не так уж и необходимы для здоровья сердца. По результатам самой обширной на сегодняшний день систематической оценки влияния омега-3 жиров на здоровье сердечно-сосудистой системы, увеличение потребления рыбьего жира практически не влияет на здоровье сердечно-сосудистой системы. Более того, только растительные омега-3, содержащиеся в семенах льна и грецких орехах, могут оказать защитное действие[2152]. А вот для здоровья мозга длинноцепочечные омега-3 важны. К счастью, так же как существуют прекрасные немолочные источники кальция[2153], есть и не загрязняющие организм источники ЭПК и ДГК (на основе водорослей)[2154].
В итоге, если рассматривать заболевания, связанные с питанием, такие как ожирение, диабет 2-го типа, психические нарушения, болезни костной ткани, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания и рак, то даже если объединить все продукты животного происхождения, игнорировать промышленное лоббирование и просто принять за чистую монету существующий массив доказательств, девять из десяти исследований показывают, что цельная растительная пища как минимум не плоха, в то время как примерно восемь из десяти обзоров, посвященных продуктам животного происхождения, показывают, что они не хороши[2155].
Бургер или жизнь?
Употребление мяса связано с повышенным риском более чем 20 различных заболеваний, но как это измерить[2156]? Чтобы сравнить между собой различные хронические риски, исследователи придумали концепцию микрожизни. Это 30 минут в сравнении с ожидаемой продолжительностью жизни. В среднем 20-летним людям остается жить около 57 лет. Это примерно 20 тысяч дней, полмиллиона часов или один миллион получасов. Микрожизнь – это один из миллионов оставшихся у нас получасов. Выкуривание двух сигарет или выпивание двух пинт пива в среднем обойдется 30-летнему мужчине в одну микрожизнь, как и каждый день, проведенный с лишним весом в 11 фунтов[2157]. Видите, как это полезно для сравнения рисков? Выпитая пинта крепкого пива, например, сокращает продолжительность жизни настолько же, насколько сокращает ее выкуривание одной сигареты. Если для вас немыслимо настолько не уважать свое здоровье, чтобы выкуривать по сигарете дважды в день, то столь же немыслимо должно быть иметь 11 фунтов лишнего веса.
В качестве альтернативы приведу виды поведения, продлевающие жизнь. Например, ежедневное употребление не менее пяти порций фруктов и овощей может увеличить продолжительность жизни в среднем на 4 года. Это примерно в 2 раза больше, чем ежедневные физические упражнения. Но даже двадцатиминутные физические упражнения могут прибавить к жизни час (две микрожизни). Хорошая новость для всех, кто говорит, что у них нет времени на занятия спортом: физические упражнения потенциально дают возврат инвестиций в соотношении три к одному. Потратив на них двадцать минут своей жизни, вы теоретически получаете шестьдесят минут жизни. Отдача от большей продолжительности тренировок немного снижается, но, занимаясь по часу в день, вы все равно сможете вернуть больше времени, чем вложили[2158].
А как насчет мяса? Один бургер приводит к потере одной микрожизни. Стоит ли съеденный гамбургер тридцати минут жизни[2159]? Таким образом, с точки зрения продолжительности жизни один гамбургер равен двум сигаретам. Если вы отказались от сигареты до и после обеда, то, возможно, вам стоит попробовать также буррито с фасолью.
Сэндвич с яичным салатом тоже не лучший выбор. В 2021 году было опубликовано крупное исследование смертности – NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study, спонсированное Национальным институтом здоровья и Американской ассоциацией пенсионеров, в котором более полумиллиона человек наблюдались в среднем 16 лет. Половина яйца в день повышала риск смерти от всех причин на 7 %[2160], что ставит яйцо на одну ступень с гамбургером в рейтинге продуктов, сокращающих продолжительность жизни[2161].
Бекон вызывает рак
Переработанное мясо еще хуже. Представьте себе двух одинаковых во всех отношениях людей, только один из них съедает около 50 г переработанного мяса в день – примерно одну большую сосиску, хот-дог или несколько полосок бекона, а другой – нет. По расчетам, стиль питания первого отнимет у него около 2 лет жизни[2162].
В качестве альтернативы можно представить расчет в дневном разрезе. Съев бутерброд с двумя ломтиками деликатесного мяса, например с балыком или ветчиной, вы потеряете около одного часа своей жизни[2163]. Бывает ли у вас иногда ощущение, что в сутках не хватает часов? Так вот, в зависимости от того, что вы возьмете с собой на обед, у вас может стать на один час меньше в реальности.
Переработанное мясо – бекон, мясные деликатесы, хот-доги и т. п. – вызывает рак. В 2015 году самый авторитетный в мире институт по изучению рака отнес переработанное мясо к канцерогенам первой группы[2164]. Специалисты ставят вопрос о том, чтобы отнести переработанное мясо к той же категории канцерогенов, что и асбест, табак[2165] и иприт[2166], но классификация зависит от силы доказательств того, вызывает вещество рак или нет, а не от того, насколько оно опасно[2167]. Все вещества, отнесенные к первой группе, не одинаково опасны[2168]. Даже если они оба являются канцерогенами первой группы, безопаснее съесть бутерброд с начинкой из пастрами, чем плутоний.
Насколько опасно переработанное мясо? Риск развития рака толстой кишки повышается на 18 % на каждые 50 г переработанного мяса, потребляемого в день. Таким образом, если каждый день на обед съедать бутерброд с двумя маленькими кусочками колбасы, то риск развития рака толстой кишки увеличится на 18 %. А полкило пастрами на ржаном хлебе может увеличить его на 80 %[2169]. Когда я выступал перед Научным комитетом по разработке диетических рекомендаций США на 2020–2025 годы, я сказал: «Мы стараемся не курить рядом с нашими детьми, так зачем же давать им в школу бутерброды с колбасой?» Возможно, это звучит как гипербола, но преувеличением на самом деле не является. По данным главного хирурга США, совместное проживание с курильщиком повышает риск развития рака легких на 15 %[2170]. Таким образом, пассивное курение изо дня в день повышает риск развития рака легких почти в той же степени, в какой ежедневное употребление одной порции переработанного мяса повышает риск развития колоректального рака.
Колоректальный рак является второй по частоте причиной смерти от рака после рака легких[2171]. Поэтому, если вы не курите, рак толстой и прямой кишки может стать вашим главным врагом. Но вы способны снизить этот риск почти на 20 %, просто исключив из своего ежедневного рациона порцию переработанного мяса.
Назад к природе
Самые полезные продукты, как правило, имеют растительное происхождение, поэтому не приходится удивляться, что здоровое растительное питание связано с более низким риском преждевременной смерти среди населения в целом[2172] и среди пожилых людей в частности[2173]. Для здорового старения[2174], долголетия[2175] и замедления развития возрастных заболеваний[2176] рекомендуются диеты, основанные на цельной растительной пище. Например, такая диета может снизить риск развития болезни Альцгеймера более чем в 2 раза и сэкономить системе здравоохранения миллиарды долларов[2177]. Всего одна дополнительная порция фруктов или овощей в день может сократить медицинские расходы в США на 5 млрд долларов в год[2178].
Преимущества растительного питания, вероятно, обусловлены двойным действием: увеличением количества защитных пищевых факторов, таких как клетчатка, и снижением потребления патогенных (вызывающих заболевания) пищевых факторов, таких как насыщенные жиры[2179]. В течение 18 лет в Балтиморском лонгитюдном исследовании старения наблюдали за людьми, средний возраст которых составлял около 60 лет. Исследователи обнаружили, что большее количество фруктов и овощей, а также меньшее количество насыщенных жиров ассоциируется с низкой вероятностью смерти от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний в течение этого периода, но только сочетание повышенного потребления растительных продуктов и уменьшения насыщенных жиров значительно снижает риск смерти от всех причин, вместе взятых[2180]. Такая диета сформировалась за долгие годы жизни наших предков.
Предполагается, что за миллионы лет до того, как мы начали молоть зерно, мастерить копья или варить сахарный тростник, вся наша физиология развивалась в контексте питания тем, чем питались наши двоюродные братья, человекообразные обезьяны, – листьями, стеблями и побегами (то есть овощами), семенами, орехами и фруктами[2181]. Мы начали использовать орудия труда в эпоху палеолита, которая насчитывает всего два миллиона лет, но мы и другие человекообразные обезьяны эволюционировали с эпохи миоцена, то есть в течение около двадцати миллионов лет[2182]. Таким образом, на протяжении первых 90 % времени своего существования гоминоиды питались преимущественно растениями[2183]. Мы были созданы для того, чтобы питательные вещества из дикой растительной пищи, особенно фруктов[2184], непрерывно поступали в наш организм[2185] при крайне низком потреблении холестерина и насыщенных жиров[2186]. Поэтому нет ничего удивительного в том, что наш организм лучше всего функционирует именно при той диете, для которой мы были созданы. Возможно, нам следует вернуться к нашим (съедобным) корням.
Без соли
Резкое увеличение потребления соли стало одним из самых драматических изменений в нашем питании. На протяжении большей части существования человечества мы получали лишь ту щепотку соли, которая естественным образом содержалась в цельных продуктах питания[2187]. Сегодня, в основном благодаря переработанным продуктам питания, мы получаем в 10 раз больше соли, чем надо[2188], и это приводит к разрушительным последствиям для здоровья[2189].
Я уже упоминал четыре из пяти самых смертельных диетических ловушек, определенных в «Исследовании глобального бремени болезней»: недостаточное потребление цельного зерна, фруктов, орехов, семян и овощей, но самый фатальный недостаток питания человечества заключается не в том, чего мы получаем слишком мало, а в том, чего мы получаем слишком много. Избыток натрия, по-видимому, является для человечества фактором риска смерти номер один[2190].
Подробный обзор этого явления приведен в главе «Как не умереть от гипертонии» в книге «Не сдохни!». Доказательства того, что натрий повышает артериальное давление, очевидны, включая двойные слепые рандомизированные исследования, проводившиеся на протяжении десятилетий[2191]. Может быть достаточно одного приема пищи. Когда испытуемым с нормальным артериальным давлением давали тарелку супа с количеством соли, обычно содержащимся в среднем американском блюде[2192], их артериальное давление повышалось в течение следующих 3 часов; у тех же, кто ел тот же суп без добавления соли, таких последствий не наступало[2193]. «Нормальное» потребление соли может привести к «нормальному» артериальному давлению, а затем – к смерти от «нормальных» причин, таких как инфаркты и инсульты.
В США у большинства взрослых в возрасте 45 лет и старше наблюдается повышенное артериальное давление и почти у девяти из десяти после 74 лет[2194], в то время как в бессолевых культурах, таких как индейцы яномами с Амазонки, потребляющих нормальное для человеческого вида количество натрия, не было выявлено ни одного случая повышенного артериального давления. Их среднее давление, как у всех человеческих младенцев[2195], составляет около 100 на 60 и остается таким на протяжении всей жизни[2196].
Отказаться от привычки к соли можно с помощью нескольких простых стратегий[2197]. Не готовьте с солью и не добавляйте ее в пищу. Когда вы только начинаете отказываться от соли, пища может показаться немного безвкусной, но уже через 2–4 недели рецепторы вкуса соли во рту становятся гораздо более чувствительными, и вкус пищи улучшается. Через 2 недели вы, возможно, даже предпочтете менее соленую пищу[2198]. Попробуйте использовать перец, лайм, лук, базилик, чеснок, помидоры, тимьян, сладкий перец, петрушку, сельдерей, порошок чили, лимон, розмарин, копченую паприку, карри и кориандр, чтобы найти новые, более яркие вкусовые ощущения[2199]. В редакционной статье престижного медицинского журнала New England Journal of Medicine утверждается, что «индивидуальные усилия, вероятно, не дадут результата», поскольку 75 % потребления соли обеспечивается за счет покупаемых в магазинах продуктов питания[2200], но я не согласен с заявлением, что мы не можем контролировать продукты, которые покупаем. Хотя в некоторых продуктах высокое содержание натрия может оказаться неожиданным.
Например, наибольшее количество соли в рационе людей в возрасте от 20 до 50 лет содержит курятина[2201]. В птицеводческой промышленности в куриные тушки регулярно добавляют соленую воду, чтобы искусственно увеличить их вес, и при этом на этикетке может быть написано «100 % натуральные». По данным журнала Consumer Reports, некоторые куры в продуктовых магазинах были настолько накачаны солью, что в каждой порции содержалось 840 мг натрия. Одна куриная грудка может превышать дневную норму натрия[2202].
Ныне не существующий Институт соли активно выступал против рекомендаций по снижению потребления натрия. В выступлении перед комитетом Конгресса по диетическим рекомендациям он опровергал предположение о том, что более здоровое питание приведет к сокращению расходов на здравоохранение, таким образом: «В действительности, – заявил один из защитников пищевой промышленности, – расходы на здравоохранение возрастают, если продолжительность жизни увеличивается». Если люди живут дольше, потому что питаются более здоровой пищей, это может быть дороже, а «если запретить табак, то увеличение ожидаемой продолжительности жизни одновременно увеличит расходы на уход за пожилыми людьми»[2203].
Очищение языка
С возрастом чувство вкуса может снижаться. Как следствие, пожилые люди часто пересаливают пищу[2204]. Инновационным способом борьбы с потерей чувствительности к соли является очистка языка от беловато-серого налета, который может закупоривать вкусовые поры[2205]. Посмотрите мой видеоролик see.nf/tonguecleaning о том, как чистка языка щеткой или скребком улучшает способность ощущать вкус соли как у молодых[2206], так и у пожилых людей[2207], эффективно снижая факторы риска[2208].
Заменители соли на основе калия
Гипертонию, или повышенное артериальное давление, называют «тихим и невидимым убийцей», поскольку она редко вызывает симптомы, но является одной из самых распространенных причин смерти[2209]. Рекомендуемая Американской кардиологической ассоциацией норма натрия составляет 1500 мг в день[2210]. Попробуйте угадать, какой процент американцев превышает эту норму. Невероятные 99,4 %[2211]! Подавляющее большинство взрослых американцев потребляют слишком много натрия и одновременно слишком мало калия – минерала, снижающего артериальное давление. (Только 2 % взрослых американцев получают минимальную рекомендуемую суточную норму калия[2212].) Это еще более поразительно, если сравнить эти данные с потреблением калия нашими предками[2213]. Вполне вероятно, что они получали с пищей более 10 000 мг в день[2214]. Сейчас рекомендуемый суточный минимум составляет лишь половину от этого количества, однако большинство из нас даже не приближается к нему.
Если сложить эти две рекомендации вместе, то окажется, что в настоящее время нормы по потреблению натрия и калия выполняются менее чем 0,015 % населения США[2215]. Почти 99,99 % не соблюдают рекомендации, и только один из примерно семи тысяч американцев следует им. А как насчет использования заменителей соли на основе калия? Вместо того чтобы приправлять пищу хлоридом натрия (солью), почему бы не добавить в нее немного хлорида калия? Это минеральная соль природного происхождения, хлорид калия получают так же, как и обычную натриевую соль[2216]. Рандомизированные контролируемые исследования показали, что простая замена обычной соли на хлорид калия может не только привести к значительному снижению артериального давления[2217], но и предотвратить развитие гипертонии, а главное – спасти жизнь. Оказалось, что даже просто переход на соль с пониженным содержанием натрия отодвигает риск смерти на 10 лет[2218]. Я рассматриваю эти исследования в своем видео see.nf/ksalt.
Кажется, что это слишком хорошо, чтобы быть правдой. Почему же до сих пор большинство людей не используют этот заменитель соли, если он так хорошо работает и так же хорош на вкус[2219]? Управление по контролю качества пищевых продуктов и лекарственных средств (FDA) считает хлорид калия «в целом безопасным»[2220]. Причина, по которой здоровым людям не нужно беспокоиться о переизбытке калия, заключается в том, что наши почки просто выводят его излишки[2221]. Однако тем, у кого диагностированы заболевания почек, диабет (поскольку диабет может привести к повреждению почек), тяжелая сердечная или надпочечниковая недостаточность, а также тем, кто принимает лекарства, нарушающие выведение калия, следует быть осторожными[2222]. Пожилым людям перед началом приема заменителей соли следует попросить врача проверить функцию почек. Более подробную информацию об этом можно найти на see.nf/ksaltsafety.

