 Полная версия
Полная версияThe Expositor's Bible: The Book of Daniel
502
Dan. v. 28, 31, vi. 8, 12, 15, 28, viii. 20, ix. 1, xi. 1.
503
The composite beast of Rev. xiii. 2 combines leopard, bear, and lion.
504
Comp. viii. 4-8.
505
Battle of the Granicus, b. c. 334; Battle of Issus, 333; Siege of Tyre, 332; Battle of Arbela, 331; Death of Darius, 330. Alexander died b. c. 323.
506
This was the interpretation given by the great father Ephræm Syrus in the first century. Hitzig, Kuenen, and others count from Alexander the Great, and omit Ptolemy Philometor.
507
Dan. xi. 21.
508
Appian, Syr., 45; Liv., xli. 24. The story of his attempt to rob the Temple at Jerusalem, rendered so famous by the great picture of Raphael in the Vatican stanze, is not mentioned by Josephus, but only in 2 Macc. iii. 24-40. In 4 Macc. it is told, without the miracle, of Apollonius. There can be little doubt that something of the kind happened, but it was perhaps due to an imposture of the Jewish high priest.
509
Porphyry interpreted the three kings who succumbed to the little horn to be Ptolemy Philometor, Ptolemy Euergetes II., and Artaxias, King of Armenia. The critics who begin the ten kings with Alexander the Great count Seleucus IV. (Philopator) as one of the three who were supplanted by Antiochus. Von Gutschmid counts as one of the three a younger brother of Demetrius, said to have been murdered by Antiochus (Müller, Fr. Hist. Græc., iv. 558).
510
Comp. viii. 23.
511
Comp. λαλεῖν μέγαλα (Rev. xiii. 5); Hom., Od., xvi. 243.
512
Comp. xi. 36.
513
Jos., B. J., I. i. 2, VI. x. 1. In Antt., XII. v. 3, Josephus says he took Jerusalem by stratagem.
514
Jahn, Hebr. Commonwealth, § xciv.; Ewald, Hist. of Isr., v. 293-300.
515
2 Macc. iv. 9-15: "The priests had no courage to serve any more at the altar, but despising the Temple, and neglecting the sacrifices, hastened to be partakers of the unlawful allowance in the place of exercise, after the game of Discus … not setting by the honours of their fathers, but liking the glory of the Grecians best of all."
516
1 Macc. i. 29-40; 2 Macc. v. 24-26; Jos., Antt., XII. v. 4. Comp. Dan. xi. 30, 31. See Schürer, i. 155 ff.
517
Jerome, Comm. in Dan., viii., ix.; Tac., Hist., v. 8; 1 Macc. i. 41-53; 2 Macc. v. 27, vi. 2; Jos., Antt., XII. v. 4.
518
1 Macc. ii. 41-64, iv. 54; 2 Macc. vi. 1-9, x. 5; Jos., Antt., XII. v. 4; Dan. xi. 31.
519
Maccabee perhaps means "the Hammerer" (comp. the names Charles Martel and Malleus hæreticorum). Simeon was called Tadshî, "he increases" (? Gk., Θασσίς).
520
The numbers vary in the records.
521
Prideaux, Connection, ii. 212. Comp. Rev. xii. 14, xi. 2, 3.
522
John x. 22.
523
On the death of Antiochus see 1 Macc. vi. 8; 2 Macc. ix.; Polybius, xxxi. 11; Jos., Antt., XII. ix. 1, 2.
524
Polybius, De Virt. et Vit., Exc. Vales, p. 144; Q. Curtius, v. 13; Strabo, xi. 522; Appian, Syriaca, xlvi. 80; 1 Macc. vi.; 2 Macc. ix.; Jos., Antt., XII. ix. 1; Prideaux, ii. 217; Jahn, Hebr. Commonwealth § xcvi.
525
Dan. vii. 26.
526
Dan. vii. 12. This is only explicable at all – and then not clearly – on the supposition that the fourth beast represents Alexander and the Diadochi. See even Pusey, p. 78.
527
Ezek. i. 26; Psalm l. 3. Comp. the adaptation of this vision in Enoch xlvi. 1-3.
528
Isa. l. 11, lx. 10-12, lxvi. 24, Joel iii. 1, 2. See Rev. i. 13. In the Gospels it is not "a son of man," but generally ὁ υἱὸς τοῦ ἀνθρώπου. Comp. Matt. xvi. 13, xxiv. 30; John xii. 34; Acts vii. 56; Justin, Dial. c. Tryph., 31.
529
Comp. Mark xiv. 62; Rev. i. 7; Hom., Il., v. 867, ὁμοῦ νεφέεσσιν.
530
Comp. Ezek. i. 26.
531
It is so understood by the Book of Enoch; the Talmud (Sanhedrin, f. 98, 1); the early father Justin Martyr, Dial. c. Tryph., 31, etc. Some of the Jewish commentators (e. g., Abn Ezra) understood it of the people of God, and so Hofmann, Hitzig, Meinhold, etc. See Behrmann, Dan., p. 48.
532
Dan. iv. 3, 34, vi. 26. See Schürer, ii. 247; Wellhausen, Die Pharis. u. Sadd., 24 ff.
533
Dan. vii. 16, 22, 23, 27.
534
Zech. ix. 9.
535
See Schürer, ii. 138-187, "The Messianic Hope": he refers to Ecclus. xxxii. 18, 19, xxxiii. 1-11, xl. 13, l. 24; Judith xvi. 12; 2 Macc. ii. 18; Baruch ii. 27-35; Tobit xiii, 11-18; Wisdom iii. 8, v. 1, etc. The Messianic King appears more distinctly in Orac. Sibyll., iii.; in parts of the Book of Enoch (of which, however, xlv. – lvii. are of unknown date); and the Psalms of Solomon. In Philo we seem to have traces of the King as well as of the kingdom. See Drummond, The Jewish Messiah, pp. 196 ff.; Stanton, The Jewish and Christian Messiah, pp. 109-118.
536
Ezra vi. 2; Neh. i. 1; Herod., v. 49; Polyb., v. 48. A supposed tomb of Daniel has long been revered at Shushan.
537
Pers., baru; Skr., bura; Assyr., birtu; Gk., βάρις. Comp. Æsch., Pers., 554; Herod., ii. 96.
538
Theodot., οὐβάλ; Ewald, Stromgebiet– a place where several rivers meet. The Jews prayed on river-banks (Acts xvi. 13), and Ezekiel had seen his vision on the Chebar (Ezek. i. 1, iii. 15, etc.); but this Ulai is here mentioned because the palace stood on its bank. Both the LXX. and Theodotion omit the word Ulai.
539
"Susianam ab Elymaide disterminat amnis Eulæus" (Plin., H. N., vi. 27).
540
See Loftus, Chaldæa, p. 346, who visited Shush in 1854; Herzog, R. E., s. v. "Susa." A tile was found by Layard at Kuyunjik representing a large city between two rivers. It probably represents Susa. Loftus says that the city stood between the Choaspes and the Kopratas (now the Dizful).
541
The Latin word for "to butt" is arietare, from aries, "a ram." It butts in three directions (comp. Dan. vii. 5). Its conquests in the East were apart from the writer's purpose. Crœsus called the Persians ὑβρισταί, and Æschylus ὑπέρκομποι ἄγαν, Pers., 795 (Stuart). For horns as the symbol of strength see Amos vi. 13; Psalm lxxv. 5.
542
Unicorns are often represented on Assyrio-Babylonian sculptures.
543
1 Macc. i. 1-3; Isa. xli. 2; Hosea xiii. 7, 8; Hab. i. 6.
544
Fury (chemah), "heat," "violence" – also of deadly venom (Deut. xxxii. 24).
545
A.V., "four notable horns"; but the word chazoth means literally "a sight of four" —i. e., "four other horns" (comp. ver. 8). Grätz reads achēroth; LXX., ἕτερα τέσσαρα (comp. xi. 4).
546
Lit. "out of littleness."
547
Hatstsebî. Comp. xi. 45; Ezek. xx. 6; Jer. iii. 19; Zech. vii. 14; Psalm cvi. 24. The Rabbis make the word mean "the gazelle" for fanciful reasons (Taanîth, 69, a).
548
The physical image implies the war against the spiritual host of heaven, the holy people with their leaders. See 1 Macc. i. 24-30; 2 Macc. ix. 10. The Tsebaoth mean primarily the stars and angels, but next the Israelites (Exod. vii. 4).
549
So in the Hebrew margin (Q'rî), followed by Theodoret and Ewald; but in the text (Kethîbh) it is, "by him the daily was abolished"; and with this reading the Peshito and Vulgate agree. Hattamîd, "the daily" sacrifice; LXX., ἐνδελεχισμός; Numb. xxviii. 3; 1 Macc. i. 39, 45, iii. 45.
550
The Hebrew is here corrupt. The R.V. renders it, "And the host was given over to it, together with the continual burnt offering through transgression; and it cast down truth to the ground, and it did its pleasure and prospered."
551
Dan. viii. 13. I follow Ewald in this difficult verse, and with him Von Lengerke and Hitzig substantially agree; but the text is again corrupt, as appears also in the LXX. It would be useless here to enter into minute philological criticism. "How long?" (comp. Isa. vi. 11).
552
LXX., φελμωνί; nescio quis (Vulg., viri).
553
Comp. for the expression xii. 6.
554
We find no names in Gen. xxxii. 30; Judg. xiii. 18. For the presence of angels at the vision comp. Zech. i. 9, 13, etc. Gabriel means "man of God." In Tobit iii. 17 Raphael is mentioned; in 2 Esdras v. 20, Uriel. This is the first mention of any angel's name. Michael is the highest archangel (Weber, System., 162 ff.), and in Jewish angelology Gabriel is identified with the Holy Spirit (Ruach Haqqodesh). As such he appears in the Qurân, ii. 91 (Behrmann).
555
Ben-Adam (Ezek. ii. 1).
556
Comp. Isa. xiv. 9: "All the great goats of the earth." A ram is a natural symbol for a chieftain. – Hom., Il., xiii. 491-493; Cic., De Div., i. 22; Plut., Sulla, c. 27; Jer. l. 8; Ezek. xxxiv. 17; Zech. x. 3, etc. See Vaux, Persia, p. 72.
557
"Strength of face" (LXX., ἀναιδὴς προσώπῳ; Deut. xxviii. 50, etc.). "Understanding dark sentences" (Judg. xiv. 12; Ezek. xvii. 2: comp. v. 12).
558
The meaning is uncertain. It may mean (1) that he is only strong by God's permission; or (2) only by cunning, not by strength.
559
Comp. 2 Macc. iv. 9-15: "The priests had no courage to serve any more at the altar, but despising the Temple, and neglecting the sacrifices, hastened to be partakers of the unlawful allowance in the place of exercise … not setting by the honours of their fathers, but liking the glory of the Grecians best of all."
560
Not merely the angelic prince of the host (Josh. v. 14), but God – "Lord of lords."
561
Comp. Esther i. 2. Though the vision took place under Babylon, the seer is strangely unconcerned with the present, or with the fate of the Babylonian Empire.
562
It is said to be the national emblem of Macedonia.
563
He is called "the King of Javan" —i. e., of the Ionians.
564
Isa. v. 26-29. Comp. 1 Macc. i. 3.
565
The fury of the he-goat represents the vengeance cherished by the Greeks against Persia since the old days of Marathon, Thermopylæ, Salamis, Platæa, and Mycale. Persia had invaded Greece under Mardonius (b. c. 492), under Datis and Artaphernes (b. c. 490), and under Xerxes (b. c. 480).
566
1 Macc. vi. 1-16; 2 Macc. ix. 9; Job vii. 6; Prov. xxvi. 20.
567
So Diodorus Siculus (Exc. Vales., p. 293); Justin, xxxii. 2; Jer. in Dan., xi.; Strabo, xvi. 744.
568
Aurel. Vict., De Virr. Illustr., c. liv.
569
He conquered Egypt b. c. 170 (1 Macc. i. 17-20).
570
See 1 Macc. iii. 29-37.
571
Comp. Ezek. xx. 6, "which is the glory of all lands"; Psalm l. 2; Lam. ii. 15.
572
1 Macc. i. 24-30. Dr. Pusey endeavours, without even the smallest success, to show that many things said of Antiochus in this book do not apply to him. The argument is based on the fact that the characteristics of Antiochus – who was a man of versatile impulses – are somewhat differently described by different authors; but here we have the aspect he presented to a few who regarded him as the deadliest of tyrants and persecutors.
573
See Hamburger, ii. 334 (s. v. "Haftara").
574
Comp. ὀργὴ μεγάλη (1 Macc. i. 64; Isa. x. 5, 25, xxvi. 20; Jer. l. 5; Rom. ii. 5, etc.).
575
Comp. xi. 21.
576
Comp. ii. 34, xi. 45. Antiochus died of a long and terrible illness in Persia. Polybius (xxxi. 11) describes his sickness by the word δαιμονήσας. Arrian (Syriaca, 66) says φθίνων ἐτελεύτησε. In 1 Macc. vi. 8-16 he dies confessing his sins against the Jews, but there is another story in 2 Macc. ix. 4-28.
577
Ver. 27, "I was gone" (or, "came to an end") "whole days." With this ἔκστασις comp. ii. 1, vii. 28; Exod. xxxiii. 20; Isa. vi. 5; Luke ix. 32; Acts ix. 4, etc. Comp. xii. 8; Jer. xxxii. 14, and (contra) Rev. xxii. 10.
578
In ver. 26 the R.V. renders "it belongeth to many days to come."
579
Comp. Gen. i. 5; 2 Cor. xi. 25. The word tamîd includes both the morning and evening sacrifice (Exod. xxix. 41). Pusey says (p. 220), "The shift of halving the days is one of those monsters which have disgraced scientific expositions 'of Hebrew.'" Yet this is the view of such scholars as Ewald, Hitzig, Kuenen, Cornill, Behrmann. The latter quotes a parallel: "vgl. im Hildebrandsliede sumaro ente wintro sehstie = 30 Jahr."
580
Matt. xxiv. 22.
581
"These five passages agree in making the final distress last during three years and a fraction: the only difference lies in the magnitude of the fraction" (Bevan, p. 127).
582
1 Macc. iv. 41-56; 2 Macc. x. 1-5.
583
See on this period Diod. Sic., Fr., xxvi. 79; Liv., xlii. 29; Polyb., Legat., 71; Justin, xxxiv. 2; Jer., Comm. in Dan., xi. 22; Jahn, Hebr. Commonwealth, § xciv.; Prideaux, Connection, ii. 146.
584
Connection, ii. 188.
585
Gesch. d. V. Isr., i. 155.
586
Some of these dates are uncertain, and are variously given by different authorities.
587
Achashverosh, Esther viii. 10; perhaps connected with Kshajârsha, "eye of the kingdom" (Corp. Inscr. Sem., ii. 125).
588
By "the books" is here probably meant the Thorah or Pentateuch, in which the writer discovered the key to the mystic meaning of the seventy years. It was not in the two sections of Jeremiah himself (called, according to Kimchi, Sepher Hamattanah and Sepher Hagalon) that he found this key. Jeremiah is here Yir'myah, as in Jer. xxvii. – xxix. See Jer. xxv. 11; Ezek. xxxvii. 21; Zech. i. 12. In the Epistle of Jeremy (ver. 2) the seventy years become seven generations (Χρόνος μακρὸς ἕως ἑππὰ γενεῶν). See too Dillman's Enoch, p. 293.
589
Dan., p. 146. Comp. a similar usage in Aul. Gell., Noct. Att., iii. 10, "Se jam undecimam annorum hebdomadem ingressum esse"; and Arist., Polit., vii. 16.
590
See Fritzsche ad loc.; Ewald, Hist. of Isr., v. 140.
591
The writer of 2 Chron. xxxv. 17, 18, xxxvi. 21, 22, evidently supposed that seventy years had elapsed between the destruction of Jerusalem and the decree of Cyrus – which is only a period of fifty years. The Jewish writers were wholly without means for forming an accurate chronology. For instance, the Prophet Zechariah (i. 12), writing in the second year of Darius, son of Hystaspes (b. c. 520), thinks that the seventy years were only then concluding. In fact, the seventy years may be dated from b. c. 606 (fourth year of Jehoiakim); or b. c. 598 (Jehoiachin); or from the destruction of the Temple (b. c. 588); and may be supposed to end at the decree of Cyrus (b. c. 536); or the days of Zerubbabel (Ezra v. 1); or the decree of Darius (b. c. 518, Ezra vi. 1-12).
592
Lev. xxv. 2, 4.
593
2 Chron. xxxvi. 21. See Bevan, p. 14.
594
See Cornill, Die Siebzig Jahrwochen Daniels, pp. 14-18.
595
The LXX. and Theodotion, with a later ritual bias, make the fasting a means towards the prayer: εὑρεῖν προσευχὴν καὶ ἔλεος ἐν νηστείαις.
596
Ewald, p. 278. The first part (vv. 4-14) is mainly occupied with confessions and acknowledgment of God's justice; the last part (vv. 15-19) with entreaty for pardon: confessio (vv. 4-14); consolatio (vv. 15-19) (Melancthon).
597
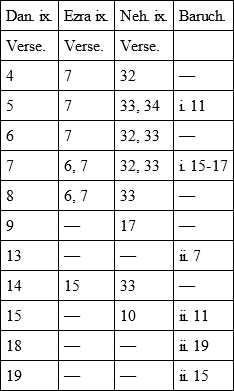
Besides the parallels which follow, it has phrases from Exod. xx. 6; Deut. vii. 21, x. 17; Jer. vii. 19; Psalm xliv. 16, cxxx. 4; 2 Chron. xxxvi. 15, 16. Mr. Deane (Bishop Ellicott's Commentary, p. 407) thus exhibits the details of special resemblances: —
598
ix. 13 (Heb.). Comp. Exod. xxxii. 13; 1 Sam. xiii. 12; 1 Kings xiii. 6, etc.
599
Comp. Jer. xxxii. 17-23; Isa. lxiii. 11-16.
600
ix. 21. LXX., τάχει φερόμενος; Theodot., πετόμενος; Vulg., cito volans; A.V. and R.V., "being made to fly swiftly"; R.V. marg., "being sore wearied"; A.V. marg., "with weariness"; Von Lengerke, "being caused to hasten with haste." The verb elsewhere always connotes weariness. If that be the meaning here, it must refer to Daniel. If it here means "flying," it is the only passage in the Old Testament where angels fly; but see Isa. vi. 2; Psalm civ. 4, etc. The wings of angels are first mentioned in the Book of Enoch, lxi.; but see Rev. xiv. 6 – cherubim and seraphim have wings.
601
In the time of the historic Daniel, as in the brief three and a half years of Antiochus, the tamîd had ceased.
602
ix. 23. Heb., eesh hamudôth; Vulg., vir desideriorum, "a man of desires"; Theodot., ἀνὴρ ἐπιθυμιῶν. Comp. x. 11, 19, and Jer. xxxi. 20, where "a pleasant child" is "a son of caresses"; and the "amor et deliciæ generis humani" applied to Titus; and the names David, Jedidiah, "beloved of Jehovah." The LXX. render the word ἐλεεινός, "an object of pity."
603
Daniel used Shabuîm for weeks, not Shabuôth.
604
In ver. 24 the Q'rî and Kethîbh vary, as do also the versions.
605
For charoots, "moat" (Ewald), the A.V. has "wall," and in the marg. "breach" or "ditch." The word occurs for "ditches" in the Talmud. The text of the verse is uncertain.
606
Perhaps because neither Jason nor Menelaus (being apostate) were regarded as genuine successors of Onias III.
607
Numb. xiv. 34; Lev. xxvi. 34; Ezek. iv. 6.
608
Comp. Jer. xxxii. 11, 44.
609
See Isa. xlvi. 3, li. 5, liii. 11; Jer. xxiii. 6, etc.
610
For the anointing of the altar see Exod. xxix. 36, xl. 10; Lev. viii. 11; Numb. vii. 1. It would make no difference in the usus loquendi if neither Zerubbabel's nor Judas's altar was actually anointed.
611
It is only used thirteen times of the Debhîr, or Holiest Place.
612
1 Macc. iv. 54.
613
Theodot., ἕως χριστοῦ ἡγουμένου.
614
Saadia the Gaon, Rashi, Von Lengerke, Hitzig, Schürer, Cornill.
615
Hag. i. 1; Zech. iii. 1; Ezra iii. 2. Comp. Ecclus. xlv. 24; Jos., Antt., XII. iv. 2, προστάτης; and see Bevan, p. 156.
616
We see from Zech. i. 12, ii. 4, that even in the second year of Darius Hystaspis Jerusalem had neither walls nor gates; and even in the twentieth year of Artaxerxes the wall was still broken down and the gates burnt (Neh. i. 3).
617
LXX., ἀποσταθήσεται χρίσμα καὶ οὐκ ἔσται; Theodot., ἐξολεθρευθήσεται χρίσμα καὶ οὐκ ἔστιν ἐν αὐτῷ; Aquil., ἐξ. ἠλειμμένος καὶ οὐχ ὑπάρξει αὐτῷ.
618
See xi. 22. Von Lengerke, however, and others refer it to Seleucus Philopator, murdered by Heliodorus (b. c. 175).
619
Syr. Aquil., οὐχ ὑπάρξει αὐτῷ; Theodot., καὶ οὔκ ἐστιν ἐν αῦτῳ; LXX., καὶ οὐκ ἔσται; Vulg., "Et non erit ejus populus qui eum negaturus est." The A.V. "and not for himself" is untenable. It would have been וְלֹא לוֹ. See Pusey, p. 182, n.
620
Steudel, Hofmann. So too Cornill, p. 10: "Ein frommer Jude das Hoher Priesterthum mit Onias für erloschen ansah."
621
Comp. ואין לו and חניו (Joël, Notizen, p. 21).
622
Jos., Antt., XII. v. 4; 1 Macc. i. 29-40.
623
Here again the meaning is uncertain; and Grätz, altering the reading, thinks that it should be, "He shall abolish the covenant [with God] for the many"; or, "shall cause the many to transgress the covenant."
624
Dan. ix. 27. Heb., Zebach oo-minchah, "the bloody and unbloody offering."
625
The special allusion, whatever it may precisely mean, is found under three different designations: (i) In viii. 13 it is called happeshang shomeem; Gk., ἡ ἁμαρτία ἐρημώσεως; Vulg., peccatum desolationis. (ii) In ix. 27 (comp. ix. 31) it is shiqqootsîm m'shomeem; Gk., βδέλυγμα τῆς ἐρημώσεως; Vulg., abominatio desolationis. (iii) In xii. 11 it is shiqqoots shomeem; Gk., τὸ βδέλυγμα ἐρημώσεως; Vulg., abominatio in desolationem. Some traditional fact must (as Dr. Joël says) have underlain the rendering "of desolation" for "of the desolator." In xi. 31 Theodotion has ἠφανισμένων, "of things done away with," for ἐρημωσέων. The expression with which the New Testament has made us so familiar is found also in 1 Macc. i. 51 (comp. 1 Macc. vi. 7): "they built the abomination of desolation upon the altar." There "the abomination" seems clearly to mean a smaller altar for heathen sacrifice to Zeus, built on the great altar of burnt offering. Perhaps the writer of Daniel took the word shomeem, "desolation," as a further definition of shiqqoots, "abomination," from popular speech; and it may have involved a reference to Lev. xxvi. 15-31: "If ye shall despise My statutes … I will even appoint over you terror … and I will make your cities waste, and appoint your sanctuaries unto desolation." The old Jewish exegetes referred the prophecy to Antiochus Epiphanes; Josephus and later writers applied it to the Romans. Old Christian expositors regarded it as Messianic; but even Jerome records nine different views of commentators, many of them involving the grossest historic errors and absurdities. Of Post-Reformation expositors down to the present century scarcely two agree in their interpretations. At the present day modern critics of any weight almost unanimously regard these chapters, in their primary significance, as vaticinia ex eventu, as some older Jewish and Christian exegetes had already done. Hitzig sarcastically says that the exegetes have here fallen into all sorts of shiqqootsîm themselves.

