 Полная версия
Полная версияBelford's Magazine, Volume II, No. 8, January, 1889
When I purchased the second lot I was very careful to proceed deliberately. I am a good deal of a carpenter, if things would only come out square when finished: but they never will. When I saw a board, somehow the saw runs off to one side, and when I try to nail it to the other board, the two won’t fit; and by the time I get around to the fourth side, one end of the concern is up in the air, and I have to sit on it to keep it down. I have often gazed with admiration on a real carpenter, to see him run his saw along, straight as a string and true as a die, and then put the pieces all together and have them fit, nice as a cotton hat. This is true genius.
Sensible of the danger and liability to mistake in putting the pieces together, I told Mrs. W., who was superintending the operation, that we would not use nails, but screws, so that in case of error – and all human judgment is fallible – we could take the screws out and take the pieces apart, which could not be done with nails. Mrs. W. conceded the suggestion to be a valuable one. So we went to work, she kindly lending her assistance. I measured all the pieces, got them the exact length, and for the greater certainty, stood them up on the floor to see if they would all fit. They certainly seemed to do so, as far as mortal vision could determine. As all this required a great deal of deliberation, a great deal of measuring, a great deal of sawing, some chiselling, etc., the hour of sunset was approaching when I had put in the last screw, and triumphantly called Mrs. W. from her afternoon nap to witness the success of my mechanical endeavors. I stood the blamed thing up on its four legs, and three of ’em were on the floor, and the fourth wasn’t. It was impossible for me to discover the defect in my workmanship. I could make any three of the legs stand on the floor, but the fourth could not be prevailed upon for any consideration. The cross-pieces, which should have been horizontal, and which, to that end, had been measured with mathematical precision, slanted up on one side and slanted down on the other. I was in despair, until Mrs. W. brought her intellect to bear upon my difficulties; when it appeared that three of the uprights were four feet six inches high, and the fourth was four feet seven inches. How it happened no one could explain.
“Now, W.,” says Mrs. W., “send for the carpenter.” I did so. He came – a rough, totally uncultured man. He could barely write his name and his clothes were principally suspenders. But that uneducated man just took these pieces of wood, and knocked them here, and knocked them there, and, by aid of some disreputable shingle nails, in twenty minutes had as neat looking a stand made as ever you saw come out of a cabinet maker’s shop. I was abashed and paid him twenty-five cents. Mrs. W. said nothing, but smiled.
We had some frames, about two feet square, covered with brown paper. These we placed on the stand and spread out the eggs. I was a little uneasy about what kind of a hen to get to hatch them, as I could find nothing in the books on the subject; but Mrs. W. called me my usual pet name, and said that the first warm day was all the hen needed. Wonderful woman that! Just as she predicted! In a few days the brown paper was covered with little dark specks in a state of agitation. Mrs. W. spoke of them contemptuously as “nasty black worms.”
They grew at a prodigious rate. I explained to the children that all they had to do was to go down to the osage-orange hedge, cut off the twigs and branches, and feed them to the worms; that in a few weeks the product would be ready for market, and if the Mills bill didn’t interfere with protection to American industry, the profits would be large, and should be equally divided between themselves and their mother. The children were highly elated and were soon discussing what should be the color of the carriage horses. One wanted black, the other blue; and the excitement ran so high that parental intervention became necessary and some spanking ensued. The next morning our early dreams were disturbed by fearful outcries from the direction of the front fence. The smallest of the children had tumbled head first into the osage-orange hedge, and could not get out. Anyone who knows the infernal, brutal intensity with which the thorns of the osage-orange sting, can understand the predicament of that child. We extracted her in a fearfully lacerated condition. She was punctured all over. Having read in a book entitled “Three Thousand Valuable Receipts, for Twenty-five Cents,” that ammonia was good for stings, I applied ammonia liberally to that bleeding child, until she became absolutely frantic. Her screams attracted Mrs. W. to the scene, and she exclaimed:
“Have you no more sense than to put ammonia on raw flesh like that?” I pointed to the “Three Thousand Valuable Receipts, for Twenty-five Cents,” which she immediately picked up and threw out of the window. The child ultimately recovered, but from that day abhorred silk culture in all its branches. Still the industry went on. The children were so stung by the thorns that the work devolved on me, and it was a task most fearful. There is a poison in the thorn of the osage-orange that not only makes the pain exquisite, but swells one up as though he had been stung all over by bees, or had chronic dropsy. My hands and arms were puffed up, and my face looked as though I had been in a prize-fight. As I observed to Mrs. W., however, these were minor difficulties, and we could put up with them in consideration of the large profits which would ensue. One day one of the servants – they are always going around and turning things up side down – left one of the frames on the floor, and all the worms, to the number of several hundred, scattered themselves profusely about the house, and without any reference to the comfort or convenience of the family. If you opened the flour barrel, there was a silk worm. They pervaded the sugar and crawled into the cream. You found them in bed and the mash was awful. How many were trodden into the parlor carpet can never be known. This, too, was but an episode; and as the worms grew in size and began to spin their cocoons, the process was quite interesting, and even Mrs. W. overcame her repugnance to the crawling little wretches.
I was startled one day, as I was feeding my silk-worms, who were consuming the osage-orange leaves at the rate of a bushel a day, making two bushels of litter, to hear Mrs. W. abruptly ask:
“W., what is a consumer?” The unexpectedness of the interrogation found me at fault for a moment; but reflecting a little while and looking at the silk-worms, I concluded the best way to put it was: “A consumer, my dear, is – well, a consumer in this country is one who consumes.” Thinking that no exception could be taken to such a definition, I was triumphant.
“W.,” said that pertinacious person, “you don’t hang together well, if any. You said the other day that this tariff thing was for the benefit of the producer, etc.”
“My dear,” I replied, “I seize the occasion. ‘My foot is on my native heath, and my name is McGregor.’ When our industries were in their infancy, it was found impossible to compete with foreign productions. Labor was so cheap abroad that they could undersell us in our own markets. We had laid the foundation of a broad, comprehensive manufacturing interest; we had taken men from agricultural and other pursuits, where they earned a livelihood, and put them in new and strange employments, about which they knew nothing, where they expected to earn more than a livelihood. But this could not be done on account of prices. So government imposed high duties, and the producer sold his articles for a higher price. In this way he was benefited and enabled to make money. The tariff added just so much to the price of the article sold, and the producer was happy.”
“But who paid this extra price?” queried Mrs. W.
“Well,” I replied, “it is a principle of political economy, I believe, that all taxes are paid ultimately by the consumer, so that in a case of this kind – ”
“The consumer is the American people,” interrupted Mrs. W.
“My dear,” I cried, “once more I am compelled to observe, you are begging the question.”
“Mendicant again,” was her arch reply, and a cry from the nursery ended the discussion.
In about six weeks we had the cocoons. Of course, during that time the house was littered with dirt, dried leaves, and all sorts of unclean things; and if you ran about the premises in the dark, barefooted, you were sure to step on an osage-orange twig; and I am satisfied, from the amount of squalling done, that if the season had lasted six months most of the children would have been exterminated.
I corresponded with some concern in one of the eastern cities, stating that I had a large amount of fine cocoons, and wanting to know what they would pay. I observed to Mrs. W. that I was confident of receiving a reply to the effect that I should ship the cocoons, draw at sight for five hundred dollars, leaving the balance to be paid as per account sales.
The reply was, to send on half-a-pound as a sample, and they would see if they could take them. When we came to weigh out half-a-pound, both Mrs. W. and I were appalled. It took about two bushels – nearly, if not quite, half of the entire crop. However, they were sent, and Mrs. W. snickered as she did up the package.
In the course of several weeks I received a specimen, say about a skein, of the most beautiful silk I had ever beheld, with an order to forward the balance of the cocoons per Adams Express, which I did at the expense of one dollar. Waited several months for acknowledgement of receipt, wrote various letters, the postage on which was two cents each. As considerable time elapsed while we were “waiting for the returns,” and as I was determined that Mrs. W. should understand this great subject of the tariff, as I knew she could if she gave her mind to it, I proceeded to eviscerate the whole matter. Said I, “When a tariff is laid upon a manufactured article, it enables the manufacturer in this country to pay his workmen higher wages.”
“And does he always do it?” said Mrs. W.
“Always,” I replied. “Statistics show that when the tariff on iron was increased twenty per cent the manufacturers of iron immediately raised the wages of all their employés twenty per cent.”
“I see,” said that clear-headed woman, “what excellent persons these iron men are. They do not hire their men for as little as they can, but pay them more than they want.”
“Exactly so,” I replied; “the general rule I admit to be that a man pays as little as he can for labor; but under the protective system, the tariff increases the price of the manufactured article, so that the manufacturer is enabled to sell his goods for that higher price, and the workman thus gets the benefit of it.”
This argument seemed to have great weight with her, as it gave her new light on things, for she said it was contrary to experience; but I explained to her that unless some flaw could be found in the syllogism, the conclusion was irresistible, all experience to the contrary notwithstanding. I then showed her how entirely disinterested the manufacturers were; that all their efforts were solely for the benefit of the workmen; that, personally, the tariff made no difference to them; that they never besought Congress to lay high tariffs; that no one ever knew of the iron men, or the sugar men, or the copper men, besieging the legislators at Washington to impose duties upon articles they made; that it was the workmen who always did it.
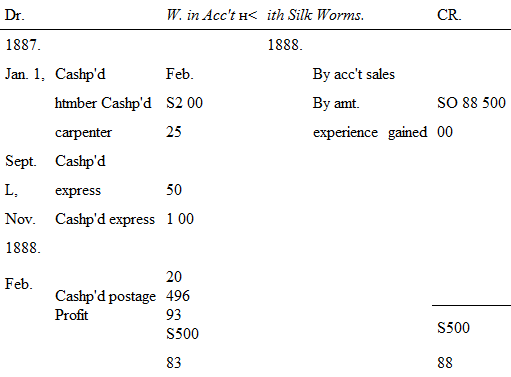
I do not know exactly how long it was that we waited to receive our fortune from those cocoons, but one day a postal card came to hand from the parties to whom I had sent my wealth, stating that they had received so many cocoons they could not tell which mine were. Inasmuch as mine were the only ones that had ever been shipped from the town wherein I reside, it occurred to me that this remark might be considered in the nature of a joke. Then there followed another voluminous correspondence. I appealed to Adams Express Company, who said they would send out a “tracer”; I did not like to betray my ignorance by showing that I did not know what a tracer was, but, frankly, I should not have known one had I met it on the street. But with the infinite knowledge of affairs that Mrs. W. has, that remarkable woman signified to me that a tracer was something that goes up and down and to and fro upon the face of the earth, like a roaring lion, seeking something, and not generally finding it. It is an immense consolation, however, to railroad men and others; for it appears that after a “tracer” has been “sent out,” nothing more can, by any possibility, be done by anybody. Whether or not the tracer had anything to do with the final result I never knew. But about six months after I had transmitted my cocoons to that large silk manufacturing house that paid such large wages to American workmen for the purpose of fostering American industry, I received a note sending a balance-sheet, and enclosing a check for eighty-eight cents.
When I received this portentous paper, I observed to Mrs. W.: “My dear, how much do you suppose we got for our cocoons?” “About seventy-five cents,” was the reply. The mind that woman has for detail is simply wonderful.
The check I have had framed, and hung up in the parlor, but when I balanced the books, I still found the profit large, thus:
IS MARRIAGE A FAILURE?
How like the ague is this boon Of matrimonial strife!The fever ends in one short moon, The chill runs on through life.EDITORIAL DEPARTMENT
THE COMMUNISM OF CAPITALThe President in his late and last message to Congress calls attention, in his incisive and felicitous style, to a condition of our people that must strike all intelligent minds with alarm. The corner-stone in the foundation of communism is that agency of the government which makes of the sovereign power that legal process which controls all private affairs for the good of the people. In popular phrase, it upholds the paternal form which enters every man’s house and regulates by law all his transactions. This is the foundation, while the holding of property in common is rather a consequence than a cause. If there are no rights pertaining to the citizen but those derived from government, to give practical effect to the scheme all property owned by the government must be held in its care in common by its dependents.
Heretofore this theory has been advocated by the poor and oppressed, and stoutly resisted by the rich. We are treated to a reversal of position in the parties, and the rich are practically pressing the scheme upon the poor.
Jefferson, the father of modern democracy, taught that the government, a mere form of expression, in the way of rule, by the people, who held the sovereignty was only a trust of power, instituted for the sole purpose of keeping the peace between the citizens. To use a popular phrase, it was nothing but the intervention of the constable.
Our central government, not being built altogether upon this broad yet simple proposition, opened in its mixed nature the door to communism found in the paternal form. Indeed, it would have been entirely divested of the Jeffersonian theory had it not been for the necessity under which the framers found themselves of conciliating the States, that then jealously fought every proposition looking to a deprivation of their sovereign rights. All that we so happily gained then came from a regard to the several States and not to any thought of popular rights.
This fact gave us a Constitution under which, we have managed to live, comparatively prosperous, for a century. Had it been otherwise, our Constitution would have gone to pieces in the first twenty-five years of its existence. A constitution is a legal recognition of certain general rules of conduct that are ever the same under all circumstances. Legislation is the adaptation of those rules to individual cases; and as these vary and change with continuously new conditions, a fixed application in a constitution is impossible. For this restriction, as far as it goes, we have to thank the States and not the sagacity of the fathers.
The Constitution was scarcely enacted before the communism of a paternal form began to manifest itself. The Federal party was of this sort. It sneered at and fought the sovereignty of the people, and found its governing element in a class that was supposed to hold in itself the intelligence and virtue of the people. It has departed and been done to death, not by the people, who failed to comprehend or feel the situation, but by the same cause that created the Constitution, – and that was the jealous opposition of the States to a centralization of power at Washington.
After the death of the Federal party the Whig organization was formed, on the same line and for the same purpose as those of its Federal predecessor. Henry Clay, its author, an eloquent but ignorant man, formulated his American system, that was a small affair in the beginning, but had deadly seeds of evil in its composition. Mr. Clay saw the necessity for manufactures in the United States; and as capital necessary to their existence in private hands could not be obtained, he proposed that the government should intervene through a misuse of the taxing power and supply the want. It was a modest want at first. “Let us aid these infant industries,” he said, “until they are strong enough to stand alone, and then the government may withdraw and leave competition to regulate prices.” It was a plausible but insidious proposition.
This was fought bitterly by the South, not altogether from a high ground of principle, although the argument was made that the government at Washington had no such power under the Constitution, but the main motive was self-interest. The South was an agricultural region, and found in cotton, rice, sugar, and tobacco staples that had their better, indeed their only, market in Europe, and saw no sense in trammelling it with laws to benefit Eastern capital. The American system was having a rough time and bidding fair to die out, when the sectional issue between the North and South culminated in war, and driving not only the South but the democracy from the government, left the paternal party in power.
This organization was made up mainly of Whigs. The abrupt dissolution of that party threw in the newly formed Republican organization the majority that from the first until now has governed its movements. How patriotic a party founded on property is, we learn from its first act after securing control of Congress. In the terrible war that followed secession, the greatest of dangers that threatened success was in European interference. Common sense, to say nothing of patriotism, dictated that Congress should at least abstain from measures likely to offend the governments abroad, if it did not do all in its power to conciliate. Greed recognized no such duty. Almost the first measure of any importance introduced and passed to a law was the Morrill tariff, that slapped the greatest war powers of Europe in the face. Under pretence of raising a war revenue, they made a deadly attack on resource from that source, for they well knew that as they increased the duties they lessened the income.
The panic and distress that followed this measure in all the markets of the world can well account for the deadly hostility to our government felt abroad. Small wonder that while arms were furnished the South in the greatest abundance, cruisers were fitted out in English ports to prey upon our helpless commerce. The greater danger of official recognition was only averted by the stubborn stand taken by Great Britain; and as it was, we now know that had the South been able to continue the war ninety days longer that intervention would have come. A French army, sent there for that purpose, would have invaded our lands from Mexico, while the fleets of allied France and England would have dissipated our so-called blockade, lifted the Confederacy’s financial credit to par, and we would have been called on to make terms of peace at Philadelphia.
All this gathered evil was shattered at Nashville by the gallant Thomas and his noble Army of the Cumberland, when he not only defeated the fifty thousand veterans under Hood, but annihilated an army.
This was the birth of the communism of wealth that is to govern our country for the next four years. Of course it is absurd to charge nearly a half of our people with corrupt motives and unpatriotic conduct. We have no such intent. We are only striving to show that the success of the Republican policy is fatal to the Republic. This party, as we have said, is in no sense a political organization. It is a great combination of private interests that seek to use the government to further their own selfish ends. Governments through all the ages have been the deadly enemies of the people they governed. Ours, controlled by the Republican party, makes no exception to the rule. The gigantic trusts, or combinations, are eating the substance out of honest toil, and back of them stands the awful shadow of a powerful organization making those trusts possible, and doing to the people precisely the cruel wrong it was created to prevent. Palaces multiply as hovels increase; and while millionaires are common, the million sink back to that hopeless poverty of destitution that has the name of freedom, as a mockery to their serfdom.
THE INFAMY OF ITFor years past it has become more and more patent to the people of the United States that the ballot has come to be a commercial affair, and instead of serving its original purpose of a process through which to express the popular will, represents only the money expended in its use. For a long time it was abused through stuffing, false counts, repeating, and switching tickets. In the late Presidential election we seemed to have passed from that stage to open and shameless bribery.
This is simply appalling to those who love their country and believe in our great Republic. The old system of roguery that attacked the integrity of the ballot was that of a few low villains, who could be met by an improved box and other stringent, legalized guards that would make the vile practices difficult, and punishment easily secured. But this open purchase of votes indicates a poison in the spring head itself, and a consent found in the apathy of the public.
What good would be the Australian system, that seeks to shield the secret ballot, where the official agents themselves would of course be corrupt and purchasable? Under this system the voter entering a stall by himself finds an official to give him such ticket as he may demand. What will be the good of this when that agent can be purchased? We really simply give the corruption into the hands of the corruptionists through the very enactment called in to protect us.
Our unhappy condition is recognized. There is not a man, woman, or child in our country possessed of any brain but knows that Benjamin Harrison was elected President by open, wholesale bribery. Mr. Foster advertised this in his well-known circulars wherein he called for funds, and quoted Senator Plumb as saying that the manufacturers ought to be squeezed. And why should they be squeezed? – because, he said, they are the sole beneficiaries of the one measure at issue in the canvass. This was followed by Senator Ingalls’ famous advice to the delegate at the Chicago convention, which said, “Nominate some such fellow as Phelps, who can tap Wall Street.” This was followed by the Dudley circular directing the purchase of “floaters in blocks of five or more,” and assuring those dishonest agents that the funds would not be wanting to close the purchase.
Under this exhibit of evidence the fact cannot be denied; but to make it conclusive, the New York World has gathered from all parts of the country clear, unmistakable proof of wide-spread, clearly planned, and openly executed purchase of voters.
The chair of the Chief Executive has followed the seats of Senators to the market, and that highest gift of the citizen has been sold to the highest bidder. The great political fabric of the fathers, built from woful expenditure of patriotic effort and blood, is honeycombed with rot, and remains, a mere sham, to shame us before the world.
Of course we are not so silly as to attach blame only to one party. The difference between the two lies in the fact that the one had more money than the other, and a stronger motive for its use. The Republicans being a “combine” of property interests, depending upon the government to make those interests profitable, were impelled to exertion far beyond the Democrats, who were struggling for the power only that a possession of the government brings. But we are forced to remember that the votes purchased came from the Democratic party. Said a prominent Democrat of Indiana to the writer of this: “We had enough money to purchase the State had we known the nature of the market, and possessed agents upon whom we could rely. The agents of our opponents were preachers, deacons, elders, class-leaders, and teachers in Sunday-schools, and could be relied on to use their swag as directed. Our fellows put our money in their pockets, and left the voting to care for itself. And then, again, while we were on the lookout for repeaters, pipe-layers, and ballot-box stuffers, they were in open market purchasing votes. We learned the nature of the business when too late to meet it, had we even had the means to make our knowledge available.”



