
Полная версия:
Memory of the World: The treasures that record our history from 1700 BC to the present day

MEMORY OF THE WORLD

Contents
The book is ordered by the date the documents were recorded
Title Page
Foreword
The emotional power of documents
World map
Memory of the World Register
MEMORY OF WORLD DOCUMENTS
The Hittite cuneiform tablets from Bogazköy
Rigveda
Papyrus Erzherzog Rainer
Commemorative stelae of Nahr el-Kalb, Mount Lebanon
The Phoenician alphabet
Huang Di Nei Jing
Ancient Naxi Dongba literature manuscripts
Mashtots Matenadaran ancient manuscripts collection
Saiva manuscripts in Pondicherry
Codex Argenteus – the ‘Silver Bible’
Codex Purpureus Beratinus
Vienna Dioscurides
Earliest Islamic (Kufic) inscription
Holy Koran Mushaf of Othman
Lucca’s historical diocesan archives
The Book of Kells
Laghukālacakratantrarājatikā (Vimalaprabhā)
The collection of the Al-Biruni Institute of Oriental Studies
Philippine Paleographs (Hanunoo, Buid, Tagbanua and Pala’wan)
Georgian Byzantine manuscripts
Deeds of sultans and princes
Illuminated manuscripts from the Ottonian period produced in the monastery of Reichenau (Lake Constance)
Enina Apostolos, Old Bulgarian Cyrillic manuscript (fragment) of the 11th century
Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute manuscripts
Codex Suprasliensis
The works of Ibn Sina in the Süleymaniye Manuscript Library
Al-Tafhim li Awa’il Sana’at al-Tanjim
Ostromir Gospel (1056–1057)
Bayeux Tapestry
Archangel Gospel of 1092
Illuminated codices from the library of the Bratislava Chapter House
Medieval manuscripts on medicine and pharmacy
The Arnamagnæan manuscript collection
Miroslav Gospel – manuscript from 1180
Tabula Peutingeriana
Song of the Nibelungs, a heroic poem from medieval Europe
Magna Carta, issued in 1215
Printing woodblocks of the Tripitaka Koreana
MS. GKS 4 2°, vol. I–III, Biblia Latina. Commonly called ‘The Hamburg Bible’
Hereford Mappa Mundi
The King Ram Khamhaeng inscription
Library Ets Haim–Livraria Montezinos
The manuscript of Ubayd Zakoni’s Kulliyat and Hafez Sherozi’s Gazalliyt
Collection of medieval manuscripts of the Czech Reformation
The Deed For Endowment: Rab’ i-Rashidi (Rab i-Rashidi Endowment)
Batu Bersurat, Terengganu (Inscribed Stone of Terengganu)
La Galigo
Persian illustrated and illuminated manuscripts
Collection of Nezami’s Panj Ganj
Baegun hwasang chorok buljo jikji simche yojeol (vol. II)
Khitrovo Gospel
The Annals of the Joseon dynasty
Kitab al-ibar, wa diwan al-mobtadae wa al-khabar
Slavonic publications in Cyrillic script of the 15th century
Treasures from National Archives and Library organizations
Corpo Cronológico (collection of manuscripts on the Portuguese discoveries)
Radziwills’ Archives and Niasvizh (Nieśwież) Library collection
Collection of Gothic architectural drawings
‘Bayasanghori Shâhnâmeh’ (Prince Bayasanghor’s ‘Book of the Kings’)
Stone stele records of royal examinations of the Le and Mac dynasties (1442–1779)
The Hunminjeongum manuscript
The Malatesta Novello Library
The 42-line Gutenberg Bible, printed on vellum
Bibliotheca Corviniana
Library of the Cistercian Abbey of Clairvaux at the time of Pierre de Virey (1472)
Mainz Psalter at the Austrian National Library
Santa Fe Capitulations
Treaty of Tordesillas
Sound Toll Registers
Letter from Pêro Vaz de Caminha
Archives Insolvente Boedelskamer Antwerpen
Universalis cosmographia secundum Ptholomaei traditionem et Americi Vespucii aliorumque Lustrationes
Tabula Hungariae
Beatus Rhenanus Library
Sixteenth to eighteenth century pictographs from ‘Maps, drawings and illustrations’ Archives of Mexico
Negros y Esclavos archives
Collection of Mexican codices
Colección de lenguas indígenas
Bašagic collection of Islamic manuscripts
Collection of the Center of Documentation and Investigation of the Ashkenazi community in Mexico
Nicolaus Copernicus’ masterpiece ‘De revolutionibus libri sex’
Codices from the Oaxaca Valley
Châtelet de Paris banner register from the reign of Francis I (National Archives Y9, France)
Collection of the manuscripts of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi
American colonial music: a sample of its documentary richness
Business archives of the Officina Plantiniana
Documentary fonds of Royal Audiencia Court of La Plata (RALP)
The Confederation of Warsaw of 28th of January 1573
Tarikh-e-Khandan-e-Timuriyah
Administrative documents of Astan-e Quds Razavi in the Safavid era
Ben Cao Gang Mu
Tolstoy’s personal library and manuscripts, photo and film collection
Jesuits of America
Codex Techaloyan de Cuajimalpaz
Documentary heritage of enslaved peoples of the Caribbean
El Primer Nueva Corónica y Buen Gobierno
Uigwe: The royal protocols of the court of Joseon dynasty
Archives of the Dutch East India Company
Donguibogam: ‘Principles and Practice of Eastern Medicine’
Sejarah Melayu (The Malay Annals)
Dutch West India Company (Westindische Compagnie) archives
The IAS Tamil medical manuscript collection
Quebec Seminary collection, 1623–1800 (17th–19th centuries)
Seungjeongwon Ilgi, the diaries of the royal secretariat
Book for the Baptism of Slaves (1636-1670)
Mining maps and plans of the Main Chamber – Count Office in Banská Štiavnica
Collection of 526 prints of university theses from 1637 to 1754
Biblioteca Palafoxiana
Hikayat Hang Tuah
Records of the Qing’s Grand Secretariat
Lu. ‘Altan Tobchi’: Golden History written in 1651
The Atlas Blaeu–Van der Hem
Golden Lists of the Qing dynasty imperial examination
Letters from and to Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Archives of the Danish overseas trading companies
Hudson’s Bay Company archival records
Arquivos dos Dembos / Ndembu archives
Woodblocks of the Nguyễn dynasty
Records of the French occupation of Mauritius
Privateering and the international relations of the Regency of Tunis in the 18th and 19th centuries
Collection of 18th-century maps of the Russian empire
Newspaper collections, Russian Federation
Collection of Arabic manuscripts and books
Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Geneva and Neuchâtel collections
Stockholm City Planning Committee archives
Emanuel Swedenborg collection
Archives of the Middelburgsche Commercie Compagnie
Linné collection
Mongolian Tanjur
Qing dynasty Yangshi Lei archives
The literary estate of Goethe in the Goethe and Schiller Archives
Ilseongnok: Records of Daily Reflections
The Endeavour journal of James Cook
National Education Commission archives
Documentary heritage of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
Colombeia: Generalissimo Francisco de Miranda’s archives
The Convict Records of Australia
Original Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (1789–1791)
Introduction of the decimal metric system, 1790–1837
The Leprosy Archives of Bergen
The Vienna City Library Schubert collection
The masterpieces of Fryderyk Chopin
Kinder- und Hausmärchen (Children’s and Household Tales)
General Archive of the Nation: Writings of The Liberator Simón Bolívar
The Søren Kierkegaard archives
Final document of the Congress of Vienna
Registry of Slaves of the British Caribbean 1817–1834
Csoma archive of the Library of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
The Bleek collection
Ludwig van Beethoven: Symphony no. 9, D minor, op. 125
Royal archives (1824–1897)
Catecismo corticu pa uso di catolicanan di Curaçao (first catechism written in Papiamentu language)
Manuscripts and correspondence of Hans Christian Andersen
Records of the Indian indentured labourers
Farquharson’s Journal
Epigraphic archives of Wat Pho
János Bolyai: Appendix, Scientiam Spatii absolute veram exhibens
Brahms collection
Memory of the Suez Canal
The Treaty of Waitangi
The Emperor’s collection
Alfred Nobel family archives
Colonial archives, Benin
The A.E. Nordenskiöld Collection
‘José Martí Pérez’ fonds
Archival documents of King Chulalongkorn’s transformation of Siam (1868–1910)
Arnold Schönberg estate
Jinnah papers (Quaid-i-Azam)
Dainu Skapis – Cabinet of folksongs
Silver men: West Indian labourers at the Panama Canal
Henrik Ibsen: A Doll’s House
Nikola Tesla’s Archive
Benz patent of 1886
Correspondence of the late Sultan of Kedah (1882–1943)
The Historical Collections (1889–1955) of St Petersburg Phonogram Archives
German records of the National Archives
Manifesto of the Queensland Labour Party to the people of Queensland
The 1893 Women’s Suffrage Petition
Early cylinder recordings of the world’s musical traditions (1893–1952)397
Lumière films
Fonds of the Afrique occidentale française (AOF)
Historic ethnographic recordings (1898–1951) at the British Library
The historical collections (1899–1950) of the Vienna Phonogrammarchiv
Letter journals of Hendrik Witbooi
Russian posters of the end of the 19th and early 20th centuries
Collection of Latin American photographs of the 19th century
Presidential papers of Manuel L. Quezon
Sakubei Yamamoto collection
The Story of the Kelly Gang (1906)
Desmet collection
Roald Amundsen’s South Pole Expedition (1910–1912)
Collection of Jewish musical folklore (1912–1947)
Original records of Carlos Gardel – Horacio Loriente collection (1913–1935)
Archives of the International Prisoners of War Agency, 1914–1923
The Battle of the Somme
Collection of Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian émigré periodicals 1918–1945
League of Nations archives 1919–1946
Constantine collection
First flight across the South Atlantic Ocean in 1922
Kalman Tihanyi’s 1926 patent application ‘Radioskop’
Metropolis – Sicherungsstück Nr. 1: Negative of the restored and reconstructed version (2001)
C.L.R. James collection
Documentary heritage on the resistance and struggle for human rights in the Dominican Republic, 1930–1961
Sir William Arthur Lewis papers
Thor Heyerdahl archives
Ingmar Bergman archives
The Wizard of Oz (Victor Fleming, 1939), produced by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Warsaw Ghetto archives (Emanuel Ringelblum archives)
Astrid Lindgren archives
The Appeal of 18 June 1940
Diaries of Anne Frank
Archive of Warsaw Reconstruction Office
Archives of the Literary Institute in Paris (1946–2000)
Federal Archives fonds
Audiovisual documents of the international antinuclear movement ‘Nevada-Semipalatinsk’
UNRWA photo and film archives of Palestinian refugees
Los Olvidados
Nita Barrow collection
The Archives of Terror
John Marshall Ju/’hoan bushman film and video collection, 1950–2000
Traditional music sound archives
Neighbours, animated, directed and produced by Norman McLaren in 1952
José Maceda collection
Derek Walcott collection
The Family of Man
Christopher Okigbo collection
Eric Williams collection
The Mabo case manuscripts
Original negative of the Noticiero ICAIC Latinoamericano
Construction and fall of the Berlin Wall and the Two-Plus-Four-Treaty of 1990
Criminal Court Case No. 253/1963 (The State versus N. Mandela and Others)
Network of information and counter information on the military regime in Brazil (1964–1985)
First Byurakan Survey (FBS or Markarian survey)
Aral Sea archival fonds
Landsat Program records: Multispectral Scanner (MSS) sensors
Human Rights Archive of Chile
Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum archives
Human rights documentary heritage, 1976–1983
Liberation Struggle Living Archive Collection
Human rights documentary heritage, 1980
Twenty-One demands, Gdańsk, August 1980
National Literacy Crusade
Radio broadcast of the Philippine People Power Revolution
The Baltic Way – Human chain linking three states in their drive for freedom
Index
Contact information
Photo credits
Acknowledgements
Copyright
About the Publisher
Foreword
by Irina Bokova
Director-General of UNESCO

© UNESCO
UNESCO launched the Memory of the World Programme in 1992 to protect and promote the world’s documentary heritage through preservation and access – access to encourage protection, and preservation to ensure access.
This vision was vindicated a few months later, when on 25 August 1992, 1.5 million books in the Bosnia National and University Library in Sarajevo were destroyed. With this, a chapter of the history of humanity vanished. Too much of our heritage is lost like this in the heat of conflicts and through the twists and turns of history. Too much also lies hidden and inaccessible in libraries, museums and archives. This documentary heritage carries the memory of human experience. It is a vehicle for identity and a wellspring of knowledge and wisdom. For twenty years, UNESCO has worked to capture and to share this wealth for the benefit of all.
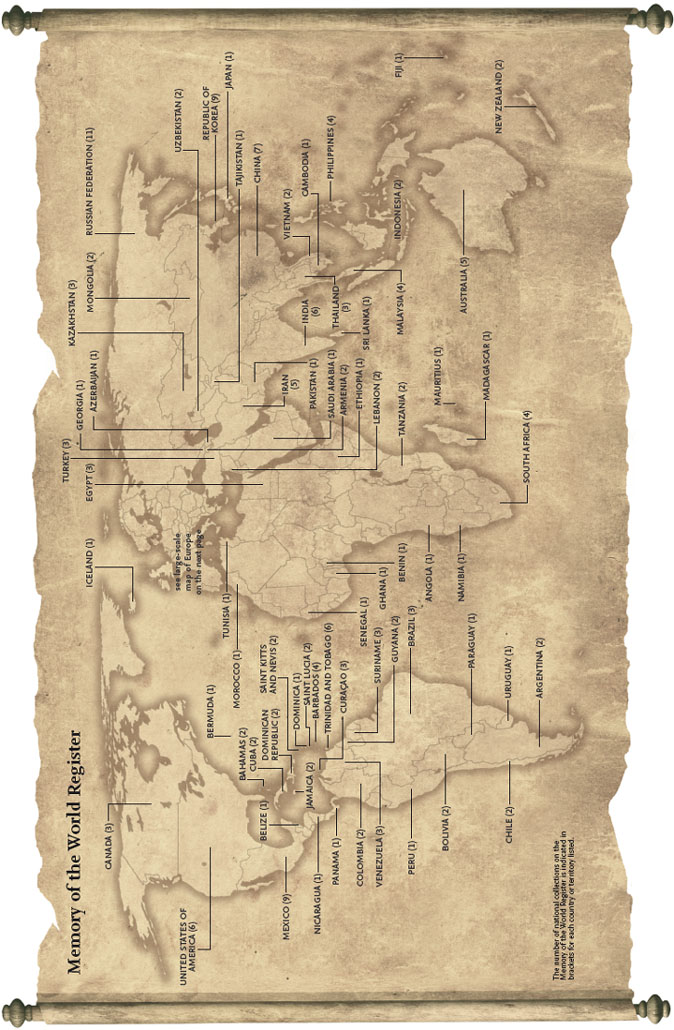
The UNESCO Memory of the World Registry contains today 245 documentary items from all parts of the world – from clay tablets, manuscripts and films to photographs, maps and web pages. This Register is our flagship to preserve, raise awareness and promote access to the documentary treasures of humanity. Preserving this heritage is important for maintaining the cultural heritage and identity of all societies. It safeguards our memories as a force shaping us as social beings in a common humanity.
The Memory of the World encourages every country to establish a national register and propose items for the international register. Heritage can be recorded on any of the carriers used to safeguard memories. These range from listings of archives relating to historical figures, such as Nelson Mandela and Alfred Nobel, to major historical events, voyages of exploration that have transformed the world, and the records of scientific discoveries and anthropological recordings. The scope is as vast, indeed, as is human experience.
Anne Frank’s Diaries or the Epigraphic Archives of Wat Pho need little explanation today. However, other items on the Register, such as the Sakubei Yamamoto collection and the 1824-1897 Royal Archives of Madagascar, may be less well-known but are no less emblematic of human ingenuity.
This book reveals this heritage in all of its diversity. For twenty years, the Memory of the World programme has gone from strength to strength. We must now take it ever further – by increasing nominations from all countries and by raising the visibility of preserving sources of knowledge of outstanding significance. Memory of the World is coming of age at a time when preserving our documentary heritage is more important than ever.
The emotional power of documents
Roslyn Russell PhD
Chair, International Advisory Committee
UNESCO Memory of the World Programme
Among the 245 inscriptions on the UNESCO Memory of the World Register is the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum archives from Cambodia. One photograph in the archives shows a young mother cradling a baby. It is an image that brings to mind countless others of the same subject – a mother and child – especially images of the Madonna and the Christ Child, the essence of serenity and spiritual grace.
But learning of the fate that met this particular mother and child can evoke an almost unbearable pain in the viewer – for these two individuals, after having been meticulously documented in this photograph, were taken out and killed, as were the other subjects of the photographs in the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum archives. These documents form a historical record, to be sure, but they also deliver a powerful emotional charge – and remind us of things that never should be forgotten, or repeated.
World significance, provenance and authenticity, and rarity and uniqueness are key values when assessing the suitability of a nomination of documentary heritage for inscription on the UNESCO Memory of the World Register. However, we must never forget the reasons why documents are so important to us, and why we believe so passionately in their preservation.
The historical evidence that documents convey is one reason; others are the beauty and craftsmanship, or the technical innovations some documents display. The capacity of documents to engage our emotions and connect us to people and events in the past is another.
Archivists, librarians and museum curators who work with collections relating to Indigenous people can testify to the powerful emotions that flow when these people find their families mentioned in documents, or see photographs or film footage of their ancestors, or hear recordings of voices speaking their language.
Holy books and writings can also evoke strong emotional responses in members of particular faith systems. For a believer, a document associated with a saint or a prophet is not just a physical object; it possesses a spiritual power over and above its historical significance, or its value as an original, rare or unique item.
The popularity of exhibitions of documents indicates how compelling these can be in connecting people with the past. An exhibition curator explains why visitors flock to see displays of letters by writers, artists, scientists, philosophers, inventors, and political figures: ‘We see the writers’ words directly, unfiltered. The manuscripts give a sense of the authors’ daily lives, friendships, concerns and ambitions, their work and their leisure.’ Original music manuscripts can have the same emotional power, as the viewer sees the erasures, the corrections and the resolutions that lie behind a finished score. Even the pen strokes can convey the passion and intensity of composition. There are few objects of material culture that are more imbued with the personality of their originators than documents such as these.
It is the task of the UNESCO Memory of the World Programme to ensure that future generations will be able to access these documents and experience their emotional power, as well as to learn about the historical memories that they convey, or appreciate their beauty and craftsmanship.
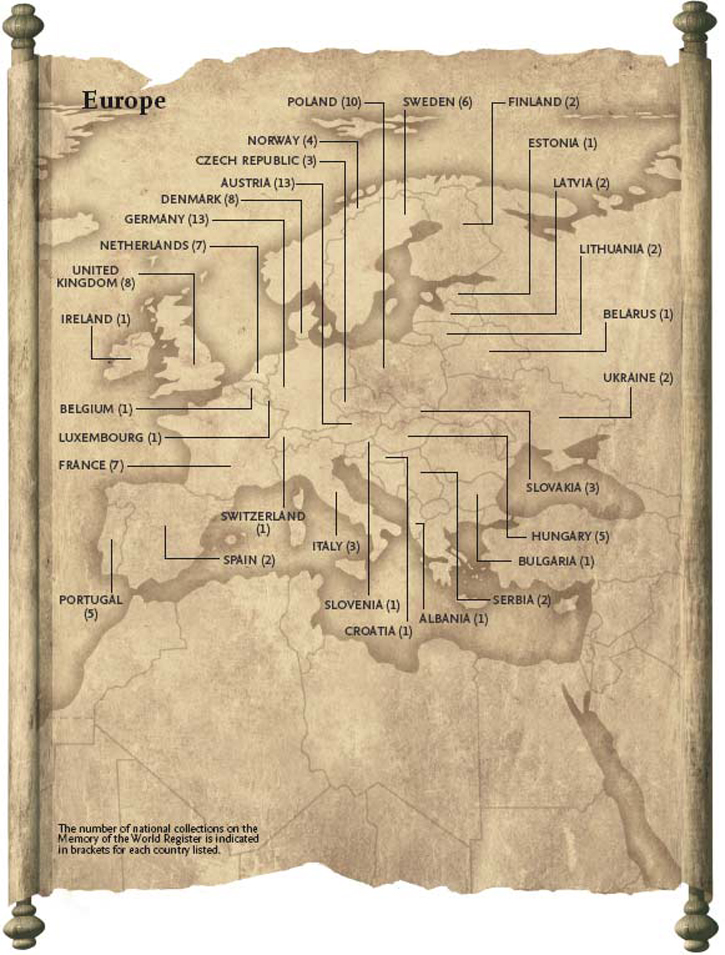
Memory of World Register
Albania
Codex Purpureus Beratinus
Angola
Arquivos dos Dembos / Ndembu archives *
Argentina
Documentary heritage of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
Human rights documentary heritage, 1976–1983
Armenia
Mashtots Matenadaran ancient manuscripts collection
First Byurakan Survey (FBS or Markarian survey)
Australia
The Endeavour journal of James Cook
The Convict Records of Australia
Manifesto of the Queensland Labour Party to the people of Queensland
The Story of the Kelly Gang (1906)
The Mabo case manuscripts
Austria
Papyrus Erzherzog Rainer
Tabula Peutingeriana
Vienna Dioscurides
Collection of Gothic architectural drawings



