
Полная версия:
History in Documents and a Document in History

О.В. Пасько
History in Documents and a Document in History
Методическая записка
Настоящее учебное пособие History in Documents and a Document in History предназначено для студентов, обучающихся по специальностям «Документоведение», «История», «Международные отношения», а также может использоваться широким кругом читателей, изучающих иностранный язык.
Данное пособие разработано на основе коммуникативного подхода и обеспечивает взаимосвязанное развитие речевой, языковой, социокультурной и информационной компетенций студента. Основная цель пособия заключается в развитии языковых и коммуникативных компетенций студентов, изучающих английский язык на направлениях подготовки «Документоведение», «История», «Международные отношения».
В пособии представлен обширный массив текстов аутентичного характера, привлеченных из современных источников, газет, журналов и Интернет-ресурсов страноведческой, исторической направленности, адаптированных для студентов данного уровня. Таким образом, пособие последовательно погружает студента в тематические пласты специальной лексики и грамматики и помогает сформировать навыки работы с литературой по специальности.
Пособие состоит из следующих частей – READING, GRAMMAR, TRANSLATION PRACTICE и VOCABULARY.
Раздел READING состоит из семи модулей, в каждом из которых представлены аутентичные тексты разного уровня сложности. Речевой материал текстов отражает богатство современного английского языка, представляет специальные языковые, речевые выражения, обороты и термины профессиональной речи.
Каждый текст снабжен упражнениями, направленными на развитие навыков устной и письменной речи: лексические, лексико-грамматические и речевые, которые позволяют проверить как общее понимание прочитанного, так и закрепить только что приобретенные навыки. Система упражнений к текстам способствует активному усвоению профессиональной лексики и повторению некоторых аспектов грамматики. Прочное закрепление лексического материала обеспечивается заданиями на словообразование, перифраз, выбор, нахождение эквивалентов, перевод. Лексические упражнения обеспечивают эффективную повторяемость лексических единиц в пределах тематического комплекса. Особенностью раздела READING является то, что он может быть задействован либо в качестве домашнего задания с последующей проверкой в учебной группе, либо самостоятельной работы.
Раздел GRAMMAR представлен тремя модулями. Каждый модуль содержит грамматические упражнения для активизации грамматических навыков устной речи, а также для выработки устойчивых навыков и умений, необходимых как для адекватного перевода текстов по специальности, так и для беспереводного чтения.
Раздел TRANSLATION PRACTICE представляет собой практикум по переводу текстов, максимально приближенных к языку специальности. По усмотрению преподавателя данный раздел можно задействовать как форму самостоятельной работы в виде письменного перевода или предлагать студентам в качестве домашнего задания.
Пособие может быть использовано для развития коммуникативной компетенции – умения получать, перерабатывать и передавать информацию. Содержание учебного материала может представлять интерес для тех, кто интересуется историей и хотел бы изучить прошлое через призму исторических документов.
Part I. Reading
Module I. Historical documents
Text 1. Historical documents
1. Study the following words:
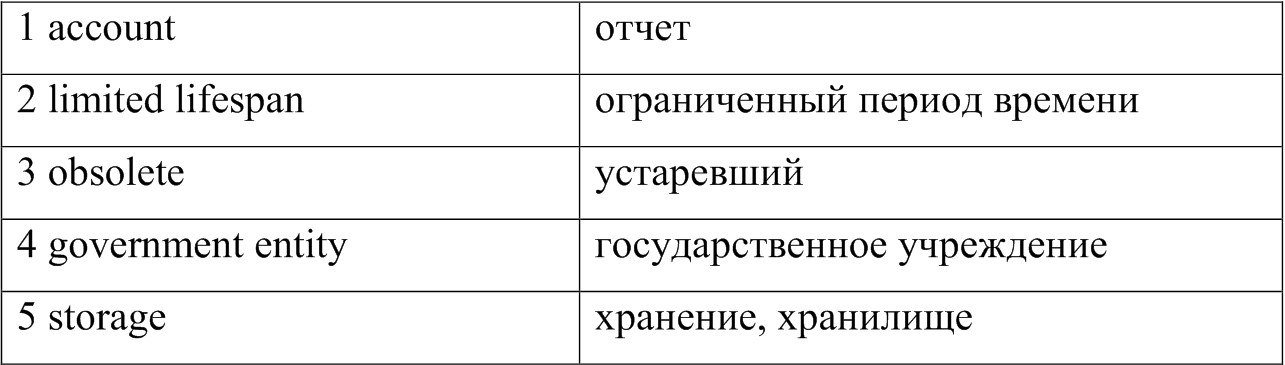
Read the text and do the tasks after it.

Historical documents are papers that contain important information about a person, place, or event.
Most famous historical documents are either laws, accounts of battles (often given by the victors or persons sharing their viewpoint), or the exploits of the powerful. Though these documents are of historical interest, they do not detail the daily lives of ordinary people, or the way society functioned. Anthropologists, historians and archeologists generally are more interested in documents that describe the day-to-day lives of ordinary people, indicating what they ate, and their interaction with other members of their households and social groups, and their states of mind. It is this information that allows them to try to understand and describe the way society was functioning at any particular time in history.
Many documents that are produced today, such as personal letters, pictures, contracts, newspapers, and medical records, would be considered valuable historical documents in the future to such people. However most of these will be lost in the future since they are either printed on ordinary paper which has a limited lifespan, or stored in digital formats that will become obsolete fairly soon.
Some companies and government entities are attempting to increase the number of documents that will survive the passage of time, by taking into account the preservation issues, and either printing documents in a manner that would increase the likelihood of them surviving indefinitely, or placing selected documents in time capsules or other special storage environments.
(Abridged from the original texts provided by Britannica Encyclopedia)
2. Answer the following questions:
1) What is a “historical document”?
2) What types of documents are mentioned in the text? Can you think of any more?
3) What details are scientists usually interested in?
4) What do these details help scientists understand?
5) What documents will become valuable in the future?
6) Why will documents be lost?
7) In what way do governments try to store and increase the number of documents?
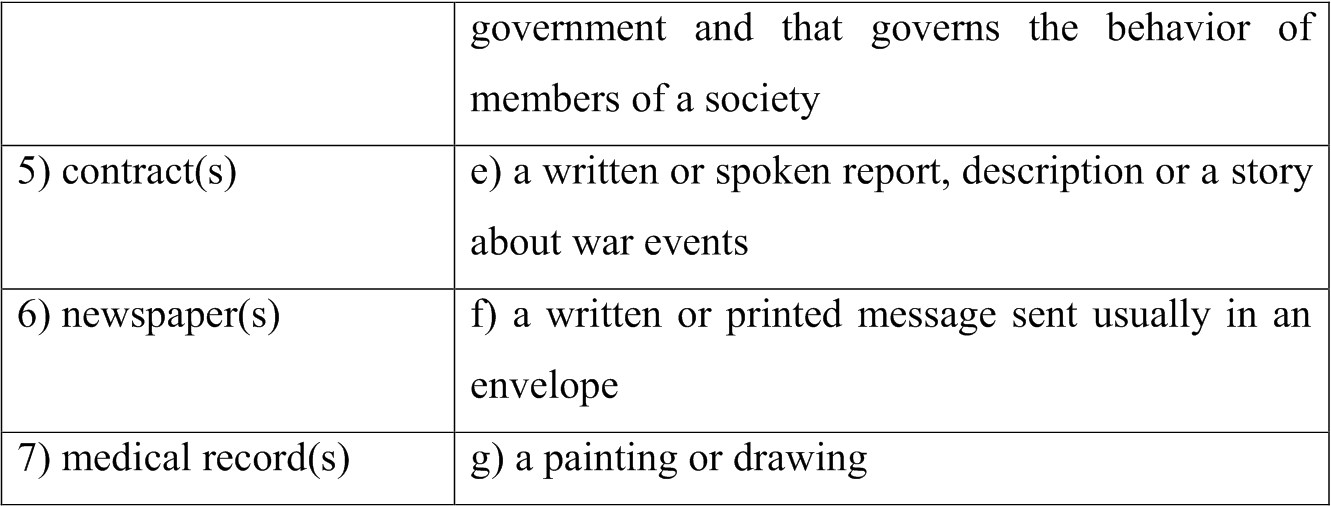
3. Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right.

4. Fill in the gaps with the words given in the box:

1) Most daily _____________s will not publish anonymous letters to the editor.
2) Historical _____________s describe the young princess as exceedingly tall, thin, and plain, but with a generous nature.
3) You can ask the children to create a different ending to the story or draw different ____________s to illustrate what they have read.
4) All citizens are equal before the _______________.
5) As written _____________s developed, they also used wooden writing boards and wax tablets for work which was not intended to be permanent.
6) Richmond Police are sending warning _____________s to parents of children caught buying or attempting to buy alcohol.
7) When an agreement is reached with the owner, a private _____________ is written and signed.
5. Find out what functions these people do:


Text 2. Four Types of Historical Documents
Read the text and do the tasks after it.
Historical documents are papers that contain important information about a country's people, laws or policies. For example, the U.S. Constitution is a historical document, and so are the birth and death certificates and military records of the country's people. Anthropologists and historians are interested in such papers, and the documents also help people research their ancestry. These are the four types of historical documents.
Political Documents. Political papers that are considered historical documents include the officially signed copy of the U.S. Declaration of Independence, U.S. Constitution and U.S. Bill of Rights. These historical documents are preserved at the offices of the National Archives and Records Administration in Maryland. Under the Freedom of Information Act, they are generally accessible to anyone.
Vital Records. Birth, marriage and death certificates are historical documents and usually are referred to as vital records. They provide people with genealogy information, such as when their ancestors were born, married or died and even cause of death. Vital records are valuable for people who are interested in reviewing or discovering their ancestry.
Census Records. Information from the first U.S. Census, which was in 1790, is available from various sources, including the offices of the National Archives and Records Administration. The United States takes a census every 10 years; the census provides information on population numbers and growth and people's birthplace, age, street address and occupation, among other details. The data is helpful to track ancestors and to confirm information. It also is necessary for government records.
Military Records. Military personnel records are historical documents, too. They contain information about when soldiers, marines and other military personnel members enlisted, their training or qualifications, whether or not they were disciplined and/or awarded medals and their discharge or retirement information. The records include additional information, too.
(Abridged from the original texts provided by http://www.ehow.com)
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What information is given in historical documents?
2) How can historical documents help scientists?
3) What political documents are mentioned in the text? Can you give more examples of political documents?
4) What type of information do vital records provide people with?
5) Who can find vital records important?
6) How often does the United States take a census?
7) What information does a census usually contain?
8) What data can be found in military records?
2. Match the words on the left with their definitions on the right:

3. Find the words in the text for the definitions given below:
1) ____________ advanced and detailed study of a subject, so as to learn new facts.
2) ____________ a person`s ancestors considered as a group.
3) ____________ to keep something in good condition for a long time by some special treatment.
4) ____________ worth a lot of money or very useful.
5) ____________ any thing or place from which something comes, arises, or is obtained; origin.
6) ___________ to enter the armed forces or a course of study.
7) ___________ the separation of a person from military service.
8) ___________ the act of leaving one`s job, career, or occupation permanently, usually because of age.
4. Give Russian equivalents for the following word combinations and pay attention to the use of prepositions:

Text 3. How to analyze a historical document
1. Study the following words and phrases:
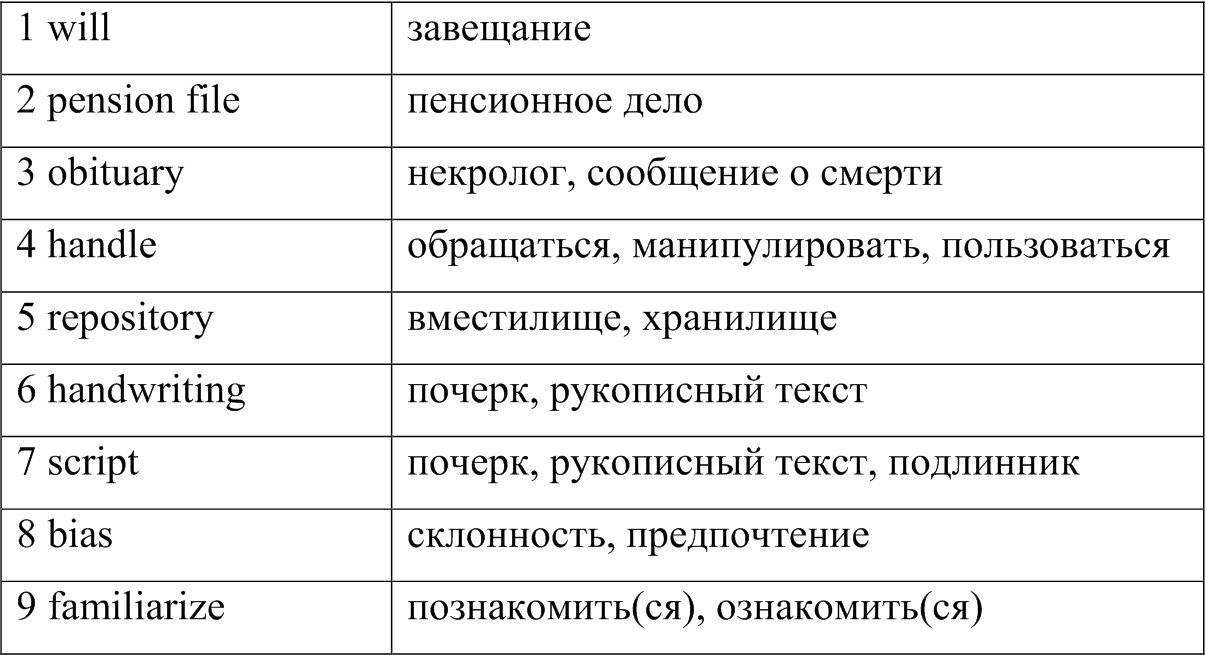
2. Read the text and choose the most suitable heading from the list A-H for each part of the text:
A Evaluate whether the information in the document is primary or secondary information.
B Compare the document to others of the same type from the same location and era.
C Determine what type of document you are analyzing.
D Learn whether your document is an original.
E Consider why the document was created.
F Familiarize yourself with the handwriting of the time and place from which your document originates.
G Determine who authored the document, and who may have contributed information.
H Consider the era in which the document was created.
How to analyze a historical document
Historians and genealogists often use old documents to gather information about the past. Evaluating old records is an effective way to learn about the past, and it's often one of the first skills historians and genealogists learn. Here are some tips for how to analyze a historical document.
1 _______________ You might be looking at a will, a pension file, an obituary, a news article, or any number of other document types. Knowing what you're looking at helps you develop an approach for handling the information the document contains. For an obituary, for example, you will want to find out whether the item appeared in a newspaper or a different publication, whether it was written by the publication's staff or a paid placement, and whether there were other newspapers in the same time and place that might cover the same person differently. For a military pension file, you'll want to find out up front which side of a war the soldier served on, since that will have a significant impact on the breadth and depth of the materials you should expect to find in the file. Understanding the background behind the document before you begin to work with it will enhance your ability to extract useful information in your analysis.
2. _______________ A census record, for example, is created primarily to count the number of people in a particular location for taxation and representation purposes. You might find useful information in a census that can be used for another purpose, like genealogical research or social studies. However, understanding the original reason a document was produced helps determine how accurate the information it contains may be for secondary purposes.
3. ________________ Primary information is given by someone with firsthand knowledge; secondary information is not. Both types of information can appear in the same item. For example, a death certificate will contain the doctor's explanation of the cause of death. This is primary information, since the doctor was present during or shortly after death. The same death certificate will usually include the date and place of birth of the deceased. This is usually secondary information, since the person giving the information is typically someone who was not present at the birth of the deceased. Generally speaking, historians consider primary information to be more reliable than secondary information.
4. _________________ Consider whether those individuals may have had accurate information, and whether they may have had biases or reasons to provide information that was not accurate or truthful.
5. ________________ This will help you interpret terms that may be unfamiliar or whose meanings have changed over time. For example, the word "infant" generally refers to a baby under the age of 2 today, but in the documents from the British colonies in the 1700s, "infant" meant anyone under the age of 21.
6. _________________ Wills, for example, often contain standard language that is other wills of a particular time and place. If your document contains different language than the norm, that might indicate a unique situation or circumstance.
7. _________________ If you obtained it from a repository (such as a library or archive), ask the staff if it is an original document. If you own the document or received it from a lay person, have a qualified professional review it to determine whether it's an original. Local historical societies and colleges can often help with this. Documents that have been transcribed, abstracted, copied or otherwise derived from the original may contain errors. Work with original documents (or photographic copies of documents) whenever possible to ensure accuracy.
8. _________________ For example, Old German handwriting has letters that are very different than those used today. Becoming familiar with the handwriting styles of the era will help ensure that you're interpreting your document correctly. Numerous books and websites are available to help you translate handwriting from different times and places. Staff at local historical societies in the location where the document originated can often help with this as well.
(Abridged from the original texts provided by http://www.ehow.com)
3. Answer the questions:
1) What document types are mentioned in the text?
2) What information is important for analyzing an obituary?
3) Why do you need to know which side of war a soldier served on?
4) What is a census record created for?
5) Why is it important to understand the purpose of creating a document?
6) What`s the difference between primary and secondary information?
7) Which type of information is more reliable?
8) Why is it important to know the period of time in which the document was created?
9) Why is it better to work with original document?
10) How can knowing the handwriting styles of the era help you to analyze the historical document?
4. Find synonyms for the following words in the text:
1) to estimate _____________
2) influence, effect ____________
3) exact, precise ______________
4) to define _______________
5) certain, undoubted ____________
6) to add, share, supply ______________
7) to show, denote, reveal _______________
8) to inspect, analyze ____________
9) mistake, fault ____________
10) to explain, decipher ______________
5. Find the words in the text for the definitions given below:
1) _______________ a manner or method of doing something.
2) _______________ to raise to a higher degree; intensify; magnify.
3) _______________ select (a passage from a text, film, or piece of music) for quotation, performance, or reproduction.
4) _______________ to come into sight; become visible.
5) _______________ the dead person.
6) _______________ to make a written copy, especially a typewritten copy, of (dictated material, notes taken during a lecture, or other spoken material).
7) _______________ to remove by drawing out gently or take away.
8) _______________ to receive or obtain from a source or origin (usually followed by from).
9) _______________ to make certain to happen.
10) _______________ to take its origin or rise; begin; start; arise.
6. Fill in the gaps with the words given in box. For some points the first letters are given. Translate the sentences into Russian:

1) I e____________ that text directly out of our new library system.
2) The point is this – we cannot a_____________ ideas from the historical epoch in which they appeared.
3) The d__________ was found with multiple head injuries on a footpath.
4) Dog owners must by law e___________ their pet wears a collar and tag with their name and address on it.
5) The word magazine d____________s from an Arabic word meaning a storehouse, a place where goods are laid up.
6) The exotic creature, which ______________ from central and South America, is probably an escaped pet.
7) Interviews were ______________ by the researcher who carried out the interview.
8) He is diplomatic and cautious in his ____________ to sticky situations.
9) From the moon, Earth a____________s as a bright blue-and-white object in the black sky.
10) She spends time on e___________ing her image with fitness routines and new styles.
7. Make the summary of the text.
Revision I.
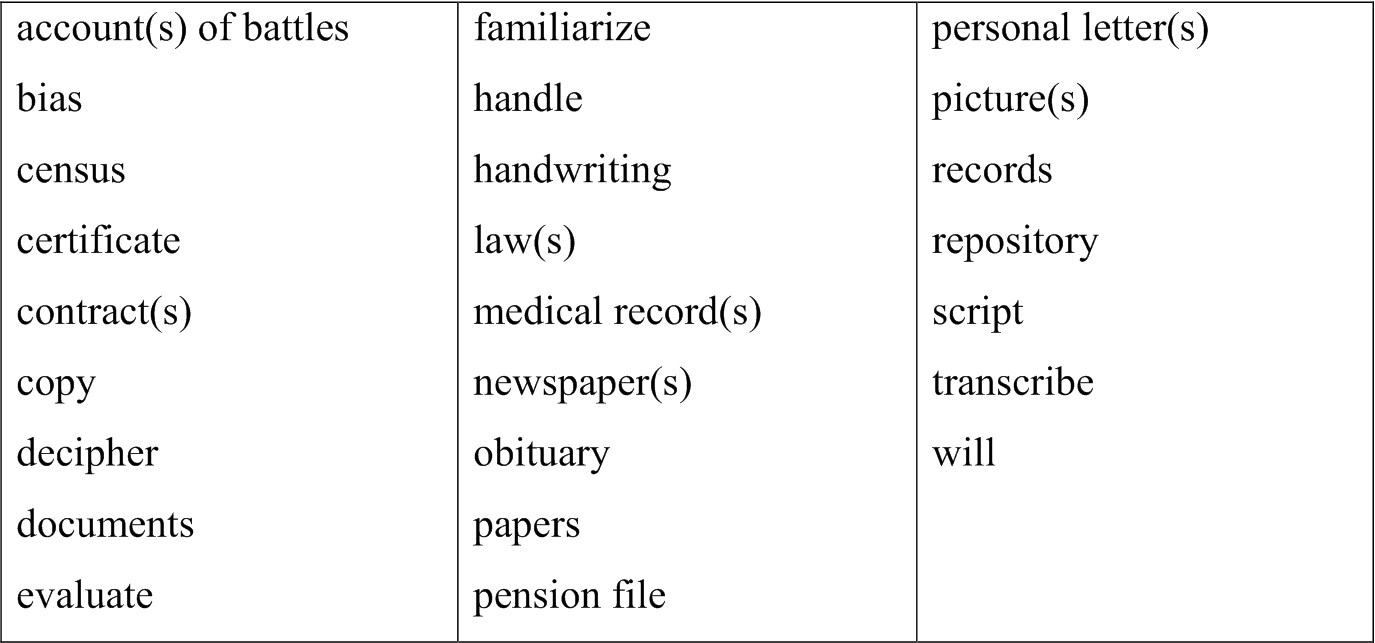
Check yourself. Remember the following words and phrases:
Module II. Early documents
Text 1. Types of documents
Read the text and do the tasks after it.

Documents that have been preserved are originals, drafts, or copies. Originals are formal documents drawn up on the order of the sender or donor, and they were designated to serve the recipient or beneficiary as evidence of the transaction recorded. Handwritten copies of documents, made either before or after the deed was actually executed (sealed), are not classified as originals. If made before an “original,” they were rough drafts of it; if made afterward, they were copies.
The particularly Anglo-Saxon method of chirography gave the possibility of producing several “originals.” By this process two or more specimens of a document were written on the same page of the vellum sheet, and the free space between the texts was filled in with the word chyrographum (“handwriting”) or other words and symbols. Then the sheet was cut irregularly right through these words or symbols. The originals thus separated could later be reassembled. An exact fit was complete proof of authenticity.
But to provide documents having the force of “originals,” copies of the original were usually made and formally certified, by public notaries, or by high ecclesiastical or secular dignitaries. Copies certified in this way were accorded the same legal value as the originals. In practice, lack of critical judgment on the part of the certifiers often led to the certification of forged records. In documents known as transumpts, which recited earlier documents or charters as part of their text, it often happened that the earlier document was forged, but, being included in the new, it received validation.
The original documents and copies considered above were issued at the request of the recipient or beneficiary or of his legal heir. It also happened quite often that the sender or donor wished for various reasons to retain a record of the documents issued by him. The chanceries (record offices) of secular rulers or great ecclesiastics therefore kept copies of outgoing documents in registers, and often of incoming documents, too. The popes were among the first to adopt the old Roman practice of keeping registers; although nearly all the earlier ones have been lost, an almost uninterrupted series of papal registers is extant from the pontificate of Innocent III onward.
An important group of registers are the rolls kept by the medieval kings of England; the earliest extant rolls date from the 12th century. The keeping of registers in the chanceries of the French kings began about the year 1200, in Aragon about 1215, in Sicily under the Hohenstaufen emperor Frederick II (died 1250), and in the German imperial chancery from the early 14th century.
Another manner of studying documents is in the formula books of the various chanceries. Notaries drawing up the various forms of medieval documents did not usually compose each new text afresh but, rather, copied from books in which such text formulas had been collected, a practice that can be traced back to Roman procedure. These model texts frequently contained only the legally relevant passages, while the individually applicable parts, such as names, figures, and dates, were either abridged or totally omitted. During the time of the Frankish kings, important collections were made, such as the Formulae Marculfi (early 8th century) and the Formulae imperiales (828–832). Significant collections of formulas serving as models for papal documents have been preserved from the 13th century.
(Abridged from the original texts provided by Britannica Encyclopedia)



