 Полная версия
Полная версияПозитивные изменения. Образование. Школа будущего. Тематический выпуск, 2022 / Positive changes. Education. The school of the future. Special issue, 2022

https://apelsino.school/
OPENING YEAR 2008 (?).
INSTRUCTION
From age 4 to 11th grade.
STUDY PROGRAM
The school’s program takes into account the state standards and gives students an opportunity to take all required exams. The Orange is a school of informal education, where children decide everything. The school is governed by the children’s parliament, which has absolute power. No decision by an adult (the principal and teachers are no exception) is valid unless it has been accepted and approved by the students. Among other things, the students can ask to add a new subject to the schedule[8].
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
The desire for new things, curiosity, creativity, ingenuity, the ability to create are the traits inherent in everyone, regardless of the age. Our task is to create the conditions in which these qualities can manifest themselves and develop. One of the main skills a person has is the ability to interact with other people, with the world, with knowledge, with himself. We all learn this together at the Orange, too.
We strive to make people feel free, to develop in many ways, to learn to choose – in both content and form. That’s why there are so many different subjects at The Orange. Most of the classes are chosen by the students themselves.
We recognize the uniqueness of each individual, we understand that the best and main driver of the educational process is personal interest, we believe that one of the main skills today is the ability to choose and the ability to interact – with the world around us, with ourselves, with knowledge, with other people and so on. Finally, we believe that a modern lesson should include all of the above.
KIT AUTHOR SCHOOL
https://future-kit.ru/
OPENING YEAR 2014.
INSTRUCTION
Grades 1–10.
STUDY PROGRAM
The curriculum includes the following classes: math, Russian, language art, English, history, biology, geography, physics, chemistry, programming, as well as preparation for the GSE in math and Russian.
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
Our students build their life paths with confidence, navigate the world with ease, and play with its challenges.
KIT School is a school where:
• you receive help in becoming a person ready for any tomorrow
• the teachers select pedagogical technologies that help children open up, feel the excitement of learning, the joy of acquiring new knowledge.
Every classroom offers:
• Classes to develop emotional and social intelligence
• A lot of play activities, aimed at the development of logical, verbal, systemic thinking
• Project activities
The school offers:
• Support, so you can answer the following questions: "who am I?”, "what am I like?", “why am I doing this?", “can I do things differently?"
• Training, so you can learn how to build your boundaries and how to maintain those boundaries sustainably
In high school, it is important for kids to make their own decisions, so we teach:
• Understanding your objectives
• Managing your time
• Understanding how, where and when you can be effective
• Planning and completing your business.
THE 21ST CENTURY ARK LYCEUM
https://covcheg.org/
OPENING YEAR 1992.
INSTRUCTION
Kindergarten, Grades 1–11.
STUDY PROGRAM
FGOS compliant.
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
THINKING
It is not just "the aggregate knowledge”, collected "just in case”, but questions of worldview significance for children and adolescents – that’s the program of our school. We teach you to think, not to repeat someone else’s thoughts, and every lesson we have is a small discovery.
COOPERATION
We don’t just "sit and listen” in class – we work individually and in teams. We don’t watch – we do it ourselves!
FREEDOM
How do we understand this word? It is about being able to think for yourself and do what you thought. We don’t demand blind obedience – we discuss all the rules together and give you the opportunity to choose. We don’t march in formation – we teach freedom and independence.
EPISCHOOL
https://promo.epischool.ru/
OPENING YEAR 1997 (?).
INSTRUCTION
Grades 1–11 (?).
STUDY PROGRAM
The school has no “subject specialization.” We strive to give students an opportunity to build their own educational routes and master the subjects that interest them most. Upon graduation, most of the children enter the leading universities of St. Petersburg and Moscow.
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
We work a lot on self-determination, self-understanding, and building each child’s social skills.
We build our curriculum around four main areas: we teach how to learn, we teach how to do, we teach how to interact, and we teach how to live:
• Developing critical thinking
• Teaching how to learn and make informed choices
• Developing responsibility for your performance
• Practicing teamwork and negotiation skills
In elementary school we preserve the child’s natural curiosity and interest, open up the world of knowledge, and instill a taste for independence.
In middle school, we create a space for trials, project activities, and living different experiences. We teach out-of-the-box thinking and creative problem solving.
In high school, we open up opportunities for the child to delve deeper into a subject of interest, to gain real-world experience with professionals from various fields, and prepare for final exams.
THE AYLON SCHOOL (THE KURBATOV SCHOOL)
https://kurbatovschool.ru/
OPENING YEAR 2020 (?).
INSTRUCTION
The school website offers no information about grades/age of students, but it says that one can graduate as an extern at the age of 14–16.
STUDY PROGRAM
Combination of classical general education subjects with classes to develop superpowers (development of intuition, photographic memory, speed reading).
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
The main tasks and priorities of the school:
THE SUCCESS AND HEALTH OF EACH STUDENT
To form in each child the qualities of a successful, morally and physically healthy personality, capable of successful socialization and adaptation to the labor market.
DEVELOPMENT OF CREATIVE ABILITIES, ACTING AND PUBLIC SPEAKING SKILLS Development of creative abilities and emotional intelligence in the visual arts, acting and public speaking, music, developing authentic products; moral development and etiquette classes.
LEARNING ENTREPRENEURIAL SKILLS AND BASICS OF BUSINESS
Financial and computer literacy training. Mastering entrepreneurial skills, basics of business, while developing communication skills: maintaining social media, creating websites, taking pictures, participating in interviews and other business communications.
THE ORION FAMILY SCHOOL
https://orionfuture.org/
OPENING YEAR 2007 (?).
INSTRUCTION
Grades 1–9.
STUDY PROGRAM
Orion Family School is a school within the family community, one that is harmoniously integrated into its life. Our children successfully pass interim and final state certification.
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
We teach with the support of joint activities of children and adults, sharing events, values, and caring interpersonal relationships.
We guarantee a friendly social environment. The child stops being afraid of communication. He or she learns communication by solving developmental problems.
We teach through play, project activities, and use elements of research work. Approaches vary depending on the child’s individual developmental goals.
Upbringing and value-based development. We not only teach but also develop the children through informal events. Children choose what events to participate in or organize them with the help of adults.
A wide range of additional education and career guidance activities is available. The kids participate in work placements so they can make a conscious choice of a profession. This is an actual internship at a production, technology, or business organization, where the children learn how to work for real, master highly demanded skills and try on the nuances of the profession.
THE WHITE CROW SCHOOL
Школабелаяворона. рф
OPENING YEAR 2016.
INSTRUCTION
Grades 1–7.
STUDY PROGRAM
Every day the school’s schedule has three blocks dedicated to:
• academic learning and hard skills,
• original courses with an emphasis on soft skills training (Understand Yourself; Critical Thinking; Projects;
Time Management),
• developmental classes (Acting; Chess; Etiquette; Sports).
ABOUT SOFT SKILLS
The White Crow School is confident in the following:
• The school should provide knowledge without disconnecting from real life, but in an interesting and engaging way,
• It is important for the child to acquire specific skills: responsibility, critical thinking, independence in action and judgment, communication, self-determination
• The atmosphere of all years of school life should be safe, supportive, comfortable, free, with acceptance and respect for everyone.
REFERENCES1. Foxford. Media. (2019) Soft skills – what they are and where to learn them. Retrieved from: https://media.foxford. ru/soft-skills/ (accessed 18 March 2019). (In Russian).
2. Mann, C. (1918) A Study of Engineering Education. Boston: The Merrymount Press.
3. Strauss, V. (2017) The surprising thing Google learned about its employees – and what it means for today's students. Retrieved from: https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/answer-sheet/wp/2017/12/20/the-surprising-thing-google-learned-about-its-employees-and-what-it-means-for-todays-students/(accessed 16 May 2022).
4. Faye, F. (2016). If You're So Smart, Why Aren't You Rich? Bloomberg. Retrieved from: https://www.bloomberg.com/opinion/articles/2016–12–22/if-you-re-so-smart-why-aren-t-you-rich (accessed 15 May 2022).
5. Heckman, J. J. & Kautz, T. (2012). Hard evidence on soft skills. Labour Economics, 19(4), 451–464. https://doi. org/10.1016//. labeco.2012.05.014
6. Gray, A. (2016) The 10 skills you need to thrive in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Retrieved from: https://www.weforum. org/agenda/2016/01/the-10-skills-you-need-to-thrive-in-the-fourth-industrial-revolution/ (accessed 16 May 2022).
7. OECD (2015). Skills for Social Progress: The Power of Social and Emotional Skills. OECD Skills Studies. Paris: OECD Publishing. http://doi.org/10.1787/9789264226159-en.
8. OECD Skills Outlook. Retrieved from: https://www.oecd-Hibrary.org/education/oecd-skills-outlocok_e11c1c2d-en(accessed 16 May 2022).
9. National Soft Skills Association (NSSA). Retrieved from: https://www.nationalsoftskills.org/(accessed 16 May 2022).
Исследования / Research Studies
Моделируем Школу будущего: исследование практик школьного образования Фабрики позитивных изменений
Иван Смекалин
DOI 10.55140/2782–5817–2022–2-S1–73–87

Доля частных школ в общем числе общеобразовательных организаций за последние два десятилетия выросла почти в 2,5 раза, свидетельствуют данные Института образования НИУ ВШЭ. Во многом это стало ответом на запрос рынка: для родителей становятся все более очевидными ограничения и недостатки образования по модели среднестатистической государственной школы, – и особенно, когда эта школа переместилась домой в период пандемии. Ответом на этот запрос стали и многочисленные новые образовательные подходы, которые активно предлагаются, как правило, частными школами – особенно теми, которые относят к числу «альтернативных».

Иван Смекалин
Аналитик Фабрики позитивных изменений
Зачастую, такие школы открываются родителями для своих детей – в ответ на ситуацию отсутствия на рынке удовлетворяющего их варианта. Все это рождает массу вопросов: что ждет Школу в будущем? Какой она должна быть? Может ли она быть отличной от той, которая есть сейчас? Эти и другие вопросы обсуждались в ходе исследования Фабрики позитивных изменений, посвященного разработке модели Школы будущего.
ДИЗАЙН ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Кабинетный обзор публикаций использовался для создания концептуального аппарата, при помощи которого было бы возможно описание школьного образования. В подготовительной части исследования рассмотрены источники информации о современных подходах к организации школьного образования в России и за рубежом. Они носили как теоретический характер и описывали концепты, которые позже использовались для формулирования гайда опросника, так и описательный характер с указанием важных кейсов образовательных моделей.
На основании выделенных концептов был составлен гайд экспертного опроса, целью которого было их содержательное наполнение с опорой на школьные кейсы. Всего в ходе исследования было опрошено 20 экспертов из разных сегментов исследуемого поля: представители педагогического сообщества, авторы собственных образовательных концепций, специалисты по управлению образованием. Задачей опроса было сопоставить разные точки зрения на перспективы развития образовательных практик в школе и составить схему, в соответствии с которой было бы возможно описывать школьный образовательный процесс, для его последующего моделирования в контексте Школы будущего.
В рамках кейс-стади были рассмотрены 27 частных учебных заведений среднего общего образования и государственных школ, образовательная модель которых отличается от модели обычной среднеобразовательной школы (СОШ). Такая выборка позволяет следовать стратегии наибольших различий в выборе кейсов – не претендуя на покрытие всей генеральной совокупности, предполагается рассматривать их различия, а не сходства.
Далее выделенные критерии легли в основу описания ключевых моделей школьного образования. Модели имеют инструментальное значение – посредством них выделяются «точки роста», которые используются для формулирования перспективной модели Школы будущего и её характеристик.
Таким образом, модель Школы будущего логически следует из концептов, полученных в результате обзора существующих исследований образования, посредством экспертных интервью и обобщения выделенных образовательных характеристик в критерии образовательных моделей. Описание этапов проведенного исследования и взаимосвязи между ними представлено на Рисунке 1.
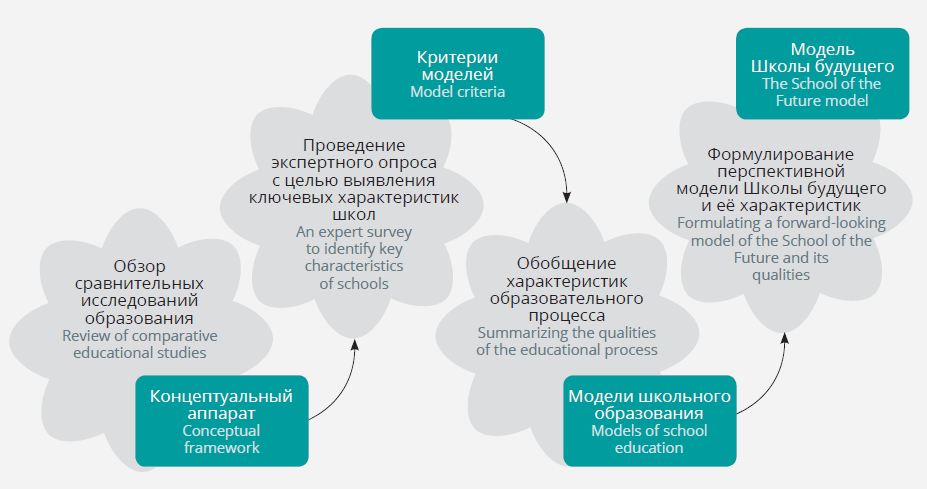
Рисунок 1. Карта проведенного исследования
КРИТЕРИИ ВЫДЕЛЕНИЯ И АНАЛИЗА МОДЕЛЕЙ ШКОЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
Как было отмечено ранее, для проведения экспертного опроса на основании кабинетного исследования был составлен гайд. Основными концептами в опросе экспертов стали:
• ожидаемые образовательные результаты учеников Школы будущего (знания, умения и навыки, или иное);
• критерии для систематизации кейсов существующих учреждений среднего общего образования, указанных экспертами;
• образовательные модели на основании выделенных критериев.
ОЖИДАЕМЫЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНЫЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ (КЛЮЧЕВЫЕ ЗНАНИЯ, УМЕНИЯ И НАВЫКИ)Формулировка вопроса предлагала сфокусироваться на обсуждении не академических знаний (которые перечислить довольно сложно), но неких внепредметных навыков. Как сказал один из экспертов, «будущее остаётся неизведанным», в связи с чем ожидаемо, что главным навыком будущего эксперты чаще всего называли когнитивную гибкость. При этом этической основой для такой гибкости выступают уважение к другому и культура толерантности к иным ценностям. Важна терпимость не только к другому, но и к себе, к своим собственным ошибкам, которые становятся частью обучения.
Однако, помимо способностей к обучению, эксперты называли вполне конкретные умения, которым не принято учить в школе сейчас, но которые были бы крайне полезны человеку в жизни и в будущем. Одним из таких становится навык работы с контентом, который выступает и образовательным элементом, призванным отойти от лекционного формата, и элементом проектной деятельности, логике которой предстоит научиться члену общества будущего. При этом в хаотичном мире, где человеку предстоит быть гибким и адаптивным, важно учиться практикам заботы о себе – для чего важны знания о правильном питании, кулинарии и собственных ресурсах человека.
Ниже представлен список из ключевых названных экспертами компетенций, которыми должен обладать ученик Школы будущего. Каждая компетенция была названа минимум двумя экспертами.
Внепредметные компетенции
• Когнитивная гибкость: умение получать новые знания и решать новые, нетиповые задачи с использованием пройденного
• Интуитивность: возможность полагаться на «чутье»
• Уважение и понимание ценности себя, другого
• Сохранение и развитие мотивации к познанию
• Культура толерантности к ошибкам (своим и чужим) и неопределенности
Конкретные знания, умения и навыки
• Понимание базовых механизмов функционирования окружающего мира, исторических процессов
• Лингвистические навыки для изучения иностранных языков
• Навыки управления своими ресурсами и практики заботы о себе
• Основы кулинарии и нутрициологии
• Творческие навыки, навыки работы с контентом
КРИТЕРИИ МОДЕЛЕЙ ШКОЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯНа основании проведенного опроса экспертов, были выделены три группы критериев: педагогические, инклюзивные и экономические.
Педагогические критерии отражают особенности учебного плана: индивидуализация, ориентация на академию или soft skills, дистанция между учеником и учителем, стиль общения с учениками и родителями. В широком смысле слова эта группа критериев относится к параметру индивидуализации образования.
Инклюзивность в широком смысле выделена в отдельную категорию критериев как характеристика доступности/комфортности образования для детей с особыми потребностями[9], ценовая доступность для целевой аудитории, доступность в плане поступления (уровень «селективности»).
Экономические признаки предлагались в основном специалистами по управлению образованием, которые рассматривали школьную модель не только со стороны образовательной части, но и как рыночный продукт. Потому данная сторона включает особенности рыночного предложения: насколько занят ребёнок в школе и может посещать в ней дополнительные занятия (секции, кружки и т. п.), окупается и масштабируется ли модель.
Ниже представлен список из ключевых названных экспертами критериев в оценке моделей школьного образования:
Педагогические критерии
• Возможность индивидуализации учебного плана: нет возможности, есть профилизация (наличие профильных классов, из которых можно выбирать свое направление), гибкий учебный план, разрабатываемый исходя из интересов и потребностей ученика (выбираются предметы, а не направления)
• Предметное содержание как следствие выбора образовательного результата: ориентация на академию или в сторону гибких навыков
• Стиль общения с учениками: коуч или лектор
• Стиль коммуникации с родителями: дашборды или просто оценки
• Возможность поступить в университет (как в России, так и за рубежом)[10] после обучения: есть или нет
Инклюзивность
• Доступность для инклюзивных детей: доступно или нет
• Доступность в цене: финансовая доступность для целевой аудитории
• Наличие отбора: есть или нет
Экономические признаки
• Занятость ребёнка в школе: первая половина дня, опция дополнительных занятий, весь день
• Необходимость дополнительных услуг для окупаемости финансовой модели: есть или нет
• Возможность масштабирования: есть или нет
ОБЗОР МОДЕЛЕЙ ШКОЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И ИХ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИОПЕРАЦИОНАЛИЗАЦИЯ КРИТЕРИЕВ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНЫХ МОДЕЛЕЙ ШКОЛ
В соответствии с ранее выделенными на основании сравнительных исследований образования и результатов экспертного опроса критериями оценки модели, решено обобщить их в виде следующего списка ниже. Соответствие моделей школьного образования каждому критерию предлагается оценивать по трехбалльной шкале:
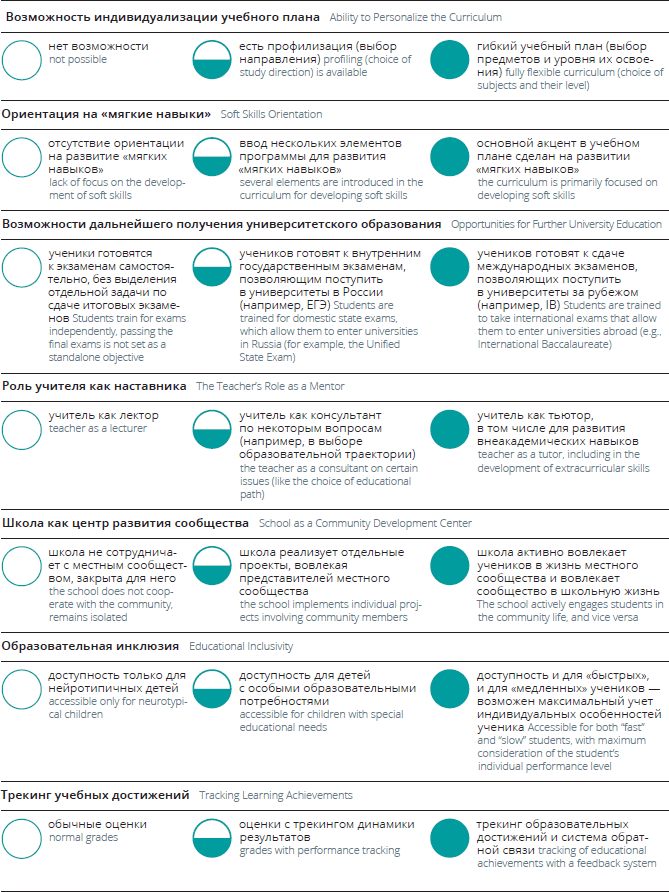
ПЕРЕЧЕНЬ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНЫХ МОДЕЛЕЙ
В ходе проведения экспертных интервью опрошенные ссылались на набор моделей школ. На основании этого набора были отобраны опорные модели с учётом упоминаний экспертами, широты применения в практике и четкости рамок:
1. Модель государственной СОШ – как точка отсчёта и сравнения.
2. Государственная школа с профильными классами – на настоящий момент в России это самый распространённый девиант от массовой школы.
3. Британская модель.
4. Международный бакалавриат – как модифицированная международная версия британской модели.
5. Альтернативные школы.
6. Азиатская модель – много раз упоминалась экспертами, критерии применялись к опыту Сингапура.
7. Финская модель.
ВИЗУАЛИЗАЦИЯ МОДЕЛЕЙ
После изучения литературных источников, проведения экспертных интервью и анализа кейсов разных школ, каждой выявленной модели школьного образования был присвоен балл от 1 до 3 по каждому из 7 названных выше критериев. Ниже приведены лепестковые диаграммы для визуализации полного перечня моделей и присвоенных им баллов по каждому критерию.
Визуализации служат для демонстрации нескольких важных результатов.
Во-первых, можно заметить, что направленность на «мягкие навыки» и успешность поступления в вуз не встречаются одновременно в одних и тех же моделях, то есть предполагают определиться с приоритетными образовательными результатами.
Во-вторых, в широком смысле инклюзивность остаётся слабым местом всех моделей, даже тех, что подразумевают индивидуализацию.
Наконец, можно увидеть схожесть следующих пар моделей: российская и азиатская с радикальным вниманием к академическим успехам; финская модель и модель альтернативных школ, фокусирующихся на «мягких навыках»; британская модель и Международный бакалавриат как попытка академически оформить обучение «мягким навыкам».

