
Полная версия:
Живи долго! Научный подход к долгой молодости и здоровью
Единственным недостатком для здоровых людей является вкус. Если вы на 100 % откажетесь от натрия и будете использовать только хлорид калия, то можете обнаружить, что он имеет немного горький или металлический привкус[2223]. Лично я считаю, что это зависит от того, куда именно я его добавляю. Хлорид калия прекрасно подходит к некоторым блюдам, но другие, по моему мнению, становятся просто несъедобными. Когда я узнал о натрии и навсегда выбросил свои солонки, мое вкусовое восприятие в течение нескольких недель полностью изменилось, все было прекрасно на вкус без соли – за исключением песто. По какой-то причине песто без соли просто не имел прежнего вкуса, поэтому я попробовал использовать заменитель соли – хлорид калия, и он прекрасно сработал. Я вообще не почувствовал разницы, так что я убил двух зайцев. Воодушевившись, я решил воссоздать любимое блюдо детства. Раньше я клал на арбуз крошечную щепотку соли, чтобы сделать его еще слаще – традиционный кулинарный прием южан, но когда я попробовал это сделать с калийной солью, меня чуть не стошнило!
Мы есть то, что мы едим
Американская диета не только главный убийца американцев, но и, отчасти благодаря эпидемии ожирения, главная причина инвалидности в США[2224]. Таким образом, от того, что мы едим, в первую очередь зависит продолжительность нашей жизни и то, станем мы инвалидами или нет.
Если наше питание является причиной смерти и инвалидности номер один[2225] и если большинство смертей можно предотвратить и они связаны с питанием[2226], то, очевидно, диетология – это предмет номер один, который преподают в медицинских школах, верно? Это первое, что обсуждает с вами врач на каждом приеме, согласны?
К сожалению, врачи страдают от серьезного дефицита знаний о питании – они не получают их в процессе обучения. Большинству студентов-медиков не рассказывают о том, как здоровое питание может повлиять на течение болезни, поэтому они выпускаются без этого мощного арсенала знаний[2227]. Существуют также институциональные барьеры, такие как нехватка времени и отсутствие компенсаций. Как правило, врачам не платят за то, что они консультируют своих пациентов о способах позаботиться о себе[2228]. Конечно, на медицинское образование и лечебную практику влияют и фармацевтические компании. Директор Института медицинских гуманитарных наук так завершил статью в журнале, посвященную влиянию фармацевтических гигантов на медицинское образование: «Даже не знаю, что является более суровым осуждением нашего профессионализма – наша готовность быть купленными или наша готовность рационализировать и отрицать, чтобы казалось, что этого не происходит»[2229]. Спросите у своего врача, когда его в последний раз угощали большим количеством брокколи.
Это похоже на курение в 1950-х годах. Уже тогда были получены научные данные, связывающие сигареты с раком, но они практически не учитывались, в частности потому, что курение было нормальным явлением[2230]. Среднедушевое потребление сигарет составляло 4000 сигарет в год[2231] – то есть средний американец выкуривал полпачки в день. В то время Американская медицинская ассоциация успокаивала всех, что «курение в меру» – это нормально[2232]. В конце концов, большинство врачей сами курили сигареты[2233]. Налицо тот же самый разрыв между наукой и медицинской практикой: неопровержимые доказательства против инерции личной привычки.
Потребовалось более 25 лет[2234], 7000 исследований и смерть бесчисленного количества курильщиков, прежде чем в 1960-х годах был опубликован первый доклад главного хирурга США, обличающий курение[2235]. Казалось бы, после первых 6000 исследований можно было бы предупредить людей, но нет. Гигантская табачная промышленность была мощной индустрией, и сегодня производители алкоголя, мяса, сахара, молочных продуктов, соли, яиц и переработанных продуктов питания используют ее тактику, пытаясь исказить научные данные и запутать общественность[2236].
Пищевая промышленность – это индустрия с оборотом в триллион долларов, тысячи торговых ассоциаций тратят сотни миллионов долларов на лоббирование наших законодателей. За переработанными пищевыми продуктами компании PepsiCo следуют сахар, мясо и молочные продукты: их производители – основные лоббисты[2237]. (Молочные продукты – единственная торговая группа, бюджет которой превышает 100 миллионов долларов[2238].) Это многое говорит нам об американском рационе питания. Cui bono?[2239] Следуйте за деньгами.
Сегодня только 1–2 % врачей курят[2240], [2241], но большинство продолжают употреблять в пищу продукты, которые способствуют эпидемии заболеваний, вызванных неправильным питанием[2242]. Пока система не изменится, мы должны взять на себя личную ответственность за свое здоровье и здоровье своей семьи. Мы не можем ждать, пока общество снова догонит науку, потому что это вопрос жизни и смерти.
Хозяин своей судьбы
Специалисты по долголетию считают питание, вероятно, «наиболее важным фактором укрепления здоровья и профилактики подавляющего большинства хронических возрастных заболеваний»[2243]. Переход от обычного питания к более оптимизированному с 20-летнего возраста увеличит продолжительность жизни женщин примерно на 11 лет, а мужчин – на тринадцать. Наибольший прирост продолжительности жизни будет достигнут при употреблении большего количества бобовых, цельного зерна и орехов при сокращении потребления мяса и напитков с высоким содержанием сахара, таких как газировка. Сделать это никогда не поздно. Начать питаться более здоровой пищей в возрасте 60 и даже 80 лет – значит добавить себе еще несколько лет жизни[2244]. Изменить свою судьбу можно уже со следующего приема пищи.
Напитки
Вы, наверное, слышали, что человеческое тело на 70 % состоит из воды. Это верно для новорожденных, но, как говорил Аристотель, «старость суха и холодна». В организме пожилого человека воды может быть только 50 %[2245]. В связи с уменьшением запасов жидкости, снижением чувства жажды[2246] и ослаблением способности почек концентрировать мочу пожилые люди сильнее других подвержены обезвоживанию[2247], особенно при приеме слабительных или мочегонных препаратов[2248]. Каков наилучший способ поддержания гидратации?
Рекомендации консенсусной группы
Существуют многочисленные диетические рекомендации по питанию, но как насчет того, что мы должны пить? В США была учреждена Комиссия по напиткам, в которую вошли ведущие эксперты в области здравоохранения, такие как доктор Уолтер Уиллетт, в то время возглавлявший кафедру диетологии в Школе общественного здравоохранения Гарвардского университета. Задача группы заключалась в том, чтобы дать рекомендации по пищевым рискам и пользе, а также относительной полезности для здоровья различных категорий напитков, ранжированных по шестиуровневой шкале: от лучших к худшим.
Газировка заняла последнее место – что неудивительно. К разряду вредных напитков, которых следует избегать, были отнесены пиво и цельное молоко. Составители рекомендаций ссылались на возможную связь употребления молока и развития рака простаты и агрессивного рака яичников: задокументировано влияние молока на уровень инсулиноподобного фактора роста 1, о котором я рассказывал в главе «ИФР-1».
А что наверху списка? На втором месте среди самых полезных напитков оказались чай и кофе, желательно без подсластителей и сливок. Догадайтесь, какой напиток занял первое место. Правильно, вода[2249].
Засуха или наводнение?
В разделе «Напитки» книги «Не сдохни!» я рассказываю о происхождении и развенчании мифа о рекомендации «пить не менее восьми стаканов воды в день», а также обсуждаю трудности установления причинно-следственных связей в многочисленных исследованиях, связывающих низкое потребление воды с широким спектром заболеваний[2250]. В видео see.nf/h2olongevity я привожу обзор всех исследований, посвященных потреблению воды и смертности. Три исследования показали корреляцию количества потребляемой воды и смертности[2251], [2252], [2253], а четыре [2254], [2255], [2256], [2257] – что связь остается туманной.
Так сколько же воды нужно пить?
По данным анализов крови, от 20 до 30 % пожилых людей испытывают обезвоживание[2258]. Они подвержены повышенному риску сердечных приступов, пневмонии, образования тромбов, что приводит к тому, что шансы стать инвалидами в течение последующих 4 лет повышаются вдвое[2259]. Как определить, что вы обезвожены? Молодые люди могут просто проверить цвет мочи. Золотой стандарт гидратации – точнее, бледно-золотой стандарт – это цвет соломы, светло-желтый. Более темно-желтый, янтарный или коричневатый цвет мочи указывал на обезвоживание, что было проверено на спортсменах[2260], беременных и кормящих женщинах[2261] и населении в целом[2262], но, похоже, этот способ не работает у пожилых людей[2263]. Ни одна из шестидесяти семи различных оценок обезвоживания, включая цвет или объем мочи, сухость во рту или чувство жажды, не оказалась стопроцентно точной для определения состояния гидратации у людей старше 65 лет. Прогностически значимым, говорящим о надвигающемся обезвоживании у пожилых мужчин и женщин, оказалось только сочетание усталости и пропуска нескольких стаканов воды между приемами пищи[2264].
Основываясь на наиболее достоверных данных, Всемирная организация здравоохранения и Институт медицины США рекомендуют выпивать 8–11 стаканов воды в день женщинам и 10–15 стаканов – мужчинам[2265]. При этом речь идет о воде из всех источников, а не только о напитках. Около четырех стаканов воды мы получаем из пищи, которую едим, и из того, что наш организм вырабатывает сам[2266] (например, при сжигании жира), так что эти рекомендации примерно означают, что при умеренной физической активности при умеренной температуре окружающей среды необходимо выпивать от четырех до семи стаканов воды в день для женщин и от шести до одиннадцати стаканов для мужчин[2267]. Однако производительность почек пожилых людей, как правило, ограничивается примерно тремя-четырьмя стаканами в час, поэтому в обычных условиях не следует превышать этот лимит[2268]. Если выпить больше рекомендованного количества, это может привести к критическому электролитному дисбалансу в мозге[2269].
Какую воду следует пить?
Многие считают, что водопроводная вода небезопасна[2270], но и бутилированная вода может быть не чище, чем вода прямо из-под крана[2271]. Однако насколько это соответствует действительности? Безопасность питьевой воды – это не только профилактика заболеваний, передающихся через воду.
Фактически наша борьба с микробными загрязнениями привела к появлению нового вида загрязнений в нашей воде – побочных продуктов дезинфекции, образующихся при хлорировании питьевой воды.
Рейтинг напитков: от лучших к худшим
Какие напитки лучше всего употреблять, кроме воды? Ниже приведен еще один график из исследования, включающего сотни объединенных метаанализов и систематических обзоров, в которых описаны защитные, нейтральные или пагубные ассоциации с хроническими заболеваниями, связанными с питанием[2272].
Данные объединенного / метаанализа или систематических обзоров, сообщающих о защитных, нейтральных или опасных свойствах продуктов при основных хронических заболеваниях, связанных с питанием (в процентах)
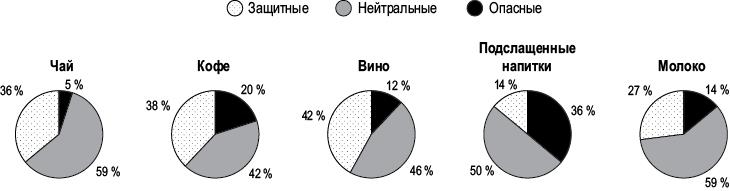
Как и ожидалось, подслащенные напитки, такие как газировка, оказались наиболее вредными, однако в 14 % обзоров сообщалось о защитном действии безалкогольных напитков. Как такое возможно? В большинстве случаев это были ссылки на перекрестные исследования, например на такое, которое показало, что девочки-восьмиклассницы, которые пили больше газировки, реже страдали от ожирения, чем те, кто пил меньше[2273]. Однако это была всего лишь фиксация момента. Как вы думаете, как так произошло? Девочки с большим весом весили больше, потому что пили меньше газировки, или они пили меньше газировки, потому что были тяжелее? Воздержание от употребления газировки может быть следствием ожирения, а не его причиной, но при этом ее наделяют защитными свойствами, поскольку меньшее количество этого напитка ассоциируется с меньшими проявлениями заболевания.
Недостатки дизайна исследований также могут объяснять и выводы, сделанные относительно вина. Обзор был опубликован в 2014 году, до произошедшего в нашем сознании переворота в понимании пользы для здоровья «умеренного» употребления алкоголя (оказалось, что польза была лишь миражом)[2274]. (О системной ошибке, связанной с неправильной классификацией бывших алкоголиков, как будто они всю жизнь были трезвенниками, см. с. 191[2275].) Иногда, однако, возникают неожиданные выводы. Например, в одном из исследований безалкогольных напитков было обнаружено, что увеличение потребления газировки связано со снижением риска развития некоторых видов рака пищевода. Позвольте мне угадать: не финансировался ли этот обзор компанией Coca-Cola? Да, обзор финансировался компанией Coca-Cola[2276]. Помогает ли аналогичный конфликт интересов объяснить «защитные» исследования молока? Финансировались ли они Национальным молочным советом? По правде говоря, в исследованиях молока было обнаружено еще больше конфликтов интересов, чем в исследованиях газировки, а финансируемые исключительно промышленностью исследования всех этих напитков в 4–8 раз чаще отвечают финансовым интересам спонсора[2277].
Однако если отбросить предвзятое отношение к финансированию, можно согласиться с тем, что для признания защитных свойств молока есть основания. В конце концов, те, кто пьет больше молока, могут пить меньше газировки, которая является еще более вредным напитком, поэтому те, кто пьет молоко, оказываются в выигрыше. Но дело может быть не только в относительной пользе. Даже такое осуждаемое всеми вредное явление, как курение табака, не является абсолютно плохим. Более чем в 40 исследованиях обнаружено защитное действие никотина на мозг больных болезнью Паркинсона[2278]. Даже пассивное курение иногда защищает[2279]. Конечно, все же лучше избегать его. Табак может снизить риск развития болезни Паркинсона, но его употребление повышает риск инсульта, еще более смертельного заболевания мозга, не говоря уже о раке легких и болезнях сердца, которые унесли жизни миллионов американцев с момента выхода первого доклада генерального хирурга о вреде курения[2280].
К счастью, употребляя в пищу некоторые никотинсодержащие овощи, мы можем получить кое-какие преимущества, ничем не рискуя[2281] (see.nf/nightshades), и тот же подход может быть верен в отношении молочных продуктов. Потребление молока связано с повышенным риском рака простаты[2282], что привело к появлению рекомендаций, согласно которым мужчинам лучше сократить или минимизировать его[2283], но молочные продукты в рационе также снижают риск рака толстой кишки[2284]. По-видимому, их защитное действие обусловлено наличием кальция[2285]. К счастью, мы можем убить двух зайцев, употребляя растительные продукты с высоким содержанием кальция, такие как зелень и бобовые[2286].
Я более подробно рассмотрел молочные продукты (см. с. 123) и рассказал о пользе кофе (см. с. 35). Однако если судить по рисунку на с. 186, каждая чашка кофе может оказаться упущенной возможностью выпить что-то еще более полезное, например чашку чая.
Самый полезный вид молока
В настоящее время в молочной отрасли появилась целая линейка новых вариантов. Молочные продукты, изготовленные из всего: от миндаля до овса[2287], – настолько популярны, что крупные молочные корпорации выходят из бизнеса[2288]. Из всех вариантов соевое молоко, пожалуй, самое полезное. Посмотрите мой видеоролик see.nf/milks. Все растительные молочные продукты не содержат лактозы, что является преимуществом, заслуживающим особого внимания[2289].
Большинство взрослых людей страдают непереносимостью лактозы, то есть испытывают трудности с перевариванием молока. Уровень фермента, отвечающего за расщепление молочного сахара – лактозы, с возрастом начинает снижаться у большинства людей во всем мире, что вполне логично: ведь молоко предназначено для младенцев[2290]. Зачем нам переваривать его после того, как нас отлучили от груди? Поэтому при употреблении молока большинство людей на планете могут испытывать такие симптомы, как вздутие живота, боли в животе, кишечные газы, водянистый стул или даже тошнота и рвота[2291].
По оценкам, мальабсорбция[2292] лактозы в среднем в мире встречается у двух из трех человек. В США это скорее один человек из трех[2293], но 95 % азиатов, 60–80 % афроамериканцев и евреев-ашкенази, 80–100 % американских индейцев и 50–80 % латиноамериканцев имеют проблемы с перевариванием молока. Выходцы из Северной Европы с большей вероятностью смогут переваривать его на протяжении всей взрослой жизни[2294]. Таким образом, утверждение о том, что все должны пить молоко, выглядит как пример расовой предвзятости в государственной политике в области питания[2295]. Спойлер: не все жители США имеют североевропейское происхождение.
По этим причинам Канада исключила молочные продукты из своих национальных диетических рекомендаций. Проведя тщательный анализ, канадские диетологи пересмотрели рекомендации и переопубликовали их в 2019 году. Особое внимание они уделили важности потребления большего количества растительной пищи[2296]. Перенос внимания с молочных продуктов на растительную пищу отчасти объясняется тем, что канадские эксперты отказались принимать к рассмотрению исследования, финансируемые промышленностью[2297]. Вот это концепция! Многие ведущие медицинские журналы уже отказываются принимать работы, финансируемые табачными гигантами[2298]. Пора подумать о том, чтобы распространить эту практику на все коммерческие организации, стремящиеся исказить научные данные и поставить прибыль выше здоровья населения.
Зеленый и черный чай
Каждый день мы потребляем буквально миллиарды чашек чая[2299]. Катехин EGCG (эпигаллокатехин галлат), содержащийся в чае, способен продлить жизнь C. elegans в стрессовых условиях[2300], а также отсрочить смерть крыс на 8–12 недель, увеличивая среднюю продолжительность жизни примерно на 14 %[2301]. Хотя мы все еще ждем долгосрочных рандомизированных контролируемых клинических исследований, обзор 96 метаанализов обсервационных исследований показал, что увеличение потребления чая до трех чашек в день может снизить риск преждевременной смерти от всех причин, вместе взятых, на 24 %[2302], что эквивалентно увеличению продолжительности жизни примерно на 2 года[2303]. Это относится как к зеленому, так и к черному чаю, хотя зеленый чай, возможно, немного предпочтительнее[2304]. (Подробности – в видео see.nf/greenblack, где я также рассматриваю довольно неутешительные данные об использовании матча для лечения болезни Альцгеймера.)
Без молока
Считается, что очевидная польза чая в значительной степени обусловлена тем, что он защищает сердечно-сосудистую систему: употребление как зеленого, так и черного чая может значительно улучшить работу артерий уже через несколько часов после употребления[2305]. Однако это сработает только в случае отказа от молока. В 2007 году мы впервые узнали, что добавление молока «полностью нивелирует эффект чая», когда речь идет об улучшении функции артерий[2306]. В 2018 году оказалось, что все обстоит еще хуже. Ученые разделили мужчин и женщин на три группы: одна в течение месяца пила черный чай, другая – черный чай с молоком и третья – обычную горячую воду. Как и ожидалось, в группе, употреблявшей только черный чай, наблюдалось значительное улучшение функции артерий. Однако у группы, пившей чай с молоком, функции артерий ухудшились в сравнении не только с первой группой, но и с группой, пившей обычную горячую воду. Таким образом, молоко не просто нейтрализовало полезный эффект: употребление чая с молоком оказалось вреднее, чем отсутствие чая вообще[2307]. Позже выяснилось, что молоко также снижает полезные свойства ягод, шоколада[2308], [2309] и кофе[2310] (см. с. 432).
Красный чай
Черный, зеленый и белый чай получают из одного и того же вечнозеленого растения (Camellia sinensis), в то время как травяной чай получают, заливая кипятком любое растение, кроме чайного. О чае из гибискуса я рассказывал в главе «AMPK», а о ромашке – в главах «Гликирование» и «Воспаление». Ройбуш[2311], также известный как красный чай или чай из красного кустарника, – еще один известный травяной чай, который может обладать антивозрастными свойствами. В условиях окислительного стресса он увеличивает продолжительность жизни C. elegans на 23 %, что, предположительно, обусловлено его антиоксидантными свойствами[2312]. В сравнительном анализе 15 видов травяных чаев ройбуш занял второе место (после одуванчика) по антиоксидантной способности in vitro[2313].
Оптимальные способы заваривания чая рассматриваются в статье see.nf/red. В идеале красный чай следует заваривать[2314] не менее 5 минут[2315]. Черный чай заваривайте 4 минуты, зеленый[2316] – 3 минуты при температуре 85 °C[2317] и белый чай – 7 минут при 98 °C[2318]. Удивительно, но пакетики лучше, чем рассыпной чай, поскольку листья в пакетиках гораздо сильнее измельчены, что позволяет получить большее количество экстракта[2319].
Газировка
Теперь, когда мы рассказали о некоторых лучших напитках, что можно сказать о худших?
В обычной банке газировки содержится около девяти ложек сахара. Учитывая, что подслащенные напитки являются самым мощным источником лишнего сахара в рационе американцев[2320], не приходится удивляться тому, что их потребление связано с преждевременной смертью. Каждая дополнительная банка газировки, содержащая сахар, в день увеличивает смертность от всех причин примерно на 8 %[2321], что, вероятно, связано с повышенным риском сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний[2322] и диабета[2323].
Диетическая газировка тоже ассоциируется с повышенным риском смертности, хотя она вдвое менее вредна, чем обычная, а при потреблении двух банок риск повышается на 8 %[2324]. Кроме того, те, кто пьет много подслащенной газировки, чаще страдают избыточным весом или ожирением. Возможно, недиетическая газировка приводит к проблемам со здоровьем, а проблемы со здоровьем заставляют людей пить диетические напитки – возникает так называемая обратная причинно-следственная связь. Однако во всех анализах при учете веса риск смертности оставался значительным. Это наблюдалось даже в тех случаях, когда в исследованиях не учитывались первые несколько лет наблюдения, чтобы исключить тех, кто мог перейти на диетическую газировку для решения проблем со здоровьем непосредственно перед смертью. В редакционной статье, содержащей выводы исследования («Инициатива по охране здоровья женщин» – Women's Health Initiative), была установлена связь между диетической газировкой и риском развития инсульта. Это было сформулировано следующим образом: «Подсластители искусственные, риски реальные»[2325]. О том, как искусственные подсластители могут нарушить наш микробиом и обмен веществ, читайте в моем разделе «Напитки» книги «Не сдохни!».
Алкоголь
Когда я сел за подготовку этого раздела, то с удивлением обнаружил работу под названием «Текила… продлевает продолжительность жизни у Drosophila melanogaster – плодовых мушек»[2326]. Я представил себе полчища маленьких жужжащих мушек, но, увы, нет. «Текила» – это просто название, которое креативный специалист по генетике мух дал некоему гену плодовой мушки[2327]. Итак, текила (спиртное), возможно, и не помогает плодовым мушкам жить дольше, но как насчет нас?
Употребление алкоголя является седьмым по распространенности фактором риска смерти в мире, ежегодно приводящим к гибели миллионов людей[2328]. Алкоголь сокращает количество потерянных здоровых лет жизни в 3 раза интенсивнее, чем употребление всех видов наркотиков, вместе взятых[2329]. Примерно половина всех смертей, связанных с употреблением алкоголя, – это происшествия, например автомобильные аварии; другая половина – это медленное разрушение печени[2330]. За последние двадцать с лишним лет в США примерно на 50 % увеличилось число случаев алкоголизма, ежегодных обращений в отделения неотложной помощи, связанных с употреблением алкоголя[2331], и количество смертей, связанных с ним[2332].
Все согласны с тем, что пьянство и употребление алкоголя во время беременности вредны для здоровья, но как быть с «умеренным» употреблением алкоголя? С точки зрения путей старения даже одна-две рюмки алкоголя[2333] могут снижать уровень NAD+ и активность сиртуинов в клетках мозга человека in vitro[2334]. С другой стороны, в нашем организме алкоголь детоксифицируется до уксусной кислоты[2335], которая активирует AMPK[2336]. К сожалению, прежде чем алкоголь полностью превратится в уксусную кислоту, образуется токсичный промежуточный продукт – ацетальдегид, который является известным канцерогеном. Возможно, именно поэтому считается, что алкоголь повышает риск развития нескольких видов рака[2337], включая рак молочной железы и колоректальный рак, даже у тех, кто пьет мало, не более одного алкогольного напитка в день[2338].

