 Полная версия
Полная версияThe Seven Lamps of Architecture
XVI. I have endeavored to give some idea of one of the hollow balls of stone which, surrounded by flowing leafage, occur in varied succession on the architrave of the central gate of St. Mark's at Venice, in Plate I. fig. 2. It seems to me singularly beautiful in its unity of lightness, and delicacy of detail, with breadth of light. It looks as if its leaves had been sensitive, and had risen and shut themselves into a bud at some sudden touch, and would presently fall back again into their wild flow. The cornices of San Michele of Lucca, seen above and below the arch, in Plate VI., show the effect of heavy leafage and thick stems arranged on a surface whose curve is a simple quadrant, the light dying from off them as it turns. It would be difficult, as I think, to invent anything more noble; and I insist on the broad character of their arrangement the more earnestly, because, afterwards modified by greater skill in its management, it became characteristic of the richest pieces of Gothic design. The capital, given in Plate V., is of the noblest period of the Venetian Gothic; and it is interesting to see the play of leafage so luxuriant, absolutely subordinated to the breadth of two masses of light and shade. What is done by the Venetian architect, with a power as irresistible as that of the waves of his surrounding sea, is done by the masters of the Cis-Alpine Gothic, more timidly, and with a manner somewhat cramped and cold, but not less expressing their assent to the same great law. The ice spiculæ of the North, and its broken sunshine, seem to have image in, and influence on the work; and the leaves which, under the Italian's hand, roll, and flow, and bow down over their black shadows, as in the weariness of noon-day heat, are, in the North, crisped and frost-bitten, wrinkled on the edges, and sparkling as if with dew. But the rounding of the ruling form is not less sought and felt. In the lower part of Plate I. is the finial of the pediment given in Plate II., from the cathedral of St. Lo. It is exactly similar in feeling to the Byzantine capital, being rounded under the abacus by four branches of thistle leaves, whose stems, springing from the angles, bend outwards and fall back to the head, throwing their jaggy spines down upon the full light, forming two sharp quatre-foils. I could not get near enough to this finial to see with what degree of delicacy the spines were cut; but I have sketched a natural group of thistle-leaves beside it, that the reader may compare the types, and see with what mastery they are subjected to the broad form of the whole. The small capital from Coutances, Plate XIII. fig. 4, which is of earlier date, is of simpler elements, and exhibits the principle still more clearly; but the St. Lo finial is only one of a thousand instances which might be gathered even from the fully developed flamboyant, the feeling of breadth being retained in minor ornaments long after it had been lost in the main design, and sometimes capriciously renewing itself throughout, as in the cylindrical niches and pedestals which enrich the porches of Caudebec and Rouen. Fig. 1, Plate I. is the simplest of those of Rouen; in the more elaborate there are four projecting sides, divided by buttresses into eight rounded compartments of tracery; even the whole bulk of the outer pier is treated with the same feeling; and though composed partly of concave recesses, partly of square shafts, partly of statues and tabernacle work, arranges itself as a whole into one richly rounded tower.

PLATE V.—(Page 88—Vol. V.)
Capital from the Lower Arcade of the Doge's Palace, Venice.
XVII. I cannot here enter into the curious questions connected with the management of larger curved surfaces; into the causes of the difference in proportion necessary to be observed between round and square towers; nor into the reasons why a column or ball may be richly ornamented, while surface decorations would be inexpedient on masses like the Castle of St. Angelo, the tomb of Cecilia Metella, or the dome of St. Peter's. But what has been above said of the desireableness of serenity in plane surfaces, applies still more forcibly to those which are curved; and it is to be remembered that we are, at present, considering how this serenity and power may be carried into minor divisions, not how the ornamental character of the lower form may, upon occasion, be permitted to fret the calmness of the higher. Nor, though the instances we have examined are of globular or cylindrical masses chiefly, is it to be thought that breadth can only be secured by such alone: many of the noblest forms are of subdued curvature, sometimes hardly visible; but curvature of some degree there must be, in order to secure any measure of grandeur in a small mass of light. One of the most marked distinctions between one artist and another, in the point of skill, will be found in their relative delicacy of perception of rounded surface; the full power of expressing the perspective, foreshortening and various undulation of such surface is, perhaps, the last and most difficult attainment of the hand and eye. For instance: there is, perhaps, no tree which has baffled the landscape painter more than the common black spruce fir. It is rare that we see any representation of it other than caricature. It is conceived as if it grew in one plane, or as a section of a tree, with a set of boughs symmetrically dependent on opposite sides. It is thought formal, unmanageable, and ugly. It would be so, if it grew as it is drawn. But the power of the tree is not in that chandelier-like section. It is in the dark, flat, solid tables of leafage, which it holds out on its strong arms, curved slightly over them like shields, and spreading towards the extremity like a hand. It is vain to endeavor to paint the sharp, grassy, intricate leafage, until this ruling form has been secured; and in the boughs that approach the spectator, the foreshortening of it is like that of a wide hill country, ridge just rising over ridge in successive distances; and the finger-like extremities, foreshortened to absolute bluntness, require a delicacy in the rendering of them like that of the drawing of the hand of the Magdalene upon the vase in Mr. Rogers's Titian. Get but the back of that foliage, and you have the tree; but I cannot name the artist who has thoroughly felt it. So, in all drawing and sculpture, it is the power of rounding, softly and perfectly, every inferior mass which preserves the serenity, as it follows the truth, of Nature, and which demands the highest knowledge and skill from the workman. A noble design may always be told by the back of a single leaf, and it was the sacrifice of this breadth and refinement of surface for sharp edges and extravagant undercutting, which destroyed the Gothic mouldings, as the substitution of the line for the light destroyed the Gothic tracery. This change, however, we shall better comprehend after we have glanced at the chief conditions of arrangement of the second kind of mass; that which is flat, and of shadow only.

PLATE VI.—(Page 90—Vol. V.)
Arch from the Façade of the Church of San Michele at Lucca.
XVIII. We have noted above how the wall surface, composed of rich materials, and covered with costly work, in modes which we shall examine in the next Chapter, became a subject of peculiar interest to the Christian architects. Its broad flat lights could only be made valuable by points or masses of energetic shadow, which were obtained by the Romanesque architect by means of ranges of recessed arcade, in the management of which, however, though all the effect depends upon the shadow so obtained, the eye is still, as in classical architecture, caused to dwell upon the projecting columns, capitals, and wall, as in Plate VI. But with the enlargement of the window, which, in the Lombard and Romanesque churches, is usually little more than an arched slit, came the conception of the simpler mode of decoration, by penetrations which, seen from within, are forms of light, and, from without, are forms of shade. In Italian traceries the eye is exclusively fixed upon the dark forms of the penetrations, and the whole proportion and power of the design are caused to depend upon them. The intermediate spaces are, indeed, in the most perfect early examples, filled with elaborate ornament; but this ornament was so subdued as never to disturb the simplicity and force of the dark masses; and in many instances is entirely wanting. The composition of the whole depends on the proportioning and shaping of the darks; and it is impossible that anything can be more exquisite than their placing in the head window of the Giotto campanile, Plate IX., or the church of Or San Michele. So entirely does the effect depend upon them, that it is quite useless to draw Italian tracery in outline; if with any intention of rendering its effect, it is better to mark the black spots, and let the rest alone. Of course, when it is desired to obtain an accurate rendering of the design, its lines and mouldings are enough; but it often happens that works on architecture are of little use, because they afford the reader no means of judging of the effective intention of the arrangements which they state. No person, looking at an architectural drawing of the richly foliaged cusps and intervals of Or San Michele, would understand that all this sculpture was extraneous, was a mere added grace, and had nothing to do with the real anatomy of the work, and that by a few bold cuttings through a slab of stone he might reach the main effect of it all at once. I have, therefore, in the plate of the design of Giotto, endeavored especially to mark these points of purpose; there, as in every other instance, black shadows of a graceful form lying on the white surface of the stone, like dark leaves laid upon snow. Hence, as before observed, the universal name of foil applied to such ornaments.
XIX. In order to the obtaining their full effect, it is evident that much caution is necessary in the management of the glass. In the finest instances, the traceries are open lights, either in towers, as in this design of Giotto's or in external arcades like that of the Campo Santo at Pisa or the Doge's palace at Venice; and it is thus only that their full beauty is shown. In domestic buildings, or in windows of churches necessarily glazed, the glass was usually withdrawn entirely behind the traceries. Those of the Cathedral of Florence stand quite clear of it, casting their shadows in well detached lines, so as in most lights to give the appearance of a double tracery. In those few instances in which the glass was set in the tracery itself, as in Or San Michele, the effect of the latter is half destroyed: perhaps the especial attention paid by Orgagna to his surface ornament, was connected with the intention of so glazing them. It is singular to see, in late architecture, the glass, which tormented the older architects, considered as a valuable means of making the lines of tracery more slender; as in the smallest intervals of the windows of Merton College, Oxford, where the glass is advanced about two inches from the centre of the tracery bar (that in the larger spaces being in the middle, as usual), in order to prevent the depth of shadow from farther diminishing the apparent interval. Much of the lightness of the effect of the traceries is owing to this seemingly unimportant arrangement. But, generally speaking, glass spoils all traceries; and it is much to be wished that it should be kept well within them, when it cannot be dispensed with, and that the most careful and beautiful designs should be reserved for situations where no glass would be needed.
XX. The method of decoration by shadow was, as far as we have hitherto traced it, common to the northern and southern Gothic. But in the carrying out of the system they instantly diverged. Having marble at his command, and classical decoration in his sight, the southern architect was able to carve the intermediate spaces with exquisite leafage, or to vary his wall surface with inlaid stones. The northern architect neither knew the ancient work, nor possessed the delicate material; and he had no resource but to cover his walls with holes, cut into foiled shapes like those of the windows. This he did, often with great clumsiness, but always with a vigorous sense of composition, and always, observe, depending on the shadows for effect. Where the wall was thick and could not be cut through, and the foilings were large, those shadows did not fill the entire space; but the form was, nevertheless, drawn on the eye by means of them, and when it was possible, they were cut clear through, as in raised screens of pediment, like those on the west front of Bayeux; cut so deep in every case, as to secure, in all but a direct low front light, great breadth of shadow.
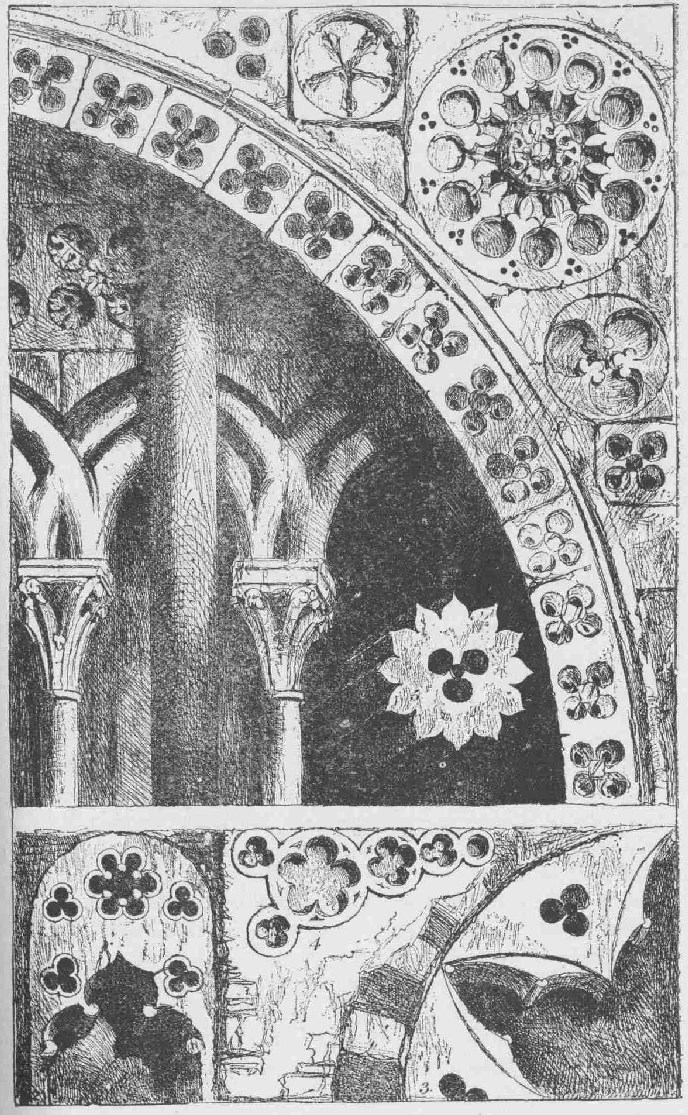
PLATE VII.—(Page 93—Vol. V.)
Pierced Ornaments from Lisieux, Bayeux, Verona, and Padua.
The spandril, given at the top of Plate VII., is from the southwestern entrance of the Cathedral of Lisieux; one of the most quaint and interesting doors in Normandy, probably soon to be lost forever, by the continuance of the masonic operations which have already destroyed the northern tower. Its work is altogether rude, but full of spirit; the opposite spandrils have different, though balanced, ornaments very inaccurately adjusted, each rosette or star (as the five-rayed figure, now quite defaced, in the upper portion appears to have been) cut on its own block of stone and fitted in with small nicety, especially illustrating the point I have above insisted upon—the architect's utter neglect of the forms of intermediate stone, at this early period.
The arcade, of which a single arch and shaft are given on the left, forms the flank of the door; three outer shafts bearing three orders within the spandril which I have drawn, and each of these shafts carried over an inner arcade, decorated above with quatre-foils, cut concave and filled with leaves, the whole disposition exquisitely picturesque and full of strange play of light and shade.
For some time the penetrative ornaments, if so they may be for convenience called, maintained their bold and independent character. Then they multiplied and enlarged, becoming shallower as they did so; then they began to run together, one swallowing up, or hanging on to, another, like bubbles in expiring foam—fig. 4, from a spandril at Bayeux, looks as if it had been blown from a pipe; finally, they lost their individual character altogether, and the eye was made to rest on the separating lines of tracery, as we saw before in the window; and then came the great change and the fall of the Gothic power.
XXI. Figs. 2 and 3, the one a quadrant of the star window of the little chapel close to St. Anastasia at Verona, and the other a very singular example from the church of the Eremitani at Padua, compared with fig. 5, one of the ornaments of the transept towers of Rouen, show the closely correspondent conditions of the early Northern and Southern Gothic.10 But, as we have said, the Italian architects, not being embarrassed for decoration of wall surface, and not being obliged, like the Northmen, to multiply their penetrations, held to the system for some time longer; and while they increased the refinement of the ornament, kept the purity of the plan. That refinement of ornament was their weak point, however, and opened the way for the renaissance attack. They fell, like the old Romans, by their luxury, except in the separate instance of the magnificent school of Venice. That architecture began with the luxuriance in which all others expired: it founded itself on the Byzantine mosaic and fretwork; and laying aside its ornaments, one by one, while it fixed its forms by laws more and more severe, stood forth, at last, a model of domestic Gothic, so grand, so complete, so nobly systematised, that, to my mind, there never existed an architecture with so stern a claim to our reverence. I do not except even the Greek Doric; the Doric had cast nothing away; the fourteenth century Venetian had cast away, one by one, for a succession of centuries, every splendor that art and wealth could give it. It had laid down its crown and its jewels, its gold and its color, like a king disrobing; it had resigned its exertion, like an athlete reposing; once capricious and fantastic, it had bound itself by laws inviolable and serene as those of nature herself. It retained nothing but its beauty and its power; both the highest, but both restrained. The Doric flutings were of irregular number—the Venetian mouldings were unchangeable. The Doric manner of ornament admitted no temptation, it was the fasting of an anchorite—the Venetian ornament embraced, while it governed, all vegetable and animal forms; it was the temperance of a man, the command of Adam over creation. I do not know so magnificent a marking of human authority as the iron grasp of the Venetian over his own exuberance of imagination; the calm and solemn restraint with which, his mind filled with thoughts of flowing leafage and fiery life, he gives those thoughts expression for an instant, and then withdraws within those massy bars and level cusps of stone.11
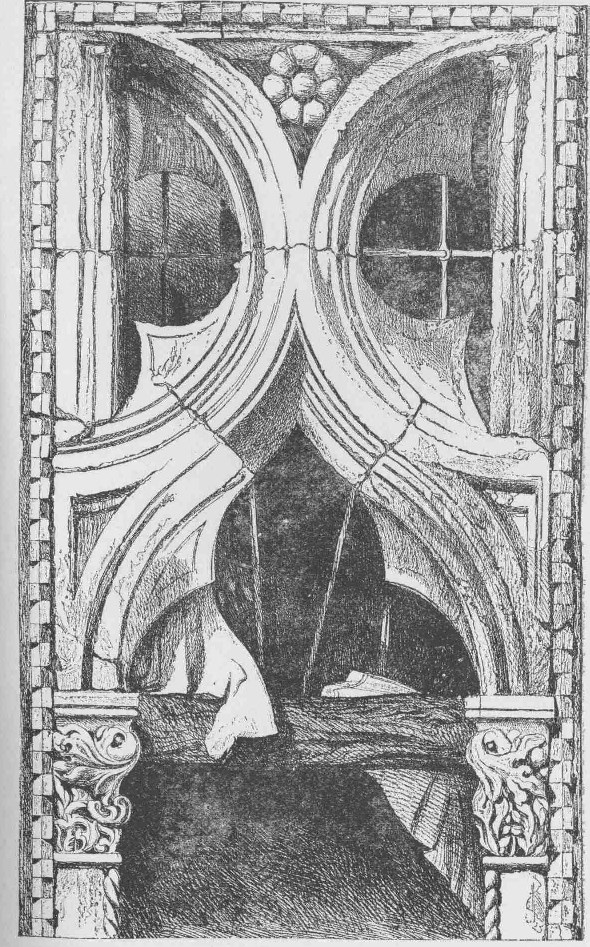
PLATE VIII.—(Page 95—Vol. V.)
Window from the Ca' Foscari, Venice.
And his power to do this depended altogether on his retaining the forms of the shadows in his sight. Far from carrying the eye to the ornaments, upon the stone, he abandoned these latter one by one; and while his mouldings received the most shapely order and symmetry, closely correspondent with that of the Rouen tracery, compare Plates III. and VIII., he kept the cusps within them perfectly flat, decorated, if at all, with a trefoil (Palazzo Foscari), or fillet (Doge's Palace) just traceable and no more, so that the quatrefoil, cut as sharply through them as if it had been struck out by a stamp, told upon the eye, with all its four black leaves, miles away. No knots of flowerwork, no ornaments of any kind, were suffered to interfere with the purity of its form: the cusp is usually quite sharp; but slightly truncated in the Palazzo Foscari, and charged with a simple ball in that of the Doge; and the glass of the window, where there was any, was, as we have seen, thrown back behind the stone-work, that no flashes of light might interfere with its depth. Corrupted forms, like those of the Casa d'Oro and Palazzo Pisani, and several others, only serve to show the majesty of the common design.
XXII. Such are the principal circumstances traceable in the treatment of the two kinds of masses of light and darkness, in the hands of the earlier architects; gradation in the one, flatness in the other, and breadth in both, being the qualities sought and exhibited by every possible expedient, up to the period when, as we have before stated, the line was substituted for the mass, as the means of division of surface. Enough has been said to illustrate this, as regards tracery; but a word or two is still necessary respecting the mouldings.
Those of the earlier times were, in the plurality of instances, composed of alternate square and cylindrical shafts, variously associated and proportioned. Where concave cuttings occur, as in the beautiful west doors of Bayeux, they are between cylindrical shafts, which they throw out into broad light. The eye in all cases dwells on broad surfaces, and commonly upon few. In course of time, a low ridgy process is seen emerging along the outer edge of the cylindrical shaft, forming a line of light upon it and destroying its gradation. Hardly traceable at first (as on the alternate rolls of the north door of Rouen), it grows and pushes out as gradually as a stag's horns: sharp at first on the edge; but, becoming prominent, it receives a truncation, and becomes a definite fillet on the face of the roll. Not yet to be checked, it pushes forward until the roll itself becomes subordinate to it, and is finally lost in a slight swell upon its sides, while the concavities have all the time been deepening and enlarging behind it, until, from a succession of square or cylindrical masses, the whole moulding has become a series of concavities edged by delicate fillets, upon which (sharp lines of light, observe) the eye exclusively rests. While this has been taking place, a similar, though less total, change has affected the flowerwork itself. In Plate I. fig. 2 (a), I have given two from the transepts of Rouen. It will be observed how absolutely the eye rests on the forms of the leaves, and on the three berries in the angle, being in light exactly what the trefoil is in darkness. These mouldings nearly adhere to the stone; and are very slightly, though sharply, undercut. In process of time, the attention of the architect, instead of resting on the leaves, went to the stalks. These latter were elongated (b, from the south door of St. Lo); and to exhibit them better, the deep concavity was cut behind, so as to throw them out in lines of light. The system was carried out into continually increasing intricacy, until, in the transepts of Beauvais, we have brackets and flamboyant traceries, composed of twigs without any leaves at all. This, however, is a partial, though a sufficiently characteristic, caprice, the leaf being never generally banished, and in the mouldings round those same doors, beautifully managed, but itself rendered liny by bold marking of its ribs and veins, and by turning up, and crisping its edges, large intermediate spaces being always left to be occupied by intertwining stems (c, from Caudebec). The trefoil of light formed by berries or acorns, though diminished in value, was never lost up to the last period of living Gothic.
XXIII. It is interesting to follow into its many ramifications, the influence of the corrupting principle; but we have seen enough of it to enable us to draw our practical conclusion—a conclusion a thousand times felt and reiterated in the experience and advice of every practised artist, but never often enough repeated, never profoundly enough felt. Of composition and invention much has been written, it seems to me vainly, for men cannot be taught to compose or to invent; of these, the highest elements of Power in architecture, I do not, therefore, speak; nor, here, of that peculiar restraint in the imitation of natural forms, which constitutes the dignity of even the most luxuriant work of the great periods. Of this restraint I shall say a word or two in the next Chapter; pressing now only the conclusion, as practically useful as it is certain, that the relative majesty of buildings depends more on the weight and vigor of their masses than on any other attribute of their design: mass of everything, of bulk, of light, of darkness, of color, not mere sum of any of these, but breadth of them; not broken light, nor scattered darkness, nor divided weight, but solid stone, broad sunshine, starless shade. Time would fail me altogether, if I attempted to follow out the range of the principle; there is not a feature, however apparently trifling, to which it cannot give power. The wooden fillings of belfry lights, necessary to protect their interiors from rain, are in England usually divided into a number of neatly executed cross-bars, like those of Venetian blinds, which, of course, become as conspicuous in their sharpness as they are uninteresting in their precise carpentry, multiplying, moreover, the horizontal lines which directly contradict those of the architecture. Abroad, such necessities are met by three or four downright penthouse roofs, reaching each from within the window to the outside shafts of its mouldings; instead of the horrible row of ruled lines, the space is thus divided into four or five grand masses of shadow, with grey slopes of roof above, bent or yielding into all kinds of delicious swells and curves, and covered with warm tones of moss and lichen. Very often the thing is more delightful than the stone-work itself, and all because it is broad, dark, and simple. It matters not how clumsy, how common, the means are, that get weight and shadow—sloping roof, jutting porch, projecting balcony, hollow niche, massy gargoyle, frowning parapet; get but gloom and simplicity, and all good things will follow in their place and time; do but design with the owl's eyes first, and you will gain the falcon's afterwards.

