 Полная версия
Полная версияHardy Perennials and Old Fashioned Flowers
The flowers are ½in. to ¾in. across, produced terminally and singly on short procumbent stems. They are of a bright purple colour; petals ovate; the longish stamens carry bold anthers furnished with dark orange-coloured pollen, which forms a pretty feature. The leaves are small, crowded, opposite, ovate, entire, leathery, fringed or ciliated, and retuse. A peculiar feature about this species is the pore at the blunt apex of each leaf. The habit is prostrate; the stems being long, tufted, or pendulous, according to the situation; the flower shoots are upright, on which the leaves are more remote. Under cultivation newly planted roots will be found not only to flower sparingly, but the blooms will be rather small until the plant grows large and strong.
On rockwork, with its roots near or between large stones, is in every way the best place for it; it however, thrives in the borders. The soil is not of much importance, but without doubt it does best in a compost of the nature of that of its wild homes. The humus and grit may be represented by sand and small stones, and peat or leaf soil, all mixed with loam. This, let me here state, will be found generally the right stuff for alpines and rockery plants. This plant is useful as a spring bedder, or for carpeting bare places; and any conspicuous part of the garden needing bright objects during March and April should give room largely for this cheerful subject. The bloom is very lasting; no storm seems to do it any hurt, and in every way it is reliable. It may be readily propagated by divisions. The procumbent stems will, in strong patches, be found to supply rootlets in abundance. These may be transplanted at almost any time of the year.
Flowering period, March and April.
S. opp. alba is a white flowered variety of the above. It is not found wild. Other dissimilarities are the smaller parts throughout the whole plant, and the less straggling habit. The white petals show up the dark orange anthers finely. There are other varieties of the above type, but their points of difference are so slight as not to need description for garden uses. It may, however, be useful to give their names: S. opp. major, S. opp. pyrenaica, S. opp. retusa, S. opp. pallida. All the above varieties may be grown like the common form; their uses, propagation, and blooming period are the same, with the exception of pyrenaica, which not only flowers a little later, but is less rampant, and not nearly so easy to propagate. I have imagined that a little limestone has helped it, bits of which are placed over its roots.
Saxifraga Paradoxa
Paradoxical Saxifrage; Nat. Ord. Saxifragaceæ
Fig. 89. Saxifraga Paradoxa.
(Two-thirds natural size.)
One of the less known and, perhaps, somewhat rare saxifrages; it is a curious, distinct, and beautiful form, being of that class which the lover of the ornamental kinds most admires, for not only is it attractive all the year round, but additionally so when there cannot be seen any part of a growing or decaying flower stem upon it, and when its silvery, but lax rosettes, with their encrustments and glistening leaf dots, are perfectly matured, which is the case during mid-winter. I fear the illustration (Fig. 89), can give but a poor idea of the pleasing silvery-grey colour, which, when the specimen is dry, overlays foliage of a dark and glossy green, to say nothing of the numerous and regular spots which so charmingly enliven the specimens. I am unable to learn to what species it is most nearly related; its name, which doubtless has reference to its peculiar form and habit, would seem to isolate it even from its parents, if such are known; it, however, belongs to that section having thick leathery leaves, ligulate, encrusted, arranged in rosette form, and having excavated dots. Saxifraga lingulata, S. crustata, S. Australis, S. longifolia, and S. carinthiaca belong to the same section; but S. paradoxa differs much in general appearance from them all, and remarkably so in one or two respects, as, indeed, it does from the whole genus, thus justifying its name. The uneven length and arrangement of leaves, the casting off of the encrustments as a skin or in flakes, exposing to view a finely-polished surface, and the general web-like appearance of the tufts, are all peculiar to it. Of all the varieties of its section it most resembles S. carinthiaca and S. Australis; these forms, however, grow in compact rosette form, having leaves of more even size and shape. Our subject is irregular in every way, many of the leaves pushing out to double the length of others, and becoming attenuated at their junction, or club-shaped.
Its flowers are insignificant and similar to those of S. Aizoon, but more dwarf in the stem. The leaves are ½in. to 3in. long, very narrow and tongue-shaped, sometimes obtuse and club-shaped; stout, dark green, with a greyish crust-like covering, and deeply dotted with bright spots. The leaves are arranged in lax rosettes and are reflexed or pressed flat to the earth nearly all their length. The habit is very pretty in established and fair-sized specimens, which accommodate themselves to the form of surface, and the longer or erratic leaves become so interlaced with the other parts as to appear woven; this habit and the bright bead-like dots go to make the plant more than ordinarily attractive. It should be in every collection of choice Saxifrages; it is charming as a pot specimen, plunged and grown out of doors the year round.
On rockwork it should have a place, too, among the gems, being a neat and slow grower; its position should be near dark-coloured stones, where it will prove most telling. In damp weather its silvery parts are obliterated, but a breeze of half-an-hour or a beam of sunshine soon brings it into full beauty again. Gritty peat and a little loam suits it well; I have it doing nicely in ordinary garden soil; but if the more carefully prepared composts are employed, the results well repay the pains so taken. Its propagation is easily carried out by root divisions; early spring is a good time for the operation.
Flowering period, May and June.
Saxifraga Pectinata
Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis belongs to the encrusted section, being most distinctly toothed; from this it takes its name; the teeth are large for such small leaves. Specimens of this Saxifrage, though small, are exceedingly pretty. Excepting when there is fog or rain, it is nearly white; and the rosettes, of various sizes, from ¼in. to 1in. across, are not only neat in themselves, but are densely and pleasingly arranged in a hard flat mass. It is never more beautiful, not even in May and June, when it flowers, than in November, when the growth is both complete and ripened, and the scaly substance which is spread over the leaves and the silvery teeth combine to render it attractive.
The flowers are of the usual form, and are produced on stems 4in. to 6in. high; they are white. The leaves seldom exceed ½in. in length and 1/8in. in width; they are spathulate in form, stout, and rigid. The rosettes are somewhat flattened and numerous, and give the idea of greenish-white flowers.
S. p. hybrida is a variety of the foregoing species, and without pretending to say what the type has been crossed with to produce this handsome form, I may, for the purpose of conveying an idea of what it is like, say that it approaches S. aizoon, which also flowers in May and June. In all its parts it is larger than the type; the leaves are greener and more strap-shaped, and are more erect, but not so rigid; the habit, too, differs—it forms more rounded tufts. In all these respects it will be seen to resemble S. aizoon. It is a lovely form; the sparkling teeth are relieved by the fine dark green ground of the foliage.
These comb-leaved Saxifrages belong to the more neat and effective rock plants; the type, at least, is of alpine origin, and under cultivation it seems most happy amongst the stones. I have grown these kinds as pot specimens, on nearly flat beds, and as edging plants; and in every position they prove attractive. It is very strange that such pretty forms are not more generally seen in gardens; they will grow well on walls and the tops of outhouses, and are good subjects for town gardens. Any kind of sandy soil will do for them; that of a vegetable character is, however, the best; they may be planted with choicer things, for, unlike many of the genus, they are not rampant growers. Practically, they need no propagating; for as the specimens spread they make new roots, and at any time one or half a dozen rosettes may be slipped off for planting elsewhere. It is better, though, to avoid this with small plants, as their full beauty is not realised until they become of considerable size.
Flowering period, May and June.
Saxifraga Peltata
Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæA new species to English gardens, hardy, herbaceous, and perennial, imported from North America; it is a truly noble plant. The illustration (Fig. 90) will convey some idea of its fine form, but the reader must rely on the description for its size when fully developed. When the flowers of this Saxifrage are in their best form, the noble foliage is scarcely half developed; a drawing, therefore (though it could hardly be made at a stage when the plant is more interesting), must necessarily fail, in this case, to give any more than an approximate idea of the parts undeveloped. Not only is this the largest species of the extensive genus at present grown in this country, but its form is both distinct and noble.

Fig. 90. Saxifraga Peltata.
(1, Single blossom, natural size.)
The flowers are produced on stems 18in. high and ¾in. thick at the base, being covered with long stiff white hairs, which are very conspicuous on the reddish stems. The flowers are similar to those of most of the genus, as may be seen by the one given in the drawing; they are arranged in massive heads, 3in. to 6in. in diameter, and rose-coloured. The leaves at the flowering time are 6in. or 9in. across, having stout, round, ruddy stems, 8in. long, covered with stiff hairs; they form a junction with the leaves in an unusual way, viz., near the centre, whence the specific name peltata, or umbrella shape; but the form of the leaves at the flowering period, which is funnel-shape, is, a little later on, reversed, the edges bending downwards. The younger leaves are folded and hooked downward, having the appearance of stout fern fronds just out of the ground, and their stalks are much contorted. The more advanced leaves are seen to be seven-cut, each lobe divided and sub-divided by cuts less deep, the whole leaf being richly toothed and veined. The under side is covered with hairs, the upper surface being smooth, shining, and of a pleasing bronze-green colour. Later, the foliage in every way increases very much in size, reaching a height of 2ft., and each leaf measuring nearly a foot across. The root or rhizoma is horizontal, progressive, jointed, and fibrous at the joints, and nearly 2in. in diameter; it may be clearly traced on the surface, but the fibrous parts go very deep.
It is said to be a bog subject; fortunately, however, this fine plant may be grown otherwise than in a bog, but it should not want for depth of rich soil. This I believe to be a more important condition than a boggy situation, inasmuch as I have grown my specimen for three years on the top of a dry mound; but the soil is good rich loam, and fully 5ft. deep; and to show that this strong-growing subject needs a good depth of soil, I may mention that I had occasion to dig up a piece, when it was found, for the operation, to require both the strength and tools that trees demand, the fibrous parts being deep and tough. When fairly established it makes rapid growth, and when in full leaf it proves very effective. Its propagation is easy with healthy plants; a length of the creeping root, with a crown to it, should be cut from the parent stock just before growth commences in early March. If planted as indicated in the foregoing remarks, and kept shaded with a leafy branch for a month or two, there need not be any fear about young plants becoming established the first season.
Flowering period, June.
Saxifraga Purpurascens
Large-leaved Purple Saxifraga, Megasea section; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæA rare plant of great beauty. It is figured here without flowers, as I consider it in finer form then than when in bloom. Fine as its flowers are, much resembling those of S. cordifolia and S. crassifolia (also of the Megasea section); the brightness and colouring of its leaves in autumn are such as to render it distinct from all the other species. I need only ask the reader to note the fine foliage indicated in the cut (Fig. 91), and inform him that in the autumn it turns to a glossy vermilion colour, and I think he will admit that it will not come far short in beauty of any flower. The species is a recent introduction from the Himalayas, and in this climate proves all but evergreen (if tinted foliage can be so called) and hardy. The latter quality has been doubted by some, but by others re-asserted. My present specimen was planted in the open garden in the spring of 1880, since which time it has withstood 22deg. of frost.
The flowers are produced on stout stems, 8in. high, arranged in branched heads, of a rose or rosy-purple colour, and bell-shaped. They are, however, soon damaged by unfavourable weather, and there is little about the plant at that period to render it more attractive than its fellows; its finer qualities are developed as more genial weather prevails. When the stout foliage grows glossy, waved, and of a deep clear green colour, the edges of the leaves become lined with red as if hemmed with red silk; the leaves also have the edges irregular in form, the outline broadly oval, 4in. to 6in. long, and they are veined and slightly wrinkled; during the autumn a yellow tint starts from the edge, and in time becomes a vermilion, which is all the more effective from the leaf being of leather-like substance.

Fig. 91. Saxifraga Purpurascens.
(One-third natural size.)
It enjoys a deep rich loam; and, evidently, to place its roots in contact with pieces of limestone is beneficial. Rare as the plant is, this is all that I do for it, and not only does it remain healthy, but it has increased greatly in size during the last year. I have not as yet tried to propagate it, but so far as I can judge there will be no difficulty in forming young stock by root division. It has hitherto enjoyed a happy immunity from all garden pests, not excepting slugs.
Flowering period, April to June.
Saxifraga Pyramidalis
Pyramidal Saxifraga; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis is a very handsome form or variety of S. Cotyledon, and belongs to the alpine regions of Europe. As a decorative subject for our gardens, it is highly and deservedly esteemed; its attractiveness consists more in the numbers and arrangement of the flowers than in any beauty which belongs to them individually, though they are not devoid of that quality.
Of the many hundreds of species and varieties of Saxifrages which bloom during the month of June, this is one of the most distinct and useful as a decorative flower, and where the Saxifrages are grown in large collections, as they often are, giving more than an ordinary amount of pleasure compared with collections of other genera, the kind now under consideration always asserts itself as one of the first order of merit. Not only in its blooming state, but all the year round, it is very effective and striking; it is a free grower, having handsome, large rosetted foliage.
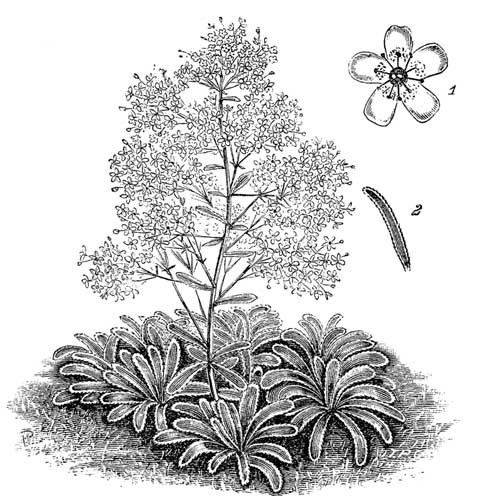
Fig. 92. Saxifraga Pyramidalis.
(One-eighth natural size; 1, single blossom, natural size; 2, leaf, one-eighth natural size)
The flowers, as will be seen by the one given, natural size, in the illustration (Fig. 92), are of the common Saxifrage form, but rather more highly coloured in the central markings than the general run. They are produced on stout stems, 2ft. high, well and evenly branched in the form of a pyramid, whence the specific name. Each flower will be ½in. or more across; they are very numerous, and, partly from the fact that they remain perfect for a very long while, and partly because of the habit of the plant being to open all its flowers about or near the same time, the large panicle of bloom is very fine. The leaves, as already hinted, are formed into lax rosettes, which are 5in. to 7in. across; they are strap-shaped, narrowing slightly at the connection, half an inch wide, the outer ones being reflexed; the edges are finely serrated, and irregularly lined with a silver colouring.
This is a capital plant for rockwork, where it shows itself to much advantage; but specimens are much finer grown in beds or borders, where the moisture and temperature at the roots are likely to be more equable; besides, I find that, owing to its small quantity of roots, all of which are very near the surface, when grown on rockwork they may often be seen bare on inclined surfaces, and the weight of the flowers drags them entirely out of the soil on one side. They may be planted as an edging to a shrubbery, in bold groups, or as ordinary border flowers. So useful has this variety been found by professional gardeners that it is now largely grown in pots in single rosettes, which, after becoming well established, send up their rich plumes of blossom, all the finer for having been kept clean under glass. So grown, nothing can better repay the small amount of trouble which they give in order to place them in the conservatory as showy specimens; all they require being a 4in. pot, well drained, a compost of half-rotted leaves, and fat loam and sand. Put in one rooted offset any time from June to the end of July, the earlier the better; plunge the pot to its rim in sand or ashes until next spring, when it may be taken under glass if desired. To have fine flowers, the offsets should be pinched off as they appear. I may also mention that a somewhat shady situation has proved conducive to large and better coloured flowers; between irises 4ft. high and shrubs 6ft. high, the opening being not more than 3ft., running north and south. The specimen from which the drawing is taken was grown along with many others. A baking or dry treatment is often not only given to plants of this genus, but believed to be of advantage to them; it may be to some, but there are exceptions, and this is one without doubt. All the sections of Saxifraga to which it belongs are fond of good loam, well enriched. It is propagated from offsets taken as soon as they are from an inch to two inches across; they may either be put into nursery beds or be planted in their blooming quarters.
Flowering period, June and July.
Saxifraga Rocheliana
Rochel's Saxifrage; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæAnother hardy evergreen species, distinct in form, foliage and flowers, and a native of the alpine regions of central Europe; it nevertheless thrives well in our climate with ordinary care. Its foliage takes the form of miniature rosettes, which are closely packed; the tiny leaves are distinctly and regularly dotted; and present a frosted appearance.
The flowers are unimportant, though they form an interesting feature of such a choice and somewhat rare plant; they are small, white, and produced on stems 3in. to 4in. high, which are thick and curiously furnished with leaves. During summer this species has a very bright silvery appearance, as if laid on in patches.
Similar treatment is required for this as for S. Burseriana, but it will be found much more difficult to propagate, as its roots are of the tap kind, and are more sparingly produced, while its seed seldom ripens, I believe, in this climate. To increase it, the better plan is to prepare the old plant by keeping it well earthed up, and so encouraging new roots; after a year's patience it may be divided in April. The small pieces should be secured by stones or verbena pins, and a supply of pebbles placed around them will keep them cool and moist during summer.
Flowering period, March and April.
Saxifraga Umbrosa
London Pride; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis common flower is well known, and is only mentioned here as the typical form, and by way of introducing a beautiful variety called S. u. variegata, broad cushions of which, from their verdant condition, good habit, and pleasing variations of leaf colour, are amongst the more attractive objects of the garden in January. It hardly need be said that the plant is not valued for its flowers, which are similar to those of the parent form and borne at a corresponding date. The leaves, however, are much less in size and more flatly arranged in rosette form, they are also recurved at the edges. The markings are of two colours, creamy-white and pink, and there are many shades of green. The forms of the markings are most irregular, as striped, flecked, marbled, dotted, and edged; the various shades of green blended with pink and white, although figured on one of the commonest plants we know, render such plant worthy of a place in every garden, and more especially on rockwork.
It has this drawback—it is not constant. In some gardens the markings die out. This, however, need not be, for a rather dry situation and rich soil will produce rosettes of large size and good figuring. Still, there will be fully half of the rosettes entirely green in a large patch; this is more desirable than otherwise. The marked ones have a more starry effect in such a green setting; it is only when all become green that disappointment is felt. Sometimes I have noticed rosettes, about the size of a penny-piece, all one colour—creamy-white—which, when cut from the plant, very much resembled a carnation. Such abnormal forms are of no moment to the botanist, but if nine out of every ten persons who see this plant are interested, not to say pleased with it, it ought not to be entirely neglected. It is most effective in patches 1ft. to 2ft. broad. In propagating it the more finely marked pieces only should be taken.
Flowering period, May to July.
Saxifraga Wallacei
Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæA hardy perennial hybrid variety, of first-class merit. Its loose and spreading panicles of large pure white flowers are something better than the ordinary run of bloom belonging to this extensive genus; it is said to be the offspring of species of the mossy section; but there is certainly a great likeness about its foliage to some of the horny section, such as S. cornutum or S. pentadactylis, or even the handsome S. geranioides. It would, however, be hard to say what it is from; but in it we have not only a showy but most useful variety (see Fig. 93). It has deservedly grown into great favour, though known to amateurs but for three years. It begins to flower in April, but in May it is in its best form, being covered with a rich mass of bloom from the foliage to the height of a foot.
The flowers, as before stated, are of a pure white—an unusual colour amongst the genus; they are bell-shaped but erect, the ovate petals reverse. Well-grown specimens with me have flowers quite an inch across. The individual blooms last more than a week, and the succession is well maintained during summer. The panicles are leafy, having small entire leaves, and others once and twice-cut. The stems of the present season's growth are stout, semi-transparent, and ruddy; the leaves are palmate, slender at the bottom, mostly five-fingered, fleshy, and covered with long silky hairs which stand well off; the fine apple-green foliage is shown to great advantage by the ruddy stems.
This plant may be grown in pots or borders, as edging, or on rockwork, and in any kind of soil; but to have fine specimens and large flowers it should be planted in calcareous loam, and be top dressed in early spring with well rotted manure. I have it as an edging to a small bed of roses; the position is bleak, but the soil is good; it furnishes large quantities of cut bloom, and otherwise, from its rich hawthorn-like scent, it proves a great treat. So freely is its handsome foliage produced that it, too, may be cut in quantities for table decoration. If the flowers, or some of them, be left on, the tufts will form a pretty setting for a few other small flowers of decided colours.

