
Полная версия:
Живи долго! Научный подход к долгой молодости и здоровью
Защита теломер с помощью питания
Индивидуальные различия скорости укорочения теломер у людей примерно в 30 % случаев обусловлены генетически, но основное влияние на то, удлиняются или укорачиваются наши теломеры и с какой скоростью, оказывают внешние факторы: окружающая среда, образ жизни и питание[2008]. Это позволяет объяснить корреляцию длины теломер у супругов, например[2009], но необязательно означает, что мы контролируем все 70 % нашей «теломерной судьбы». Мы можем потерять теломеры еще до рождения в результате пренатального воздействия алкоголя[2010], курения[2011] или загрязнения воздуха[2012]. Но выбор, который мы делаем каждый день – или три раза в день, – может изменить ситуацию.
Основными факторами ускоренной потери теломер могут быть окислительный стресс и воспаление[2013]. (О причинах этого смотрите see.nf/ttaggg.) Поэтому неудивительно, что в обзоре, посвященном роли питания, был сделан вывод о том, что более длинные теломеры выявлены у тех, кто употребляет овощи, фрукты, бобовые, орехи и другие продукты с высоким содержанием клетчатки и антиоксидантов. Напротив, потребление переработанного мяса, алкоголя, газировки и других продуктов и напитков, богатых насыщенными жирами и сахаром, вызывает укорочение теломер[2014].
Как перевести часы назад
Дин Орниш провел рандомизированное контролируемое исследование и первым показал, что диета, в основе которой – цельные продукты растительного происхождения, может обратить вспять прогрессирование сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний[2015]. Затем он выявил, что те же изменения в рационе питания могут изменить траекторию развития рака простаты на ранней стадии[2016], а в настоящее время он изучает, возможно ли таким образом задержать развитие болезни Альцгеймера на ранней стадии[2017]. В исследовании того, как здоровое питание и образ жизни могут повлиять на клеточное старение, частично финансируемом Министерством обороны США, Орниш сотрудничал с доктором Элизабет Блэкберн, удостоенной Нобелевской премии по медицине за роль в открытии теломеразы[2018].
Тридцати мужчинам в возрасте от 49 до 80 лет было предложено придерживаться низкокалорийной диеты, основанной на употреблении цельной растительной пищи: фруктов, овощей, цельного зерна и бобовых, а также заниматься спортивной ходьбой и практиковать управление стрессом. В течение 3 месяцев активность теломеразы у них возросла почти на 30 %. Это первое в истории вмешательство, которое показало значительное повышение активности фермента теломеразы. Результаты исследования были опубликованы в одном из ведущих медицинских журналов мира[2019], а в сопроводительной редакционной статье был сделан вывод о том, что эти знаменательные результаты «должны побудить людей к здоровому образу жизни, чтобы избежать возрастных заболеваний и рака или излечиться от них»[2020].
В последующем исследовании, длившемся 5 лет, ученые измерили длину теломер испытуемых, чтобы определить, действительно ли повышение уровня теломеразы привело к замедлению потери теломер. У мужчин аналогичного возраста из контрольной группы, которые придерживались обычного рациона питания, длина теломер с возрастом предсказуемо сокращалась. Однако в группе, ведущей здоровый образ жизни, теломеры не просто не уменьшились или остались на прежнем уровне, а выросли. Через 5 лет после первой оценки их теломеры были в среднем даже длиннее, чем в начале исследования, что впервые свидетельствует о том, что растительная пища и здоровый образ жизни могут повысить активность фермента теломеразы и эффективно обратить вспять клеточное старение[2021]. Но в чем причина – в диете, в физических упражнениях или в борьбе со стрессом?
Можем ли мы снять напряжение с теломер?
В голливудском блокбастере «The Holiday»[2022] героиня Камерон Диаз заявляет: «Сильный стресс… приводит к тому, что ДНК в наших клетках сжимается, и клетки больше не могут воспроизводиться»[2023]. Правильна ли трактовка Голливуда? Как отмечается в ролике see.nf/destress, данные о стрессе и теломерах противоречивы: например, среди одной группы людей, ухаживающих за больными деменцией, наблюдается снижение активности теломеразы[2024], а среди другой – ее повышение[2025]. В видеоролике вы увидите, что данные о роли медитации также неоднозначны[2026]. Как бы то ни было, в замечательных результатах Орниша, по-видимому, есть нечто большее, чем просто компонент снижения стресса. А как же физические упражнения и снижение веса?
Длина теломер в долгосрочной перспективе
Мы не всегда можем изменить судьбу, но мы всегда можем выйти на прогулку. Исследование тысяч близнецов показало, что у тех, кто больше занимался спортом, вместе с мышцами увеличивались теломеры[2027]. Хотя некоторые данные свидетельствуют о том, что ходьба в течение всего 150 минут в неделю связана с увеличением длины теломер[2028] и в среднем те, кто занимается спортом, имеют более длинные теломеры, чем те, кто не занимается[2029], большинство исследований, посвященных физической активности и длине теломер, не выявили значимой связи[2030]. «Неясно, – говорится в заключении одного из обзоров, – является ли физическая активность защитой от укорочения теломерной ДНК».
Представители спортивной элиты – те, кто участвует в национальных или международных соревнованиях[2031], а также спортсмены, выступающие в профессиональном спорте, как правило, имеют более длинные теломеры, чем неспортсмены того же возраста[2032]. Ультрамарафонцы, марафонцы[2033] и триатлонисты, пробегающие по 50 миль в неделю в течение 35 лет[2034], могут иметь более длинные теломеры, но как быть с теми из нас, кто не пробежал три раза вокруг земного экватора?
Из пяти рандомизированных контролируемых исследований, в которых физические упражнения действительно подвергались испытаниям, только одно показало значительную разницу в изменении длины теломер[2035], [2036], [2037], [2038]. Шестимесячные аэробные тренировки на выносливость (бег) и высокоинтенсивные интервальные тренировки (HIIT) увеличивали активность теломеразы и длину теломер, тогда как тренировки на сопротивление в течение того же периода к этому не приводили[2039]. Однако ни одно из других интервенционных исследований не выявило значимых результатов, каким бы ни был режим тренировок, что ставит под сомнение любое воздействие физических упражнений на длину теломер, по крайней мере в краткосрочной перспективе[2040].
Меню или движение?
Чтобы найти ответ на важнейший вопрос исследования Орниша – в чем причина: в растительной диете, в физических упражнениях или в снижении веса, – в идеале нужно было бы разделить людей как минимум на три группы: контрольную, которая ничего не делала (питалась как обычно), группу, которая бы только занималась физическими упражнениями, и группу, которая худела, питаясь практически той же пищей, но меньшими порциями. И именно такое исследование было опубликовано группой американских и канадских ученых[2041].
Около 400 женщин в постменопаузе были рандомизированы в одну из четырех групп на год: контрольная группа, группа физических упражнений, группа контроля питания, группа физических упражнений и контроля питания. Как и ожидалось, после 12 месяцев ничегонеделания в контрольной группе мало что изменилось. А что же после года физических упражнений? Ничем не лучше. Причем участники группы физических упражнений не просто ходили полчаса, как в исследовании Орниша, а выполняли 45-минутные упражнения умеренной интенсивности, например бег трусцой. А как успехи группы контроля питания? Снижение веса не дало никакого эффекта. Не произошло и значительного изменения длины теломер в группе, сочетавшей физические упражнения и снижение веса. Это соответствует результатам, полученным при проведении мероприятий по снижению веса, направленных на восстановление целостности теломер[2042].
Таким образом, пока мы питаемся как привыкли, насколько бы малы ни были наши порции, сколько бы мы ни теряли в весе или как много бы мы ни занимались спортом, через год мы не увидим никаких результатов. Напротив, люди в исследовании Орниша, придерживавшиеся цельной растительной диеты, которые занимались спортом в 2 раза меньше и имели такую же потерю веса всего через 3 месяца[2043], как оказалось, приобрели значительную защиту теломер[2044]. Другими словами, ни снижение веса, ни физические упражнения не обратили вспять процесс старения клеток путем восстановления теломер. Дело было в продуктах, а не просто в диете. В аналогичном исследовании за аналогичный период времени – четыре с половиной года более умеренных рекомендаций по питанию, таких как выбор молочных продуктов с низким содержанием жира и куриной грудки без кожи, а также увеличение количества фруктов, овощей и цельных зерен[2045], – не удалось существенно повлиять на длину теломер[2046].
Продукты, которых следует избегать
Не все растительные продукты полезны. Например, употребление картофеля фри вызывает укорочение теломер[2047]. Да, овощи способствуют увеличению длины теломер, но эффект может быть перечеркнут использованием фритюрницы[2048]. Рафинированные углеводы, такие как печенье и крекеры, также могут сократить теломеры[2049]. Таким образом, отказ от вредных продуктов и преобладание цельной растительной пищи – это первый шаг к оздоровлению теломер. У любителей ультрапереработанной пищи теломеры почти в 2 раза короче[2050], не говоря уже о более высоком риске ожирения, депрессии[2051], сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, инсульта и преждевременной смерти в целом[2052].
Алкоголь – еще один переработанный растительный продукт. В ходе исследования, проводившегося в Хельсинки на протяжении почти 30 лет, было обнаружено, что у самых пьющих теломеры старели на десятилетие раньше. Хотя ученые также обнаружили, что даже незначительное потребление алкоголя в среднем возрасте может привести к укорочению теломер[2053], вывод в систематическом обзоре наблюдений, опубликованном в 2021 году, таков: негативное влияние алкоголя на теломеры, по-видимому, ограничивается тяжелыми случаями алкогольной зависимости[2054].
Участникам исследования Орниша было предложено отказаться не только от алкоголя, но и от переработанного мяса. Употребление таких продуктов, как бекон, ветчина, хот-доги и колбаса, было связано как с раком[2055], так и с укорочением теломер, хотя непереработанное красное мясо, например стейк, не имеет аналогичной связи с длиной теломер[2056]. Были проведены исследования рационов питания, содержащих мясо, включая дичь, птицу[2057] и рыбу[2058], и выяснилось, что эта проблема, по-видимому, в большей степени связана с переработанным мясом[2059].
Предполагалось, что длинноцепочечные жиры омеги-3, содержащиеся в рыбе и рыбьем жире, благоприятно влияют на теломеры, так как по диетическому индексу воспаления они относятся к противовоспалительным веществам[2060]. В 2010 году в популяционном исследовании было установлено, что более высокий исходный уровень омеги-3 жирных кислот в крови в течение 5 лет сопровождался меньшим укорочением теломер, что запустило серию рандомизированных контролируемых исследований[2061]. Хотя вторичный анализ клинического исследования выявил повышение активности теломеразы[2062], к сожалению, ни одно из рандомизированных контролируемых исследований, в которых применялся рыбий жир, не показало значительного влияния добавки на длину теломер[2063], [2064], [2065], [2066].
Самым провоспалительным компонентом пищи являются насыщенные жиры[2067]. Решив, что никогда не рано начать питаться более здоровой пищей, исследователи разделили более тысячи младенцев на две группы: с диетой с низким содержанием насыщенных жиров и контрольную группу – и наблюдали за ними в течение первых 20 лет их жизни. Это замечательное финское исследование показало, что по сравнению с теми, кто рос на более здоровой диете, у испытуемых из контрольной группы ежегодная потеря теломер была вдвое выше. Однако это может быть не только результатом снижения содержания насыщенных жиров. Несмотря на то что именно на это было направлено исследование, испытуемым из первой группы также рекомендовалось снизить потребление соли и есть больше фруктов, овощей и цельного зерна, что не позволяет выделить решающий фактор[2068].
На другом конце спектра изучения проблемы находится серия рандомизированных контролируемых диетических тестов, которые длились всего 4 недели, но имели инновационный дизайн исследования. Клетки из пуповины (удобный источник получения человеческой ткани) культивировались в крови пожилых людей, разделенных на две группы: одна соблюдала диету с высоким содержанием сливочного масла, другая – аналогичную диету, но с высоким содержанием оливкового масла. Больший процент клеток, «купавшихся в крови со сливочным маслом», имел укороченные теломеры[2069]. Но и диеты средиземноморского типа, в которой обычно больше оливкового масла и меньше молочных продуктов, может оказаться недостаточно. Хотя в исследованиях было обнаружено, что приверженность средиземноморской диете коррелирует с более длинными теломерами, единственное лонгитюдное контролируемое исследование выявило, что длина теломер была такой же или даже короче[2070].
В ходе национального исследования, в котором приняли участие тысячи американцев, была обнаружена связь между усилением биологического старения и потреблением молока с высоким содержанием жира. Эту связь можно объяснить неблагоприятным воздействием насыщенного сливочного жира. Даже увеличение жирности молока всего на 1 %, например переход с молока 1 %-ной жирности на молоко с жирностью 2 %, приводит к значительному укорочению теломер, что, предположительно, связано с воспалительной реакцией и окислительным стрессом, вызванными насыщенными жирами[2071].
Продукты, благоприятные для теломер
Наиболее противовоспалительным компонентом пищи является клетчатка[2072]. В ходе того же репрезентативного исследования, проведенного среди тысяч взрослых жителей США, было обнаружено, что чем больше клетчатки потребляли люди, тем длиннее были их теломеры. Поскольку увеличение этого показателя было линейным, исследователи смогли провести математические расчеты. Оказалось, что увеличение количества клетчатки на 10 г на 1000 калорий приводит к замедлению старения теломер на 4 года[2073]. Столько же лет можно потерять, употребляя переработанное мясо (4,0 года)[2074], выпивая 600 мл газировки в день (4,6 года)[2075] или куря табак (4,6 года)[2076]?
Потребление клетчатки может быть просто маркером рациона, состоящего из растительной пищи, поскольку, по определению, только в ней она и содержится[2077]. Таким образом, очевидная связь между потреблением клетчатки и длиной теломер может объясняться не клетчаткой, а какими-либо другими защитными компонентами растительной пищи. Это похоже на исследования, выявившие более длинные теломеры у людей с более высоким потреблением каротиноидов[2078] – растительных пигментов, таких как бета-каротин, – или их уровнем в крови[2079]. Опять же это может быть просто косвенным показателем следования растительной диете. Более длинные теломеры коррелируются с потреблением кофе[2080], в котором нет ни клетчатки, ни каротиноидов. Интересно, что кофеин вызывает уменьшение длины теломер[2081], предположительно потому, что в наши дни так много кофеина поступает в организм с газировкой и энергетическими напитками с высоким содержанием сахара[2082].
Тестирование зеленого чая показало, что он способствует увеличению длины теломер у пожилых мужчин[2083] и защищает теломеры у крыс[2084]. Однако клинические испытания этого напитка были проведены только в 2016 году. Сложно сделать убедительный чай-плацебо, поэтому исследователи использовали капсулы с экстрактом зеленого чая. В своем видеоролике see.nf/nutsandtea я показываю, как у людей, в течение 5 месяцев пивших по четыре чашки зеленого чая[2085] в день, наблюдалось значительное увеличение длины теломер по сравнению с группой плацебо[2086].
Зеленый чай – это, по сути, зеленый листовой овощ, замоченный в горячей воде. А как насчет самих зеленых листовых овощей? В видеоролике я рассказываю, как ежедневное употребление одной с четвертью чашки капусты – приготовленной, а не сырой – повышает активность теломеразы всего за 5 дней. В исследовании впервые были получены доказательства того, что пищевое вмешательство может за несколько дней активизировать теломеразу. Причем такую реакцию вызывает самая полезная пища – крестоцветные, темно-зеленые листовые овощи. Однако уже через 16 дней после прекращения употребления капусты активность теломеразы вернулась к исходному уровню[2087]. Поэтому постарайтесь включить крестоцветные овощи в свой рацион.
Добавки
Одной из причин, по которой я не рекомендую принимать добавки с экстрактом зеленого чая, является риск токсического поражения печени. Раньше мы считали, что такие реакции встречаются редко, примерно один случай на 100 тысяч[2088]. Но теперь, когда появились крупные исследования, такие как Minnesota Green Tea Trial, мы понимаем, что опасность возрастает до одного случая из двадцати[2089]. (В отличие от этого, ни в одном из исследований, в которых зеленый чай употреблялся в виде обычного напитка, не было зарегистрировано ни одного случая заболевания печени[2090].) Существуют ли другие добавки, которые не так рискованны, но могут защитить наши теломеры?
Витамин DПрактически все исследования, проведенные на сегодняшний день, не выявили положительного воздействия витамина D на теломеры. Добавки с рыбьим жиром не привели к замедлению укорочения теломер [2091], [2092], [2093],[2094]. То же можно сказать и об оливковом масле экстра-класса[2095], витаминах группы В[2096] или добавках с цинком[2097]. Из десяти исследований витамина D и теломер только два были двойными слепыми, рандомизированными, плацебо-контролируемыми[2098], но оба показали положительный эффект (в дозе 60 000 МЕ раз в месяц[2099] и 800 МЕ раз в день[2100]). Подробности – в ролике see.nf/dtelomeres.
АстрагалКорень астрагала – одна из самых популярных трав в традиционной китайской медицине[2101]. Уже несколько тысячелетий он широко рекламируется как «тонизирующее» средство, продлевающее жизнь[2102]. Оказалось, что содержащееся в корне вещество циклоастрагенол (TA-65) умеренно усиливает активацию теломеразы in vitro[2103], но единственное исследование, показавшее клиническую пользу, финансировалось компанией, которая продает его[2104] в интернете по 600 долларов за бутылку. До того как Федеральная торговая комиссия обвинила ее в ложных заявлениях и практиках, компания заработала более 50 млн долларов[2105]. Для тех, кто хочет узнать больше, я рассматриваю все плюсы и минусы в видео see.nf/astragalus.
Готу колаВ 2019 году в центелле азиатской (centella asiatica), известной также как gotu kola, был обнаружен самый мощный на сегодняшний день активатор теломеразы. Оказалось, что он вызывает почти девятикратное увеличение активности теломеразы, в 4 раза превышающее активность TA-65[2106]. Готу кола широко используется в аюрведической и китайской медицине[2107]. Готу кола – это зеленый листовой овощ, который в Малайзии и Индонезии употребляют в свежем виде в салатах или в супах, а в Индии и Таиланде – в виде сока или чая. В Индии он считается «пищей для мозга»[2108]. Было установлено, что он улучшает когнитивные функции у мышей[2109], однако метаанализ немногочисленных исследований, проведенных до настоящего времени с участием людей, не выявил значительного влияния на когнитивные функции человека[2110].
Пища для размышлений
Теломеры – один из путей старения, который прочно вошел в общественное сознание. Увеличение длины теломер для замедления или даже предотвращения старения – популярная идея, хотя, как я уже говорил, научные данные противоречивы[2111]. Удлинение теломер возможно за счет активации фермента теломеразы, но существует постоянная борьба между силами, разрушающими наши теломеры, такими как старение, окислительный стресс и воспаление, и жизненными решениями, которые могут помочь восстановить их[2112].
Некоторые люди высказывают опасения, что усиление активности теломеразы теоретически может повысить риск развития рака[2113], поскольку известно, что опухоли захватывают теломеразу и используют ее для обеспечения собственного бессмертия[2114]. Изменения образа жизни, которые доктор Орниш использовал для защиты теломер, как оказалось, замедляют, останавливают или даже обращают вспять прогрессирование раковой опухоли в рандомизированном контролируемом исследовании диеты и образа жизни при раке простаты на ранних стадиях[2115].
В ответ на работу Орниша, показывающую, что теломераза может активизироваться, а теломеры – удлиняться при растительном питании и активном образе жизни, в сопроводительной редакционной статье было высказано предположение, что подобные исследования могут сыграть на руку фармацевтическим гигантам, поскольку «в современном мире здоровый образ жизни не всегда возможен»[2116]. Надеемся, что это не так: если вы читаете эту книгу, то у вас есть мотивация сделать хотя бы один-два шага в этом направлении, которые могут включать отказ от курения[2117] и сокращение потребления обработанного зерна[2118], газировки[2119], переработанного мяса[2120] и молочных продуктов[2121] – при увеличении потребления фруктов[2122], овощей[2123] и других продуктов, богатых антиоксидантами[2124].
Чтобы замедлить старение:
• соблюдайте рекомендации, данные в главах «Воспаление» и «Окисление»;
• придерживайтесь диеты с высоким содержанием клетчатки, в основе которой лежит цельная растительная пища;
• выбирайте чай или кофе вместо газировки или молока;
• ешьте крестоцветные овощи;
• принимайте 800–2000 МЕ витамина D в день, если уровень витамина D в крови ниже 20 нг/мл (50 нмоль/л).
Заключение
Большинство крупных достижений в понимании этих путей старения произошло за последние 20 лет, уже после того, как я окончил медицинский факультет; поэтому многое из того, что я обнаружил в ходе работы над этой книгой, стало для меня открытием. Чем больше мы узнаем о них, тем больше находим их взаимосвязь. Вместо того чтобы существовать как отдельные сущности, пути старения переплетаются в сложную схему: усиление AMPK снижает уровень mTOR, повышает аутофагию и уровень NAD+, что, в свою очередь, повышает активность сиртуина, который снижает уровень ИФР-1 и возвращается к AMPK[2125]. Поэтому неудивительно, что у них много общих триггеров.
В таблице приведена схема мероприятий, которые могут помочь замедлить старение путем воздействия на каждый из одиннадцати путей старения.
Мероприятия по регулированию одиннадцати путей старения
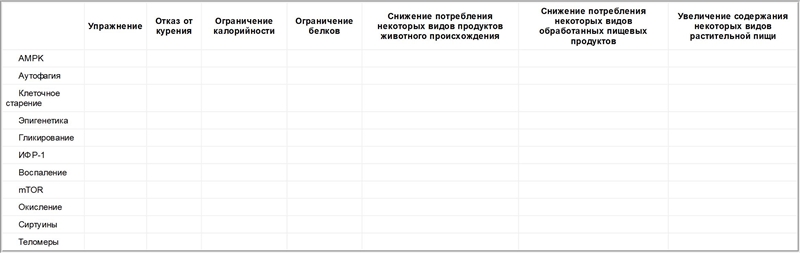
Примечательно, что только с начала века в ходе исследований было обнаружено полдюжины отдельных соединений, способных значительно продлить жизнь млекопитающих. Хотя между многими путями старения существует сложное перекрестное взаимодействие, препараты или добавки, продлевающие жизнь, в основном направлены только на тот или иной путь. Например, метформин может увеличить продолжительность жизни мышей за счет усиления AMPK, а рапамицин – за счет подавления mTOR[2126]. Когда они принимаются вместе, то оказывают синергическое действие – не только лучше, чем каждый из них в отдельности, но и лучше, чем простое сложение каждого действия[2127]. Это может быть одним из главных преимуществ диеты и образа жизни, поскольку они позволяют одновременно воздействовать на несколько путей старения.
Часть II
Оптимальный антивозрастной режим
Диета
Ежегодно в перерасчете на всех жителей Земли из-за недостатка физической активности мы теряем более 10 миллионов лет здоровой жизни, но рацион питания увеличивает эту цифру в 20 раз[2128]. По данным «Исследования глобального бремени болезней» (Global Burden of Disease Study), наиболее полного и систематического анализа причин смерти[2129], убийцей номер один в США[2130] и вообще на Земле является неправильное питание[2131]. Нездоровое питание ежегодно сокращает жизни людей без инвалидности суммарно на сотни миллионов лет[2132]. Именно поэтому я посвятил свою жизнь изучению питания.
Лучшие блюда
В «Исследовании глобального бремени болезней», финансируемом Фондом Билла и Мелинды Гейтс, приняли участие около 500 исследователей из более чем трехсот институтов в пятидесяти странах мира. Они изучили почти 100 тысяч источников данных[2133]. Они определили, что убийцей американцев номер один является американская диета, оттеснившая курение табака на второе место. В настоящее время от курения ежегодно погибает около полумиллиона американцев, в то время как от нашего рациона питания, судя по всему, погибает намного больше[2134].

