 Полная версия
Полная версияHardy Perennials and Old Fashioned Flowers
Cultivation and flowering period, as given under Heuchera.
Heuchera Metallica
Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis was presented to me in 1881 by a lady, who informed me that it was introduced by the late Miss Hope. It is a beautiful plant; the hues somewhat justify the name, but to the touch the leaves are more like a soft fabric, as cloth or velvet. The flowers are of no value, but the foliage is bloom of no mean order, so much so, that everyone stops to admire this handsome plant.
Cultivation and flowering period, as given under Heuchera.
Heuchera Micrantha
Small-flowered Heuchera; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæFrom Columbia. Flowers a yellowish-green; leaves nearly round, bluntly lobed, crenate or round toothed, the teeth horned or pointed; the colour is inclined to auburn during autumn, but it varies, and for a botanical description it would be hard to state a particular colour. The gardener, however, will find in this a most useful plant, where different forms and tints of foliage are desirable. Into the sub-tropical garden it may be introduced with good effect. I may add that the leaf stalks are 9in. to 12in. long, also of a rich brown colour, and the leaves are 3in. to 5in. across.
Cultivation and flowering period, as described under Heuchera.
Heuchera Purpurea
Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis seems to be a less known or newer variety. If the name has reference to the colour of the foliage, it is not inappropriate. The bold leaves are a dark green, shading to a bronze, then a purple, the whole having a soft downy effect. It is a charming kind.
Cultivation and flowering period, the same as for the Heuchera.
Heuchera Ribifolia
Currant-leaved Heuchera; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis is another dwarf kind, producing such leaves as the name denotes. Of this species the only useful feature for a garden seems to be its habit of neatly carpeting the ground under deciduous trees. It has also a remarkably fresh appearance during winter.
Cultivation and flowering period, as for other Heucheras.
Heuchera Richardsoni
Richardson's Heuchera; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæA taller variety than H. Drummondi. The most striking distinctions are the pale green colour of the young leaves contrasting with the bronzed appearance of the older ones, and the larger size of its flowers, which, however, are green.
Cultivation and flowering period, as for other species.
Houstonia Cœrulea
Bluets; Nat. Ord. Gentianaceæ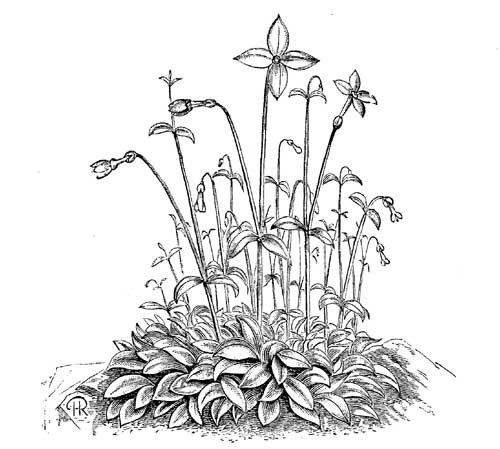
Fig. 52. Houstonia Cœrulea.
(Natural size.)
Hardy and evergreen. This pretty little shining plant never exceeds a height of 3in. Like most species of this order, both flowers and foliage have much substance and endure for a long time in perfection, but its neat form and bright parts most commend it—it almost sparkles in both leaf and flower. This species, as implied by the specific name, bears a blue flower, but there is a variety (H. c. alba or H. albiflora) which bears white flowers, from a specimen of which the illustration (Fig. 52) is drawn, and, as the colour of the flower is the only dissimilarity, a description of the typical form will in all other respects apply to both.
The flowers, which are produced singly on slender stems 2in. high, are composed of a four-toothed calyx; corolla, four petals, or four-toothed and funnel-shaped; when fully expanded each flower is ½in. across, and shows a distinct yellow eye. The leaves of the root are spathulate, those of the stems opposite and lanceolate; all the parts are shown of the natural size in the illustration.
All the known Houstonias are natives of North America; still, our winters seem to kill strong plants. From an impression that the plants were destroyed by insects amongst their roots and foliage, I had several tufts lifted, well shaken out, and divided in the autumn; they were replanted in leaf soil and sand and kept rather moist. When planting them, all amongst the roots was thickly strewn with dry silver sand, so as to leave no space for the lodgment of vermin; the results were fine, fresh, green tufts throughout the following winter, which, however, was not severe; still, the plants not so treated dwindled and were unhealthy, whereas the others were finely in bloom, the subject of the drawing being one of them. These minute plants do well and look well wedged between large stones on rockwork, where they flower nearly all the year round; they also form pretty pot specimens under cold frame treatment; and they may be used with good effect for surfacing the pots in which other hardy but tall and bare stemmed things—such as lilies—are grown.
The mode of propagation has been indicated by the above autumnal treatment.
Flowering period, April to July.
Hutchinsia Alpina
Syn. Lepidium Alpinum; Nat. Ord. CruciferæAn alpine species, from South Europe, which may be said to be evergreen in this climate, and, according to my experience of it, flowering throughout the year. Though found in some gardens to be difficult to establish, when it finds a suitable home it becomes a pretty addition.
This alpine seldom exceeds 2in. in height. The flowers are a glistening white and very small, produced in numerous heads, and they are very enduring; the calyx is concave and falls off; the four petals are inversely ovate; the little leaves are deeply lobed, of a pale shining green colour, with plenty of substance; its habit is spreading or creeping. Neither slugs nor any other pests seem to meddle with it. It may be transplanted at any time, and the mode of propagation may be gathered from the following remarks.
Probably because its name implies its alpine character, some may be misled to plant it on rockwork; whether that be so or not, I so tried it, and found it would not grow in such a situation. A bed of dwarf and moisture-loving subjects was being planted, in which a bit of this Hutchinsia was dibbled, and it found a home in the moist vegetable soil. For two or three years I do not remember to have seen it, or the seedlings, without flowers; its pretty, dwarf, rue-like foliage grew so thickly that it threatened to kill the edging of gentianella and such things as Polemonium variegatum, the double cuckoo-flower, and the little Armeria setacea; it also filled the walks, and its long wiry roots have been eradicated with difficulty. From this it will be seen how much depends, with some plants, on the position in which they are placed.
Hydrangea Paniculata Grandiflora
Large-panicled Hydrangea; Nat. Ord. SaxifragaceæThis dwarf shrub is perfectly hardy and deciduous; it comes from Japan, and is one of the best hardy things I have come across for some time. It is quite a new introduction, and has many fine qualities; the fact of its producing immense clusters of white flowers, 12in. long and 12in. in circumference, as well-established plants, is enough to induce its extended cultivation; but when it is stated that its clusters are numerous and durable, that the shrub begins to flower in summer and continues in great beauty until damaged by frosts, it will doubtless be recorded on the lists of desiderata of those who do not possess it. The usefulness of such a subject is notable not only to the gardener who has a keen eye to artistic effect, but to the lover of showy flowers (see Fig. 53).
The flowers are male and female kinds, and, as is usual with the genus, the fruitful ones are interspersed with unfruitful, being shorter in the stalks and nearly covered over by the latter, which are much larger; in fact, they are not the true flowers from a botanist's point of view, but with the florist it is exactly the opposite; their colour is white, more or less tinted with pink, which, if the autumn season proves fine and dry, becomes purple. As the name denotes, the bloom is arranged in massive panicles, pyramidal form, 6in. to 12in. long, and 4in. to 8in. in diameter. They slightly bend with the great weight, but are otherwise well supported by the woody stems. The latter are somewhat short, seeing they carry such large clusters. The leaves are oval, subcordate (varying), distinctly ribbed, and finely toothed, also varying much in size. The habit of the shrub is much branched, of strong growth, and very floriferous. The flowering shoots issue from the hard wood of the previous season's growth. In the shrubbery it is very attractive, its flowers out-numbering, out-measuring, and out-lasting most of its neighbours. Kept dwarf, what a grand bedder it would make! Grown in pots it is a first-class indoor subject. It has that rare quality, even when in small pots, of being adapted for the company of large ferns, palms, &c., from the great size of its panicles, and I need scarcely say that for cutting purposes it is valuable, more especially in decorations which are not closely viewed.
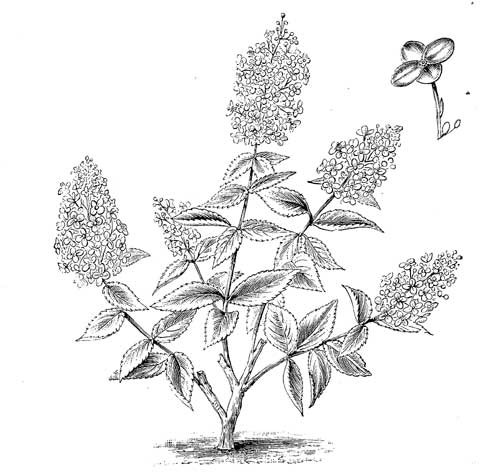
Fig. 53. Hydrangea Paniculata Grandiflora.
(One-tenth natural size; blossom, natural size.)
The culture of this shrub is very simple; it does best in rich loam. The situation should be sunny, that it may well ripen its wood. In order to have clusters of large size, it should be closely pruned, like roses, by which treatment the bush may also be kept in the desired form. Its propagation is by cuttings; they should be of fairly well-ripened wood of the last season's growth. The degree of ripeness, like that of such things as roses and fuchsias, may vary according to the method by which the cuttings are to be treated. Half-ripened shoots will root well in a little heat; the harder wood will root equally well, but more slowly, in the open in sandy loam.
Flowering period, July to end of September.
Hypericum Calycinum
Large-calyxed St. John's Wort, or Rose of Sharon; Nat. Ord. HypericaceæA very ornamental deciduous shrub, but often green throughout the winter. This I claim the privilege of introducing amongst herbaceous perennials; it is a well-known and favourite "old-fashioned" flower, in fact, a native of Ireland. The old name for it was "Cup St. John's Wort." In July it is in splendid form, and, familiar as we are with it, it never fails to win admiration. How charming are its large, shining, golden blossoms, nestling amongst the bright but glaucous foliage! the bundled tassels composed of numerous filamentary stamens glistening like threads of gold; and though often seen one can never tire of it. As a flower, it is distinct in form, showy, and richly effective.
It grows to the height of 1ft. or 18in.; the flowers are 4in. across, of a rich golden-yellow colour, and produced singly on the very leafy stems which, at the base or at their more woody parts, are square, the upper parts being nearly round. Short flower-stalks issue from the side and near the top, a small new growth being produced in juxtaposition with the blossom, the said growth being composed of half-a-dozen or so smaller-sized leaves of a pale apple-green, charmingly suffused with a glaucous hue. The calyx of five sepals is very large, whence the specific name, and each sepal is nearly round and cupped, whence the old common name, "Cup St. John's Wort"; the five petals are 2in. long and widely apart; stamens very numerous, long, thready, and arranged in tufts. These are very beautiful, and form the most conspicuous part of the flower; like the other seed organs, and also the petals, they are of a rich, glistening, yellow colour. The leaves are closely arranged in pairs, opposite, and nearly sessile; they are 2in. to 3in. long, and about 1in. broad, oval-oblong, blunt, smooth, and leathery. When young, they are as above described, but when older, they are of a dark, shining green colour, and somewhat reflexed. The under sides are finely reticulated or veined, and sometimes the foliage is spotted with brown. The habit of the shrub is neat, the short stems being numerous and semi-prostrate, forming dense, even masses of verdant foliage.
Such a subject as this cannot be too highly esteemed on the score of the merits already set forth; but there are other good qualities which I will briefly refer to presently. There can be little doubt that the fine parts and many uses, decorative and otherwise, of most of the "old-fashioned" flowers have much to do with the high and continued esteem in which they are held. Not one of the least recommendations of this St. John's Wort is that it can be grown with great success under the shade of trees. It is one of the very few subjects that will bloom freely in such situations. It is, therefore, very valuable; besides, as regards its period of flowering, it comes in nicely after the vincas are over. These two genera are, perhaps, the best hardy flowering shrubs we possess for planting in the shade of trees. I scarcely need add that for more open situations, as rockwork and borders, it is in every way suitable.
To the lover of cut flowers this must prove one of the most satisfactory, not only because of its beauty, but also because they are produced for fully three months—into September—and they are sweetly scented, like wallflowers. A flower-topped stem forms a perfect and unique decoration for a lady's hair; sprays in small vases are exquisite, whilst a bowlful for the table (without any other flower) is very fine indeed—let the reader try these simple styles of decoration. Also, mixed with other flowers, it is one of the most telling; none of the yellow exotics can excel it. It is now before me, with a few sprays of the pink sweet pea and a bold spike of the white variety of goat's-rue; the blend is both delicate and effective. As a cut flower it can hardly be misused, provided it is not crowded.
Its culture is simple. Any sort of garden soil suits it, but it prefers a sandy loam. A winter top dressing of stable litter will help to produce greater luxuriance and a longer succession of flowers. It quickly and broadly propagates itself by means of its creeping roots; these may be at any time chopped off, with a sharp spade, in strong pieces, which, if planted in deeply-dug loam, will make blooming specimens for the following season.
Flowering period, July to September.
Iberis Correæfolia
Nat. Ord. CruciferæThis is a hybrid and much improved variety of the well-known evergreen and shrubby Candytuft, often called "Everlasting Candytuft." A more pronounced remove from its parents could hardly be found in any plant or shrub than is this. There are evident improvements in colour, size, and habit, both in foliage and flowers. It is also a robust grower and perfectly hardy, in these respects being very different from I. Gibraltarica. None of the shrubby Candytufts can compare with this for usefulness and beauty; it comes into flower in May, and is in its greatest beauty in early June. It remains in fine form for fully four weeks. At first the flowers seem small, but later they form broad masses of dazzling whiteness, the corymbs being the size of a crown piece. Not only is this wholly distinct from its relatives, but it is one of the most useful flowers and evergreen shrubs which can be introduced to a garden. It cannot be planted wrong as regards either soil or situation. It forms a rich surfacing subject, all the year round, to other tall plants, as lilies, &c. It looks well as a front specimen in the shrubbery, makes an effective and neat appearance at the angles of walks, or as an edging it may be cut and trimmed as a substitute for a grass verge; it thrives on sunny or almost sunless outhouse tops, and on rockwork it is superb; moreover, it grows fairly well in reeky towns, and though its white flowers may be soiled the day they open, its bright green leaves and dense habit render it a pleasing object.
The flowers are arranged in flat heads at first, but as the stems become elongated and the succession of buds open, a long round cluster is formed by the old flowers remaining (as they do for weeks), such heads or spikes sometimes being 3in. long. There is much substance in the petals, which causes them to glisten in strong light; the flower stems are produced 5in. or 6in. above the foliage, their total height rarely exceeding a foot. The leaves are numerous, of a dark shining green colour; in length 1½in., and over ¼in. broad near the ends; their shape is spathulate, obtuse, entire, and smooth; the new set of foliage contrasts pleasingly with the old, and its growth is completed during the flowering period; the woody and slender branches are numerous and procumbent.
Besides the positions already mentioned, in which this shrub may usefully be planted, there is none more so, perhaps, than that of rough or unsightly corners, where, if it is provided with a little loam, it will soon adapt its form to the surroundings. The flowers in a cut state are not only sweet-smelling, but very useful where white bloom is needed in quantity, as for church decorations. I. correæfolia can scarcely be said to need cultural treatment, but it is useful to bear in mind that it may be much more finely bloomed if generously treated, which simply consists in nothing more than giving it a sunny place and sandy loam, well enriched with old manure. Specimens so treated, which were cuttings only two years ago, are now 2ft. in diameter, and covered densely with large flowers; and how lovely some of the pretty weeds which have sprung up amongst the bushes, and mingle their flowers among the masses of white, appear—such as Spring Beauty (Claytonia), pink flowers; the Maiden Pink (Dianthus deltoides), rose; Self-heal (Prunella pyrenaica), purple; and the forget-me-nots! This comparatively new Candytuft is as easily increased as grown, by either layers or cuttings; the latter may be put in almost any time, early spring being the best; if put in in June, no better quarters can be given than under the shade of shrubs, where the soil is sandy loam.
Flowering period, middle of May to middle of June.
Iris Fœtidissima
Gladdon, Gladwin, or Spurge-wort; Nat. Ord. IridaceæA British species, occurring largely in some parts, in shady woods and swampy places near the sea. It is evergreen and of a pleasing form throughout the year. Its flowers are of a dull colour, and not likely to be much esteemed, more especially when in midsummer there are so many beautiful kinds around; still, it merits a place in our gardens. Its handsome berry-like seeds, which are so attractively conspicuous in December, are much more desirable than its flowers, ready as they are for our use at Christmas time.
It grows 2 ft. high, and is a water-loving plant, but may be easily grown in the more moist parts of the garden. The large pod is three-cornered; the husks having turned brown, become divided, and expose to view the large, orange-coloured seeds, which, later, turn to a reddish-brown. They are held in the husks for many weeks and strong winds do not displace them; they are very effective amongst the dark green foliage, and may be cut if desired, as they often are, for indoor decoration. They may be used in a hundred different ways, but never do they show to more advantage than when cut with long stems and placed in a vase with some of their own dark green sword-shaped leaves; these last-named, by the way, may be appropriated throughout the winter as a dressing for other flowers. There need be no difficulty in growing this species, for if the soil is not naturally moist in summer, a thick dressing of rotten stable manure will meet the case. As a matter of fact, my specimen is grown in a bed fully exposed to the sun; the soil is well drained, and stone-crops are grown in the next bed to it; no water is ever given to established plants, and still the Gladwin is well fruited; the soil is deeply tilled, and there is a thick covering of manure. It is easily propagated by division of the roots in autumn or early spring.
Flowering period, June to August.
Isopyrum Gracilis
Slender Isopyrum; Nat. Ord. RanunculaceæThis is a hardy herbaceous plant, of great beauty. The flowers are not showy, but their great numbers and arrangement render them of importance in what may be termed a fine-foliaged subject. The Isopyrums are very nearly related to the thalictrums or rues, and this one greatly resembles the maidenhair-like section, one of which it is often taken for. There is, however, an important botanical difference between the two genera: the thalictrums have no calyx, and the Isopyrums have. Still, as the flowers of both are very small, that feature is not very observable. As a decorative plant it may be classed with the maidenhair-like rues, and the illustration may be said to give a fair idea of three or four species.
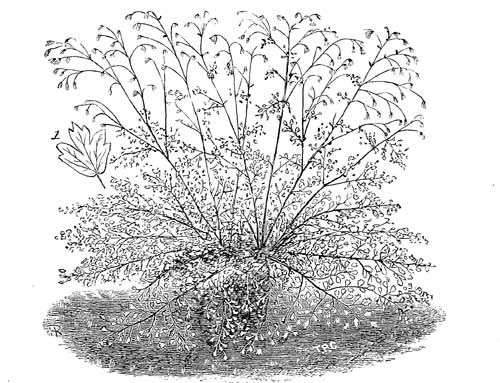
Fig. 54. Isopyrum Gracilis.
(One-eighth natural size; 1, leaflet, full size.)
The Isopyrum under notice grows 12in. or 15in. high, and produces its dark brown flowers on slender, well-branched stems, forming feathery panicles, which have a graceful appearance. The flowers are very small, and composed of a five-cleft calyx, five equal petals, and numerous long, pendent seed-organs; the stems are elegantly furnished with the fine-cut foliage. The leaves are large, but the leaflets small, as may be seen by the one given, full size, in the drawing (Fig. 54), being somewhat cordate, lobed, and dentate; they have hair-like stalks, which add to their elegance of arrangement, and their glaucous colour further enhances their effectiveness.
This light and diffuse subject may be usefully planted to relieve other kinds; in beds or lines it looks well, having a lace-like effect; as a cut flower or spray it nearly equals maidenhair, and for mixing with large flowers, it perhaps excels. Either cut or in the growing state it is very durable. It may be grown in average garden soil, but to have it fine, it should be given vegetable soil and a moist situation, not shaded. It is propagated by seeds or division of the roots in autumn.
Flowering period, July and August.
Jasminum Nudiflorum
Nude-flowered Jasmine; Nat. Ord. Jasminaceæ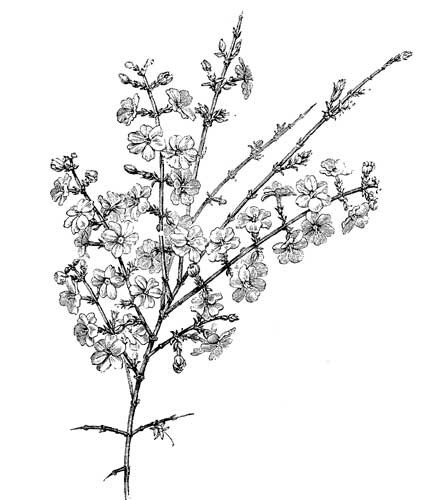
Fig. 55, Jasminum Nudiflorum.
(One-third natural size.)
This was brought to this country from China a little less than forty years ago, and, as proof of its sterling worth, it is already in extensive use. The whole genus is a favourite one; but there is a special and most attractive feature about this species that is sure to render it desirable to all—it flowers freely in midwinter, and it does so in the open garden. Like many of the genus, this species comes from a very warm climate, and for a time it was grown in glasshouses as a tender shrub, where it flowered during the winter months. It is now found to be a perfectly hardy subject, not only withstanding our most trying seasons without the least injury, but also proving true to the month of December as the period when it begins to produce its numerous golden flowers. It is a climbing deciduous shrub, though it has neither the habit of clinging nor twining.
The shrub produces bloom when only 18in. high, but it often grows to as many feet, and even taller. The flowers are borne singly at the joints from which the leaves have fallen, and as the latter were opposite, the blossom appears in pairs on the new twigs. In the bud state they are drooping, and are marked with a bright chestnut tint on the sunny side. The calyx is ample, almost leafy, but these parts are hidden when the flower opens and becomes erect. The form of the Jasmine blossom is well known; in size this one is rather larger than a full-blown violet, and quite as sweetly scented, which is saying very much, but the colour is yellow; the petals are of good substance and shining; the flowers last a long time, even during the roughest weather, they open most during sunshine, but do not wait for it, and they remain open until they fade. The leaves, which are produced in early spring, are very small and ternate; leaflets of unequal size, ovate, downy, and of dark green colour. The wood is very pithy, square, with sharp corners, and having the appearance almost as if winged; the younger branchlets are dark bronze green. The habit of the shrub is rampant, climbing, much branched, and very floriferous. The green leafless sprigs of bloom are very serviceable in a cut state for vase decoration, especially if mixed with dry grasses or well-foliaged flowers; the sweet odour, too, reminds one of spring time. Specimens growing against the house or other walls, either nailed or in a trellis, have a happy effect in winter, from the slender whip-like growths hanging down and being well bloomed. From the dark green colour and great number of branchlets, although leafless, a well-grown example has quite the effect of an evergreen.

