
Полная версия:
Crown and Country: A History of England through the Monarchy


Crown and Country
A History of England through the Monarchy
DAVID STARKEY
Copyright
Published by HarperPress in 2010
Copyright © Jutland 2010
1 London Bridge Street
London SE1 9GF
www.harpercollins.co.uk
The Monarchy of England: Volume I, The Beginnings first published by Chatto and Windus, a division of Random House, 2004 © Jutland 2004
Monarchy: From the Middle Ages to Modernity first published by HarperPress 2006 © David Starkey 2006
All rights reserved under International and Pan-American Copyright Conventions. By payment of the required fees, you have been granted the non-exclusive, non-transferable right to access and read the text of this ebook on-screen. No part of this text may be reproduced, transmitted, down-loaded, decompiled, reverse engineered, or stored in or introduced into any information storage and retrieval system, in any form or by any means, whether electronic or mechanical, now known or hereinafter invented, without the express written permission of HarperCollins ebooks
David Starkey asserts the moral right to be identified as the author of this work
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library
Some images were unavailable for the electronic edition.
HB ISBN 9780007307708
TPB ISBN 9780007307715
Ebook Edition © 2010 ISBN: 9780007424825
Version: 2018-08-08
To all those who worked with me on the Channel 4 Monarchy series for helping me understand history better and write it more clearly
Contents
Cover
Title Page
Copyright
Family Trees
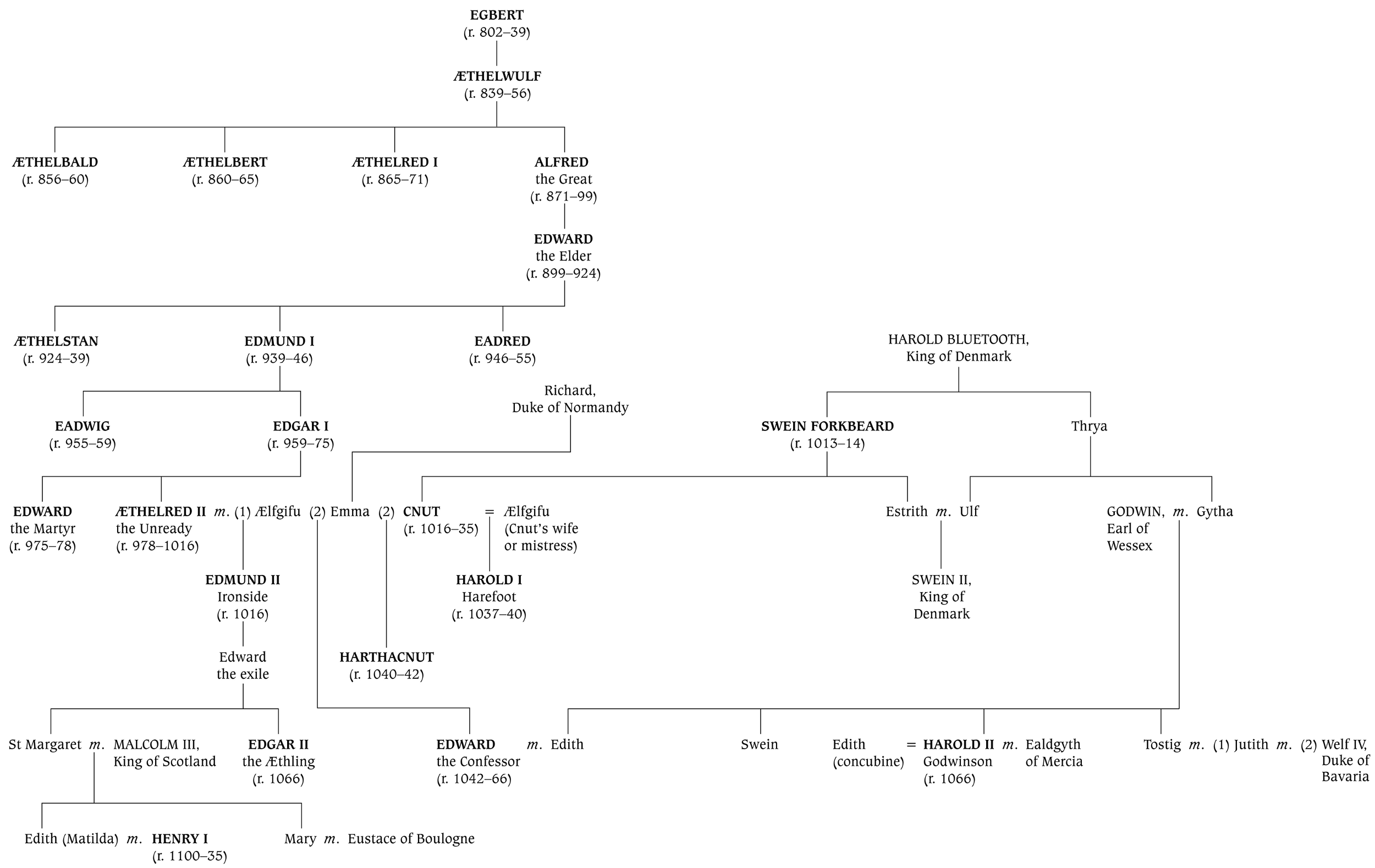
Houses of Godwin and Wessex
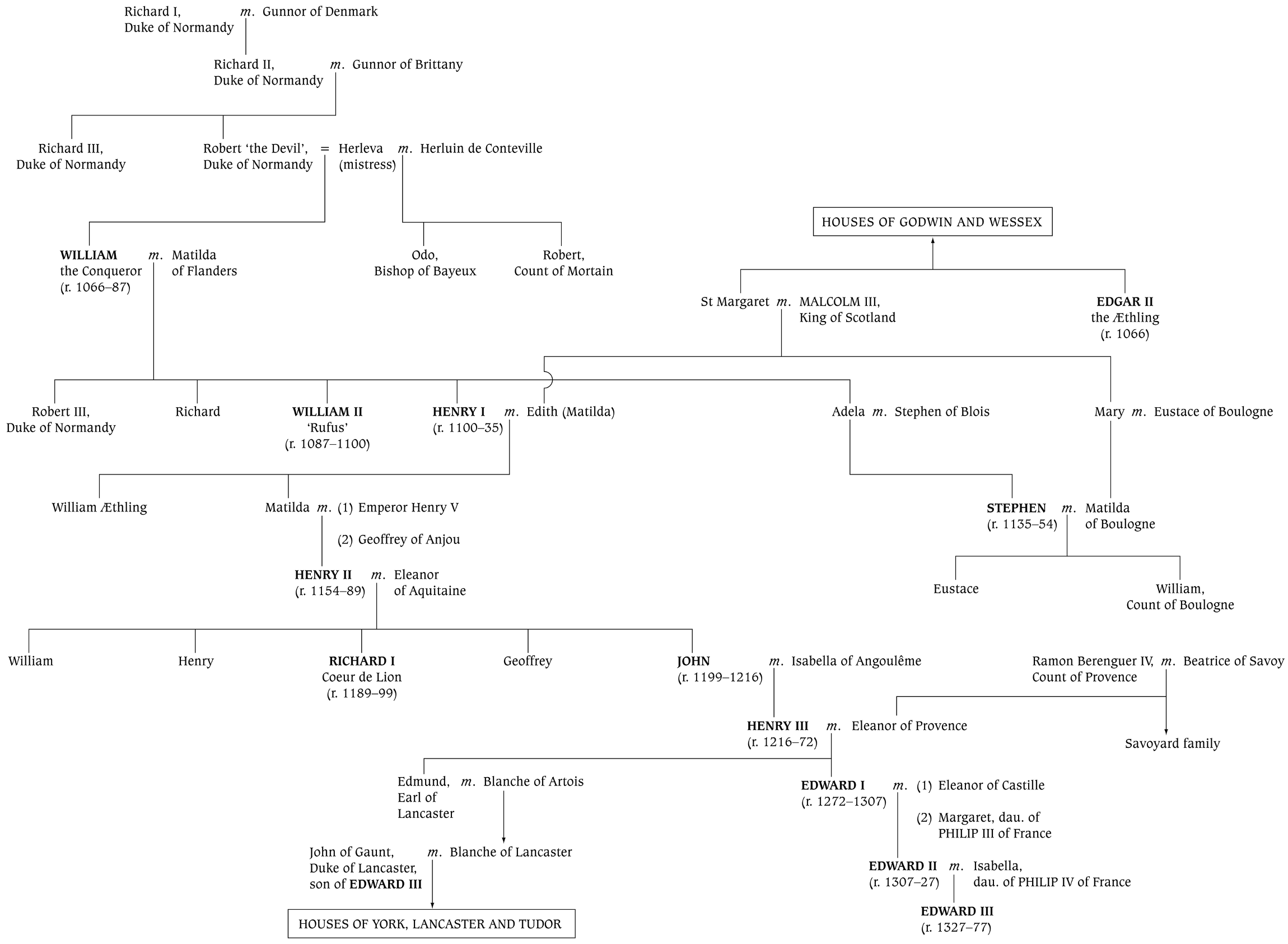
Houses of Normandy, Anjou and the Plantagenets
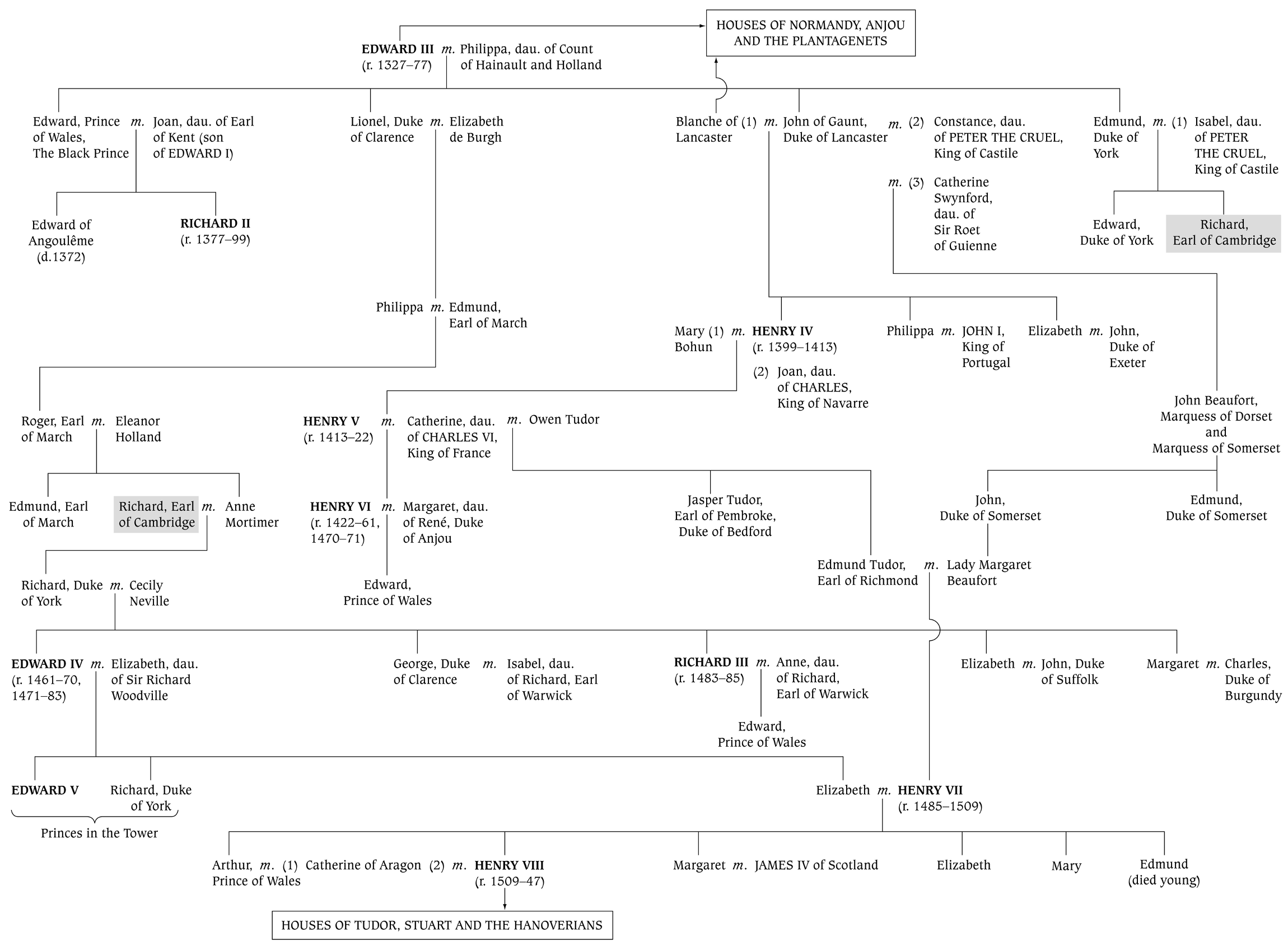
Houses of York, Lancaster and Tudor
Houses of Tudor, Stuart and the Hanoverians
House of Windsor
Foreword
PART I - BEGINNINGS
Chapter 1 - The Shadow of Rome
Chapter 2 - Christian Kingship
Chapter 3 - Wessex
Chapter 4 - Triumph and Disaster
Chapter 5 - Confessor and Conquest
PART II - THE MEDIEVAL MONARCHY
Chapter 6 - Subjugation
Chapter 7 - Sons of Conquest
Chapter 8 - The Triumphant King
Chapter 9 - Civil War
Chapter 10 - ‘Touch Not Mine Anointed’
Chapter 11 - The Curse of Anjou
Chapter 12 - War Monarchy
Chapter 13 - Death of a Dynasty
PART III - THE IMPERIAL CROWN
Chapter 14 - The Man Who Would Be King
Chapter 15 - King and Emperor
Chapter 16 - Shadow of The King
Chapter 17 - Rebellion
Chapter 18 - New Model Kingdom
PART IV - EMPIRE
Chapter 19 - Restoration
Chapter 20 - Royal Republic
Chapter 21 - Britannia Rules
Chapter 22 - Empire
Chapter 23 - The King is Dead, Long Live The British Monarchy!
PART V - MODERNITY
Chapter 24 - The Modern Monarchy
Chapter 25 - New Kingdom
Index
Also By David Starkey
About the Publisher
FAMILY TREES
HOUSES OF GODWIN AND WESSEX
HOUSES OF NORMANDY, ANJOU AND THE PLANTAGENETS
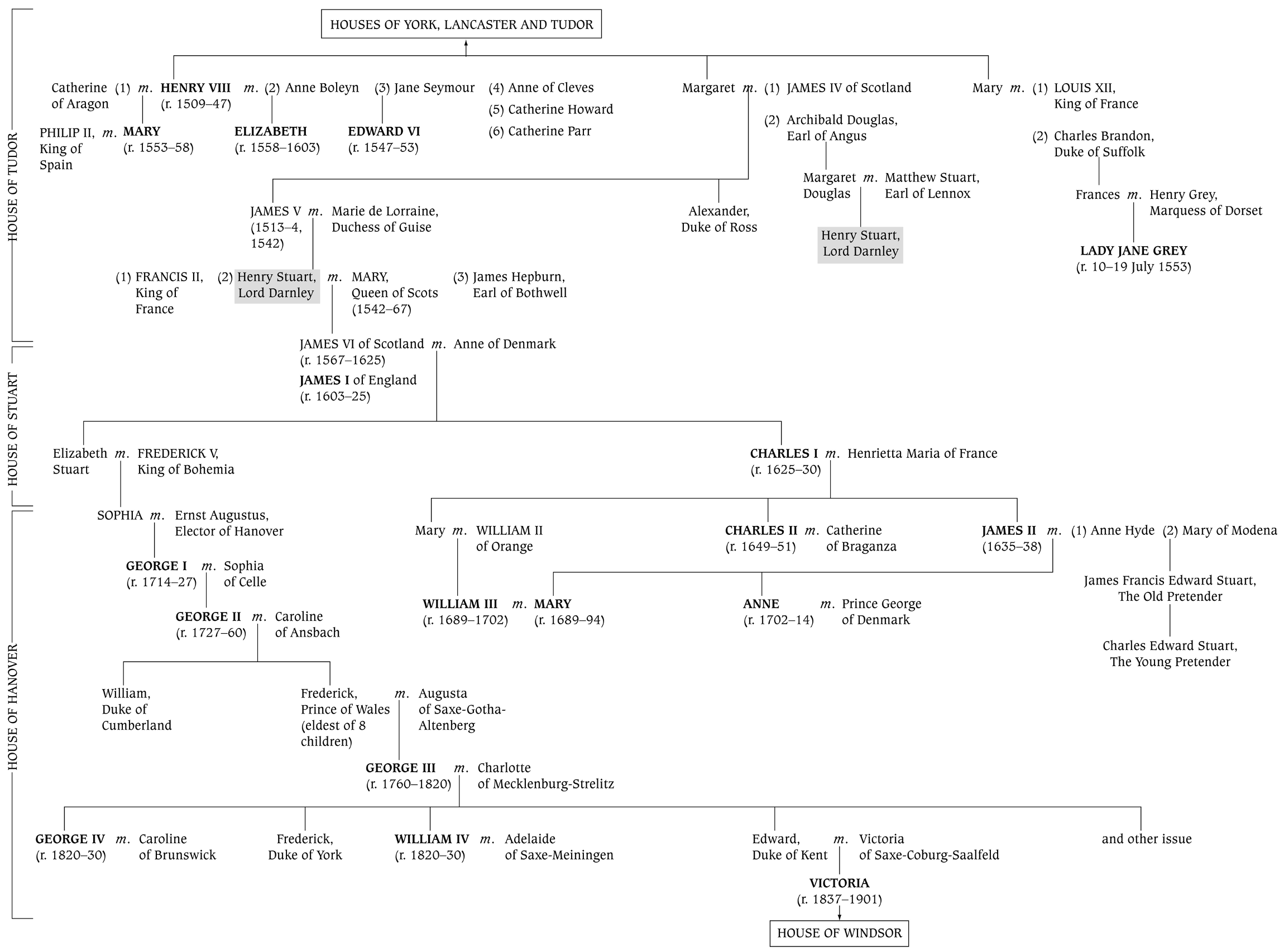
HOUSES OF YORK, LANCASTER AND TUDOR
HOUSES OF TUDOR, STUART AND THE HANOVERIANS
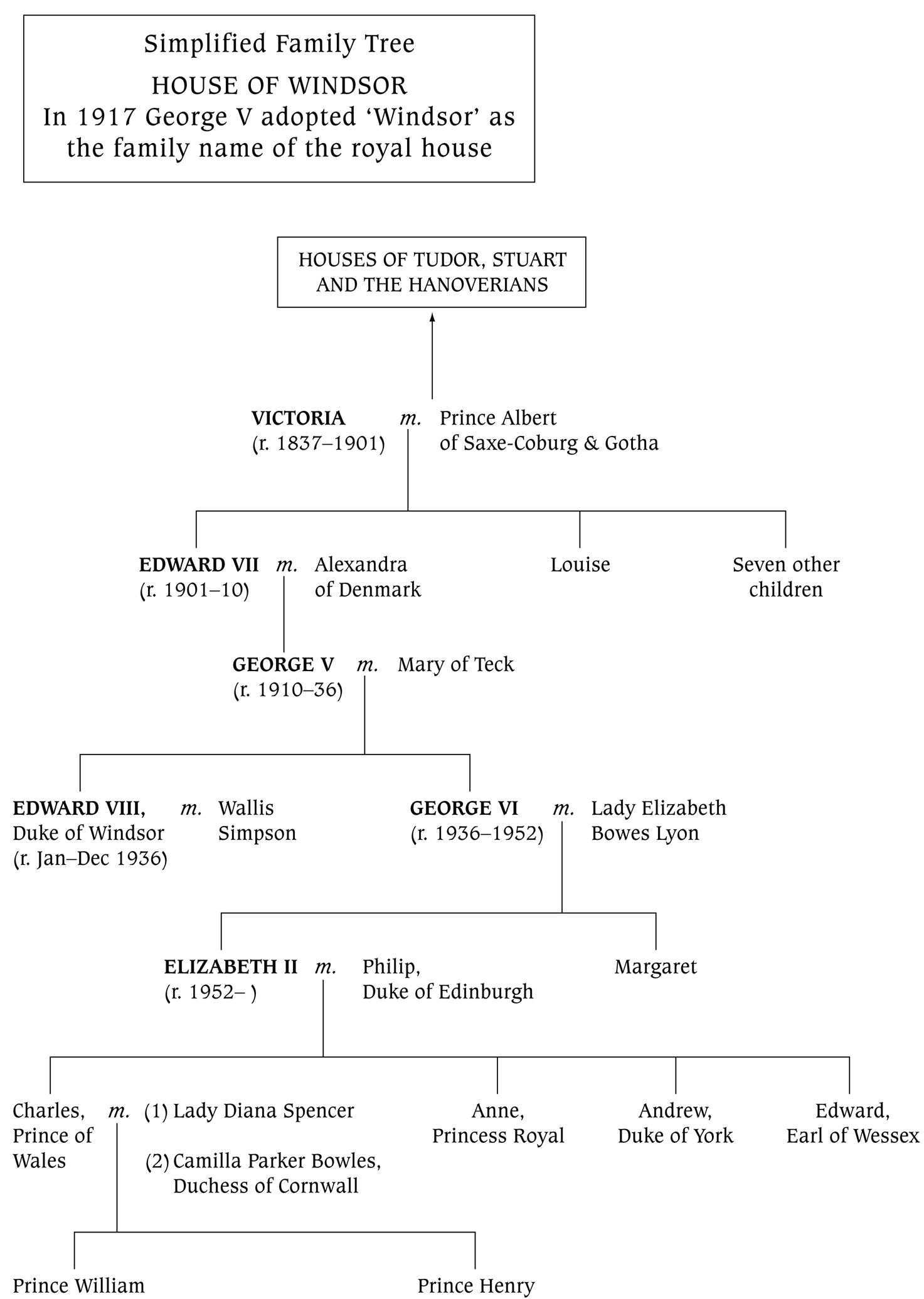
HOUSE OF WINDSOR
Foreword
THIS BOOK IS THE STORY of the crown of England and of those who wore it, intrigued for it and died for it. They include some of the most notable figures of English and British history: Alfred the Great and William the Conqueror, who shaped and reshaped England; the great Henrys and Edwards of the Middle Ages, who made England the centre of a vast European empire; Henry VIII, whose mere presence could strike men dumb with fear; Elizabeth I, who remains as much a seductive enigma to us as she was to her contemporaries; and Charles I, who redeemed a disastrous reign with a noble, sacrificial death as he humbled himself, Christ-like and self-consciously so, to the executioner’s axe.
Such figures leap from the page of mere history into myth and romance. I have painted these great royal characters – and the dozens of other monarchs, who, rightly or wrongly, have left less of a memory behind – with as much skill as I could.
But this is not a history of Kings and Queens. And its approach is not simply biographical either. Instead, it is the history of an institution: the Monarchy. Institutions – and monarchy most of all – are built of memory and inherited traditions, of heirlooms, historic buildings and rituals that are age-old (or at least pretend to be). All these are here, and, since I have devoted much of my academic career to what are now called Court Studies, they are treated in some detail.
But the institution of monarchy – and I think this fact has been too little appreciated – is also about ideas. Indeed, it is on ideas that I have primarily depended to shape the structure of the book and to drive its narrative. These are not the disembodied, abstract ideas of old-fashioned history. Instead, I present them through lives of those who formulated them. Sometimes these were monarchs; more usually they were advisers and publicists. Such men – at least as much as soldiers and sailors – were the shock-troops of monarchy. They shaped its reaction to events; even, at times, enabled it to seize the initiative. When they were talented and imaginative, monarchy flourished; when they were not, the crown lost its sheen and the throne tottered.
So monarchy depends on its servants: its advisers and ideologues; its painters, sculptors and architects, and – not least – its historians. And these, too, are given voice, sometimes as chorus to the swelling scene, occasionally as actors themselves.
The result is a task completed. It began in 2004 with the publication of The Monarchy of England: The Beginnings. That book covered the period from the fall of Roman Britain to the Norman Conquest and its aftermath, and was intended to be the first of three volumes to accompany a Channel 4 series of the same name. A further volume, Monarchy: From the Middle Ages to Modernity, appeared in 2006. But the Middle Ages themselves remained untreated. This book brings together the two previously published volumes. And it fills in the missing centuries in the same style and with similar emphases.
I have also changed the book’s title. Monarchy was chosen because of the fashion at the time for portentous one-word titles for major television series. And it did the job well enough. But Crown and Country does it better. The crown is the oldest English institution and the most glittering. But its story, as I tell it, is finally the means to an end: the history of England herself.
The Red House
Barham, Kent
July 2010
PART I
BEGINNINGS
Chapter 1
The Shadow of Rome
SOMETIMES, EVEN WHEN you are a case-hardened professional, you see history differently. I had one such moment when I first visited the Great Hall of the National Archives in Washington. I was faintly shocked by the way in which the Constitution and the Bill of Rights were displayed, like Arks of the Covenant, on a dimly lit altar and between American flags and impossibly upright American marines.
But what really struck me was the presence of a copy of Magna Carta. It was, as it were, in a side chapel. Nevertheless, here it was, this archetypically English document, in the American archival Holy of Holies.
It was placed there out of the conviction that it was the ancestor, however remote, of the Constitution and the Bill of Rights. And its presence set me thinking. Was this assumption correct? Does it help explain current concerns – like Britain’s, or England’s, reluctance to be absorbed in the European Union? Does it mean that there is an Anglo-Saxon way and a European way, as the French undoubtedly think? Does the difference derive from the contrast between Roman Law and English Common Law? Is it, finally, England versus Rome?
The first part of this book attempts to answer some of these questions. It uses the medium of narrative, which I think is the only proper means of historical explanation. And it goes back to the beginning, which is the only right place to start.
Indeed, if I may be excused Irish, it goes back before the beginning. The idea of the English does not appear until the eighth century, and the reality of England not till two hundred years later still. But I start a millennium earlier with the Roman invasions and occupation of Britain. I do so for two reasons. The first is that the great Anglo-Saxon historian Bede, who, more than anyone else, invented the idea of England, thought that this was the right place to start his Ecclesiastical History of the English People. The second is that Rome is indeed ‘our common mother’ and is the fount from which all modern western European countries spring.
But, in the case of England, Rome is at best a stepmother. There is, uniquely in the Western Empire, an absolute rupture between the Roman province of Britannia and the eventual successor-state of Anglo-Saxon England. Elsewhere, in France, Italy or Spain, there are continuities: of language, laws, government and religion. In Britain there are none. Instead the Anglo-Saxon invaders of the fifth century found, or perhaps made, a tabula rasa.
This is normally regretted. Civilization was destroyed, the common story goes, and the Dark Ages began. I am not so sure. For Rome was not as civilized as we think and the Dark Ages – at least in Anglo-Saxon England – were by no means so gloomy. The roots of the misunderstanding, I think, lie in the importance we attach to material culture. We too live in a comfortable age, so we are impressed – too impressed – with the apparatus of Roman comfort: the baths, the sanitation, the running water, the central heating and the roads.
All these are, indeed, very sophisticated. But the politics that underpinned them was surprisingly crude. Not only was the Empire a mere military despotism, it was also peculiarly mistrustful of any form of self-help, much less self-government, on the part of its subjects. This is shown by a famous exchange of letters between the Emperor Trajan and the senatorial aristocrat and man of letters Pliny the Younger, who was then governor of the province of Bithynia in Asia Minor. The important provincial city of Nicomedia, Pliny informed the emperor, had suffered a devastating fire. Might he encourage the citizens to set up a guild of firemen to fight future conflagrations? On no account, replied the emperor, since such bodies, whatever their ostensible purpose, become fronts for faction and political dissent.
It was this enforced passivity on the part of its civilian populations that helped make the Empire such easy meat for the barbarian invaders. It is also its sharpest point of contrast with the kingdom of Wessex, round which England coalesced in the ninth and tenth centuries. Wessex was not a democracy, or even a peasant commonwealth, as some of its more enthusiastic Victorian historians assumed. But it was a participatory society, which balanced a powerful and effective monarchy at the centre with institutions of local government which required – and got – the active involvement of most free men. It was this combination, which was unique in Europe at the time and long after, as well as good luck and inspired royal leadership, which enabled Wessex to survive, and finally to thrive, in the face of the Viking invasions that destroyed all the other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
The result was England. It was an early, perhaps indeed the earliest, nation-state, with a remarkable unity of language, culture and politics. The vernacular, Anglo-Saxon or Old English, not Latin as elsewhere, was the language of politics and administration. It was also the language of The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle. This was no episodic monastic annal; it was a book of national record that charted, self-consciously and deliberately, the birth and development of a nation. All this gave Anglo-Saxon England a powerful sense of national solidarity: it could negotiate collectively with its kings even when they were conquerors; it could also strive to settle political disputes without the bloodshed of civil war.
It was, in short, different.
I
Two thousand years ago there was only one power that counted in the Western world: Rome. It was perhaps the purest, the most absolute monarchy the world has ever seen. The emperor incorporated in his own person all the powers of the state: military, executive, judicial and (in practice if not at first in theory) legislative. As imperator, he was commander of the army; as holder of the ‘tribunican powers’, he represented the sovereign majesty of the people and was protected by the terrible penalties of laesa maiestatis or treason; as pontifex maximus, he was chief priest. He was even regarded as a god himself, who was worshipped by many of his subjects in life and by more in death. His person, his palace and his very treasury were ‘sacred’.
And Britain, the province of Britannia, was just a tiny part of this monarchy, which, at its maximum extent, stretched from the Bay of Biscay in the west to the River Euphrates in the east and from the moors of Scotland in the north to the sands of the Sahara in the south.
The myriad peoples inhabiting the Empire spoke many different languages and honoured many different gods. But there were also powerful, supervening forces of unity as well. First, there was the army. It was the Roman army which had conquered most of the known world for Rome and it was the army which kept it Roman. So everywhere in the Empire the imperial army performed the same drills; built similar forts and wore the same uniforms. Close behind the soldier marched the tax collector and the lawyer. So everywhere too the imperial bureaucracy, which was mind-numbing in its size, hierarchical complexity and expense, collected the same taxes; enforced the same Roman law on all free men and used the same Roman weights and measures.
In these and all other forms of governmental administration, one official language was employed: Latin – though in the Eastern Provinces Greek also enjoyed a high status as a second, as yet unofficial, language. Everywhere, therefore, anybody who aspired to be anybody had to speak, read and write one or preferably both of these languages, which also carried a common Classical literature and culture with them. The same went for the visual arts where, yet again, there was a single official style – the Roman version of Classicism – which was used for buildings, arte-facts and decoration throughout the Empire.
How would Britain, which the Romans disparaged as the ‘ends of the earth’, fit in with all this?
The first Roman expeditions to Britain were led by the proto-emperor Julius Caesar, in 55 and 54 BC. Born in c.102 BC. into a noble if impoverished family, Caesar soon proved himself as ambitious as he was multi-talented. And, in achieving his ends, he set in train the events which transformed Rome from a Republic – a commonwealth of free men, if bitterly divided by class and interest group – into the absolute monarchy of the Empire.
Caesar’s expeditions to Britain were an interlude in his conquest of Gaul. This established his reputation both as the power-broker of the Roman world and, thanks to his account of the conquest in his De Bello Gallico (The Gallic War), as a great, if self-serving, military historian. The first British expedition was little more than an armed reconnaissance raid. But in the second Caesar brought a substantial force of five legions with their auxiliaries, amounting to about 27,000 men. He defeated Cassivellaunus, and penetrated north of the Thames. Caesar never makes clear Cassivellaunus’s precise status. But the best guess is that he was tribal king of the Catuvellauni. There was some attempt among the warring British tribes to sink their differences with the appointment of Cassivellaunus as overall commander, and some success with guerrilla tactics. But, finally, what turned the day for Caesar was not the force of the Roman army but the weakness and divisions of the British coalition. Nevertheless, Cassivellaunus had held out long enough to stop Caesar capitalizing on his gains. Instead, after signing treaties, Caesar withdrew to deal with more pressing problems in Gaul. The Roman legions would not return to Britain for nearly a hundred years.
In 44 bc, ten years after he had left Britain, Caesar was made life-dictator, though he ostentatiously refused the crown itself. Months later he was dead of multiple stab-wounds from the daggers of former friends and foes alike. The assassination was intended to save the Republic. In fact, it administered the death blow. For the man who emerged victorious from the years of civil war that followed Caesar’s assassination was Caesar’s great-nephew by marriage and adoptive son and heir Octavius, later surnamed Augustus.
Unlike Caesar, Augustus was as subtle as he was ruthless. So, instead of treating republican institutions with contempt, he cherished them. Indeed, he loved them to death. The Republic was ‘restored’, with much fanfare, in 27 BC. But, one by one, Augustus took over all the powers which had been carefully separated under the republican constitution.
But what to call this monarchy that dared not speak its name? Augustus himself liked to be addressed as princeps – that is, ‘first (among equals)’. But he also used the style imperator or general. Since the command of the army was now the real key to power, his successors soon started to use imperator or emperor as their principal title. The title was deliberately not royal to avoid alienating residual republican feeling. But it betokened, as it still does, power that was greater, in both extent and intensity, than that of any mere king.
In ad 43, Claudius, one of the most historically minded emperors, determined to complete the task that Caesar had started. Claudius was eager to establish his warlike credentials, but could not afford to take any personal risks. The result was that this second Roman invasion of Britain became as much a piece of theatre as a military expedition, with its two initial leaders effectively acting the corresponding roles of impresario and general. They were Aulus Plautius, whom the Roman historian Tacitus called a ‘famous soldier’, and Narcissus, Claudius’s all-powerful secretary and an imperial freedman, who accompanied Plautius as a kind of political commissar. But the oddly matched soldier and the manumitted ex-slave proved an effective double act. Plautius, with his Gaulish auxiliaries, fought his way to the Thames, at which point Narcissus informed the emperor that it was time for him to set out. Claudius eventually arrived, complete with ceremonial elephants and a vast cavalcade – and stayed only sixteen days. But it was long enough for him to take part in a set-piece campaign masterminded by Narcissus. He crossed the Thames ‘at the side of his troops’; ‘caused the barbarians to come to hand in battle’ and entered Colchester, capital of the Catuvellauni, in triumph. He was repeatedly acclaimed imperator by the troops and received the submission of no less than eleven British kings.
And all this in barely more than a fortnight! The sense of theatrical artificiality was only heightened by the fact that, when he had returned to Rome, Claudius immediately ordered a repeat performance. He took part in an even grander triumph and laid on a re-enactment of the highlights of his campaign in the Campus Martius. The scenes included ‘the assault and sacking of a town’ and ‘the surrender of the British kings’. We don’t know who played the British kings. But Claudius, ‘presiding in his general’s cloak’, appears to have played himself.
Meanwhile, back in the real world of Britannia, the political situation was more complex. For in ad 43 the Romans, whatever the textbooks might say, did not conquer Britain. Instead, in the smallest of small colonial wars, they defeated a single dominant tribe, the Catuvellauni, and took over their territories in the south-east. Outside this area, other tribal kings continued to exercise their sway under Roman protection. Indeed, the Romans added to their number by setting up the renegade British prince Cogidubnus as king of a new, artificially created tribe called, significantly, the Regnenses (‘The King’s Folk’).
The reason for this apparent generosity was straightforward. British kings, who had started to issue Roman-style coins and to give themselves the Latin title of rex, had been the most effective agents of Romanization before Claudius’s invasion and, led by that accomplished quisling Cogidubnus, they continued to play the same role afterwards.
But not for long. For rebellions, like that of Boudicca, queen of the Iceni, in ad 60, and deliberately fostered quarrels in the British royal families took their toll. The result was that, within thirty years, direct Roman rule covered most of southern Britain and was being aggressively extended far into modern Scotland.
There were to be no more kings in Britain till the Romans had gone.
With the coming of direct Roman rule, Romanization became a matter of public policy. It was pursued especially effectively by Agricola, who was governor for the unusually long period of six years from ad 78 to 84. Within a year of his arrival he had embarked on a major building programme, giving ‘private encouragement and public aid to the building of temples, courts of justice and private dwelling houses’. He also provided a sophisticated Classical education for the sons of the British elite.
His campaign seems to have enjoyed quick success. As early as ad 79 or 81, an inscription was set up at Verulamium (St Albans) to commemorate Agricola’s role in the creation of a splendid new Forum or marketplace. And the British elite at least eagerly embraced Latin, the toga, hot and cold baths and banqueting while reclining on couches. ‘They called [it] civilization’, Tacitus sardonically observes, ‘when it was but a part of their servitude.’
Perhaps. But the prosperity brought to Britain by the pax Romana – ‘the Roman peace’ – was real enough: some six thousand miles of well-engineered, solidly metalled roads were built; towns grew and flourished; farmsteads expanded into substantial, luxurious villas; the spa-complex at Aquae Sulis (Bath) reached its greatest extent in the third and fourth centuries and the population of Britain rose to about four million, a figure that would not be reached again for a millennium.



