
Полная версия:
Разработка Android-приложений с Augmented Reality
// Now that we have the plugin created let’s add it to our world.
// NOTE: It is better to load the plugins before start adding object in to the world.
mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin);
mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this);
mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15));
mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null);
// Lets add the user position
GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l);
user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ());
user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag);
user.setName («User position»);
mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user);
}
}
После запуска приложения на Android устройстве появится список с примерами.
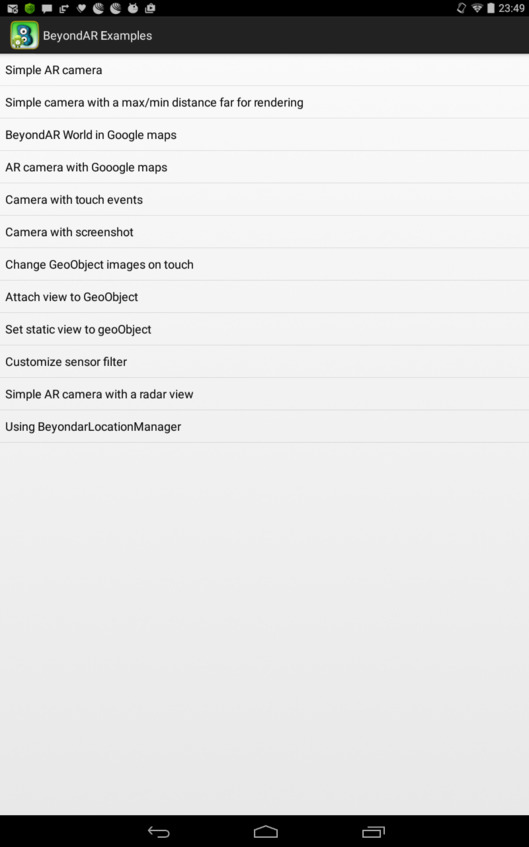
Simple AR camera – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры. При этом изображения расположены в пространстве вокруг устройства.
Simple camera with a max/min distance far for rendering – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с возможностью регулировки расстояния до изображений.
BeyondAR World in Google maps – показывает набор изображений на карте.
AR camera with Google maps – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с кнопкой переключения на карту.
Camera with touch events – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, а также сообщение при нажатии на одном из изображений.
Camera with screenshot – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с кнопкой скриншота.
Change GeoObject images on touch – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, которые заменяются на другие изображения при нажатии.
Attach view to GeoObject – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с добавлением вида к изображению при нажатии.
Set static view to geoObject – вместо изображений показывает виды на фоне камеры, а также сообщение при нажатии на одном из видов.
Customize sensor filter – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры с возможностью регулировки чувствительности датчика ориентации.
Simple AR camera with a radar view – показывает набор изображений на фоне камеры, а также расположение изображений вокруг устройства.
Using BeyondarLocationManager – показывает набор изображений на карте с кнопкой обновления местоположения.
Для работы BeyondAR фреймворка в файле манифеста приложения декларируются необходимые разрешения и наличие сенсоров устройства.
android: layout_width=«match_parent» android: layout_height=«match_parent» android: id="@+id/parentFrameLayout»> android: id="@+id/beyondarFragment» android:name="com.beyondar.android.fragment.BeyondarFragmentSupport» android: layout_width=«match_parent» android: layout_height=«match_parent» /> Далее создается объект World – контейнер объектов дополненной реальности, который затем добавляется во фрагмент BeyondarFragmentSupport. Метод mBeyondarFragment.showFPS (true) показывает количество кадров в секунду в левом верхнем углу экрана. Вся магия по созданию объектов дополненной реальности осуществляется в классе CustomWorldHelper. Здесь создается новый контейнер World, устанавливается его местоположение в реальном мире, а также на основе изображений создаются объекты GeoObject, которые добавляются в контейнер World. public static World sharedWorld; sharedWorld = new World (context); sharedWorld.setGeoPosition (41.90533734214473d, 2.565848038959814d); GeoObject go4 = new GeoObject (4l); go4.setGeoPosition (41.90518862002349d, 2.565662767707665d); go4.setImageUri("assets://creature_7.png»); go4.setName («Image from assets»); sharedWorld.addBeyondarObject (go4); По умолчанию для контейнера World и для его объектов, в классе CustomWorldHelper, задаются фиксированные координаты в реальном мире. Исправим это, привязав координаты контейнера World к местоположению устройства. Для определения местоположения устройства используем Fused location provider API (Android API Level> v9, Android Build Tools> v21). Изменим код классов CustomWorldHelper, GoogleMapActivity и SimpleCameraActivity. import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.content.Context; import android. location. Location; import android.widget.Toast; import com.beyondar.android.world.GeoObject; import com.beyondar.android. world. World; @SuppressLint («SdCardPath») public class CustomWorldHelper { public static final int LIST_TYPE_EXAMPLE_1 = 1; public static World sharedWorld; public static World generateObjects (Context context, Location mCurrentLocation) { sharedWorld = new World (context); // The user can set the default bitmap. This is useful if you are // loading images form Internet and the connection get lost sharedWorld.setDefaultImage(R.drawable.beyondar_default_unknow_icon); // User position (you can change it using the GPS listeners form Android // API) if (mCurrentLocation== null) { mCurrentLocation=new Location (»»); mCurrentLocation.setLatitude (41.90533734214473d); mCurrentLocation.setLongitude (2.565848038959814d); } sharedWorld.setGeoPosition(mCurrentLocation.getLatitude(),mCurrentLocation.getLongitude ()); // Create an object with an image in the app resources. // And the same goes for the app assets GeoObject go = new GeoObject (1l); go.setGeoPosition(mCurrentLocation.getLatitude()+0.00005,mCurrentLocation.getLongitude () -0.0001); go.setImageUri("assets://creature_7.png»); go.setName («Image from assets»); // Add the GeoObjects to the world sharedWorld.addBeyondarObject (go); return sharedWorld; } } import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android. location. Location; import android. os. Bundle; import android.support.annotation.NonNull; import android.support.annotation.Nullable; import android.support.v4.app.ActivityCompat; import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity; import android.widget.Toast; import com.beyondar.android.plugin. googlemap. GoogleMapWorldPlugin; import com.beyondar.android.world.GeoObject; import com.beyondar.android. world. World; import com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult; import com.google.android.gms.common. api. GoogleApiClient; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationListener; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationRequest; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationServices; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps. GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps. GoogleMap. OnMarkerClickListener; import com.google.android.gms.maps. OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker; public class GoogleMapActivity extends FragmentActivity implements OnMarkerClickListener, OnMapReadyCallback, LocationListener, GoogleApiClient.ConnectionCallbacks, GoogleApiClient. OnConnectionFailedListener { private GoogleMap mMap; private GoogleMapWorldPlugin mGoogleMapPlugin; private World mWorld; GoogleApiClient mGoogleApiClient; Location mCurrentLocation; LocationRequest mLocationRequest; @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super. onCreate (savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.map_google); ((SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager () .findFragmentById(R.id.map)).getMapAsync (this); buildGoogleApiClient (); } /** * Builds a GoogleApiClient. Uses the {@code #addApi} method to request the * LocationServices API. */ protected synchronized void buildGoogleApiClient () { mGoogleApiClient = new GoogleApiClient. Builder (this) .addConnectionCallbacks (this) .addOnConnectionFailedListener (this) .addApi (LocationServices. API) .build (); createLocationRequest (); } protected void createLocationRequest () { mLocationRequest = LocationRequest.create (); // Sets the desired interval for active location updates. This interval is // inexact. You may not receive updates at all if no location sources are available, or // you may receive them slower than requested. You may also receive updates faster than // requested if other applications are requesting location at a faster interval. mLocationRequest.setInterval (10000); // Sets the fastest rate for active location updates. This interval is exact, and your // application will never receive updates faster than this value. mLocationRequest.setFastestInterval (5000); mLocationRequest.setPriority(LocationRequest.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY); } @Override public void onStart () { super. onStart (); mGoogleApiClient.connect (); } @Override public void onStop () { super. onStop (); mGoogleApiClient. disconnect (); } @Override public void onResume () { super. onResume (); // Within {@code onPause ()}, we pause location updates, but leave the // connection to GoogleApiClient intact. Here, we resume receiving // location updates if the user has requested them. if (mGoogleApiClient.isConnected ()) { startLocationUpdates (); } } @Override protected void onPause () { super. onPause (); // Stop location updates to save battery, but don’t disconnect the GoogleApiClient object. if (mGoogleApiClient.isConnected ()) { stopLocationUpdates (); } } protected void startLocationUpdates () { if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED && ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { return; } LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.requestLocationUpdates ( mGoogleApiClient, mLocationRequest, this); } /** * Removes location updates from the FusedLocationApi. */ protected void stopLocationUpdates () { // It is a good practice to remove location requests when the activity is in a paused or // stopped state. Doing so helps battery performance and is especially // recommended in applications that request frequent location updates. // The final argument to {@code requestLocationUpdates ()} is a LocationListener // (http://developer.android.com/reference/com/google/android/gms/location/LocationListener.html). LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.removeLocationUpdates (mGoogleApiClient, this); } @Override public boolean onMarkerClick (Marker marker) { // To get the GeoObject that owns the marker we use the following // method: GeoObject geoObject = mGoogleMapPlugin.getGeoObjectOwner (marker); if (geoObject!= null) { Toast.makeText (this, «Click on a marker owned by a GeoOject with the name: " + geoObject.getName (), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show (); } return false; } @Override public void onMapReady (GoogleMap googleMap) { mMap=googleMap; // We create the world and fill the world mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this, mCurrentLocation); // As we want to use GoogleMaps, we are going to create the plugin and // attach it to the World mGoogleMapPlugin = new GoogleMapWorldPlugin (this); // Then we need to set the map in to the GoogleMapPlugin mGoogleMapPlugin.setGoogleMap (mMap); // Now that we have the plugin created let’s add it to our world. // NOTE: It is better to load the plugins before start adding object in to the world. mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin); mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this); mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15)); mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null); // Lets add the user position GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l); user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ()); user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag); user.setName («User position»); mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user); } @Override public void onConnected (@Nullable Bundle bundle) { if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED && ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { return; } Location mLastLocation = LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.getLastLocation (mGoogleApiClient); if (mLastLocation!= null) { mCurrentLocation = mLastLocation; String lat = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLatitude ()); String lon = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLongitude ()); Toast toast = Toast.makeText (this, «Last location» + lat + " " + lon, Toast. LENGTH_LONG); toast.show (); mWorld.clearWorld (); mMap.clear (); mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this, mCurrentLocation); mGoogleMapPlugin = new GoogleMapWorldPlugin (this); mGoogleMapPlugin.setGoogleMap (mMap); mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin); mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this); mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15)); mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null); GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l); user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ()); user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag); user.setName («User position»); mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user); } else { startLocationUpdates (); } } @Override public void onConnectionSuspended (int i) { } @Override public void onConnectionFailed (@NonNull ConnectionResult connectionResult) { } @Override public void onLocationChanged (Location location) { mCurrentLocation = location; String lat = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLatitude ()); String lon = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLongitude ()); Toast toast = Toast.makeText (this,«Current location " + lat+" "+lon, Toast. LENGTH_LONG); toast.show (); mWorld.clearWorld (); mMap.clear (); mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this, mCurrentLocation); mGoogleMapPlugin = new GoogleMapWorldPlugin (this); mGoogleMapPlugin.setGoogleMap (mMap); mWorld.addPlugin (mGoogleMapPlugin); mMap.setOnMarkerClickListener (this); mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(mGoogleMapPlugin.getLatLng (), 15)); mMap.animateCamera (CameraUpdateFactory. zoomTo (19), 2000, null); GeoObject user = new GeoObject (1000l); user.setGeoPosition(mWorld.getLatitude (), mWorld.getLongitude ()); user.setImageResource (R. drawable. flag); user.setName («User position»); mWorld.addBeyondarObject (user); } } import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android. location. Location; import android. os. Bundle; import android.support.annotation.NonNull; import android.support.annotation.Nullable; import android.support.v4.app.ActivityCompat; import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity; import android.view. Window; import android.widget.Toast; import com.beyondar.android.fragment.BeyondarFragmentSupport; import com.beyondar.android. opengl. util. LowPassFilter; import com.beyondar.android. world. World; import com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult; import com.google.android.gms.common. api. GoogleApiClient; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationListener; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationRequest; import com.google.android.gms. location. LocationServices; public class SimpleCameraActivity extends FragmentActivity implements LocationListener, GoogleApiClient.ConnectionCallbacks, GoogleApiClient. OnConnectionFailedListener { private BeyondarFragmentSupport mBeyondarFragment; private World mWorld; GoogleApiClient mGoogleApiClient; Location mCurrentLocation; LocationRequest mLocationRequest; /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super. onCreate (savedInstanceState); // Hide the window title. requestWindowFeature (Window. FEATURE_NO_TITLE); setContentView(R.layout.simple_camera); mBeyondarFragment = (BeyondarFragmentSupport) getSupportFragmentManager () .findFragmentById(R.id.beyondarFragment); // We also can see the Frames per seconds mBeyondarFragment.showFPS (false); // We create the world and fill it… mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this, mCurrentLocation); // … and send it to the fragment mBeyondarFragment.setWorld (mWorld); LowPassFilter.ALPHA = 0.003f; buildGoogleApiClient (); } /** * Builds a GoogleApiClient. Uses the {@code #addApi} method to request the * LocationServices API. */ protected synchronized void buildGoogleApiClient () { mGoogleApiClient = new GoogleApiClient. Builder (this) .addConnectionCallbacks (this) .addOnConnectionFailedListener (this) .addApi (LocationServices. API) .build (); createLocationRequest (); } protected void createLocationRequest () { mLocationRequest = LocationRequest.create (); // Sets the desired interval for active location updates. This interval is // inexact. You may not receive updates at all if no location sources are available, or // you may receive them slower than requested. You may also receive updates faster than // requested if other applications are requesting location at a faster interval. mLocationRequest.setInterval (10000); // Sets the fastest rate for active location updates. This interval is exact, and your // application will never receive updates faster than this value. mLocationRequest.setFastestInterval (5000); mLocationRequest.setPriority(LocationRequest.PRIORITY_HIGH_ACCURACY); } @Override public void onStart () { super. onStart (); mGoogleApiClient.connect (); } @Override public void onStop () { super. onStop (); mGoogleApiClient. disconnect (); } @Override public void onResume () { super. onResume (); // Within {@code onPause ()}, we pause location updates, but leave the // connection to GoogleApiClient intact. Here, we resume receiving // location updates if the user has requested them. if (mGoogleApiClient.isConnected ()) { startLocationUpdates (); } } @Override protected void onPause () { super. onPause (); // Stop location updates to save battery, but don’t disconnect the GoogleApiClient object. if (mGoogleApiClient.isConnected ()) { stopLocationUpdates (); } } protected void startLocationUpdates () { if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED && ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { return; } LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.requestLocationUpdates ( mGoogleApiClient, mLocationRequest, this); } /** * Removes location updates from the FusedLocationApi. */ protected void stopLocationUpdates () { // It is a good practice to remove location requests when the activity is in a paused or // stopped state. Doing so helps battery performance and is especially // recommended in applications that request frequent location updates. // The final argument to {@code requestLocationUpdates ()} is a LocationListener // (http://developer.android.com/reference/com/google/android/gms/location/LocationListener.html). LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.removeLocationUpdates (mGoogleApiClient, this); } @Override public void onConnected (@Nullable Bundle bundle) { if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED && ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission (this, android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION)!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { // TODO: Consider calling // ActivityCompat#requestPermissions // here to request the missing permissions, and then overriding // public void onRequestPermissionsResult (int requestCode, String [] permissions, // int [] grantResults) // to handle the case where the user grants the permission. See the documentation // for ActivityCompat#requestPermissions for more details. return; } Location mLastLocation = LocationServices.FusedLocationApi.getLastLocation (mGoogleApiClient); if (mLastLocation!= null) { mCurrentLocation = mLastLocation; String lat = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLatitude ()); String lon = String.valueOf(mCurrentLocation.getLongitude ()); Toast toast = Toast.makeText (this, «Last location» + lat + " " + lon, Toast. LENGTH_LONG); toast.show (); mWorld.clearWorld (); mWorld = CustomWorldHelper.generateObjects (this, mCurrentLocation); mBeyondarFragment.setWorld (mWorld); } else {

